- The document discusses banana cultivation, including its botanical classification as Musa sp. and originating from Southeast Asia.
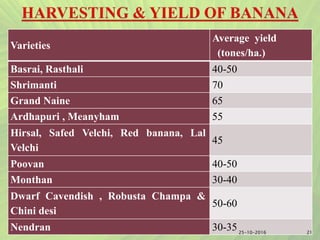
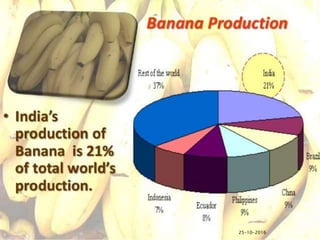
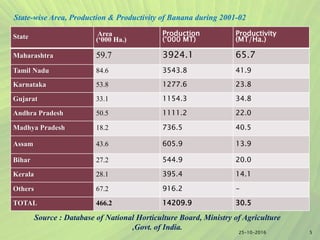
- It provides information on major banana producing states in India like Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka. Optimal growing conditions and important cultivars are also mentioned.
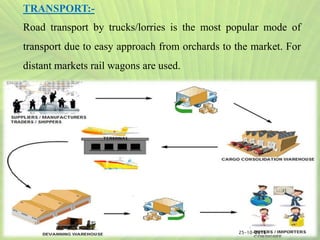
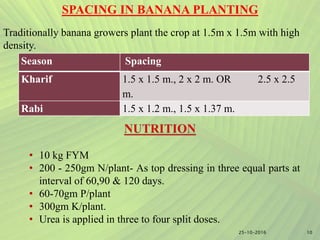
- Cultural practices for banana cultivation are outlined, including land preparation, planting, spacing, fertilizer application, intercropping, and pest and disease management.











![DISEASES:-
1. Panama wilt (Fusarium oxysporam)
2. Anthracnose (Gleosporium musarum)
3. Leaf spot (Sigatoka) [Mycosphaarella musicola & Cercospora
musae]
4. Shoot rot (Ceratostomella paradoxa)
BANANA WEEVIL
Weevil infestation of young plants causes stunting of growth,
production of small bunches and sometimes plants death. 1525-10-2016](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bananacultivation-161025041527/85/Banana-cultivation-15-320.jpg)