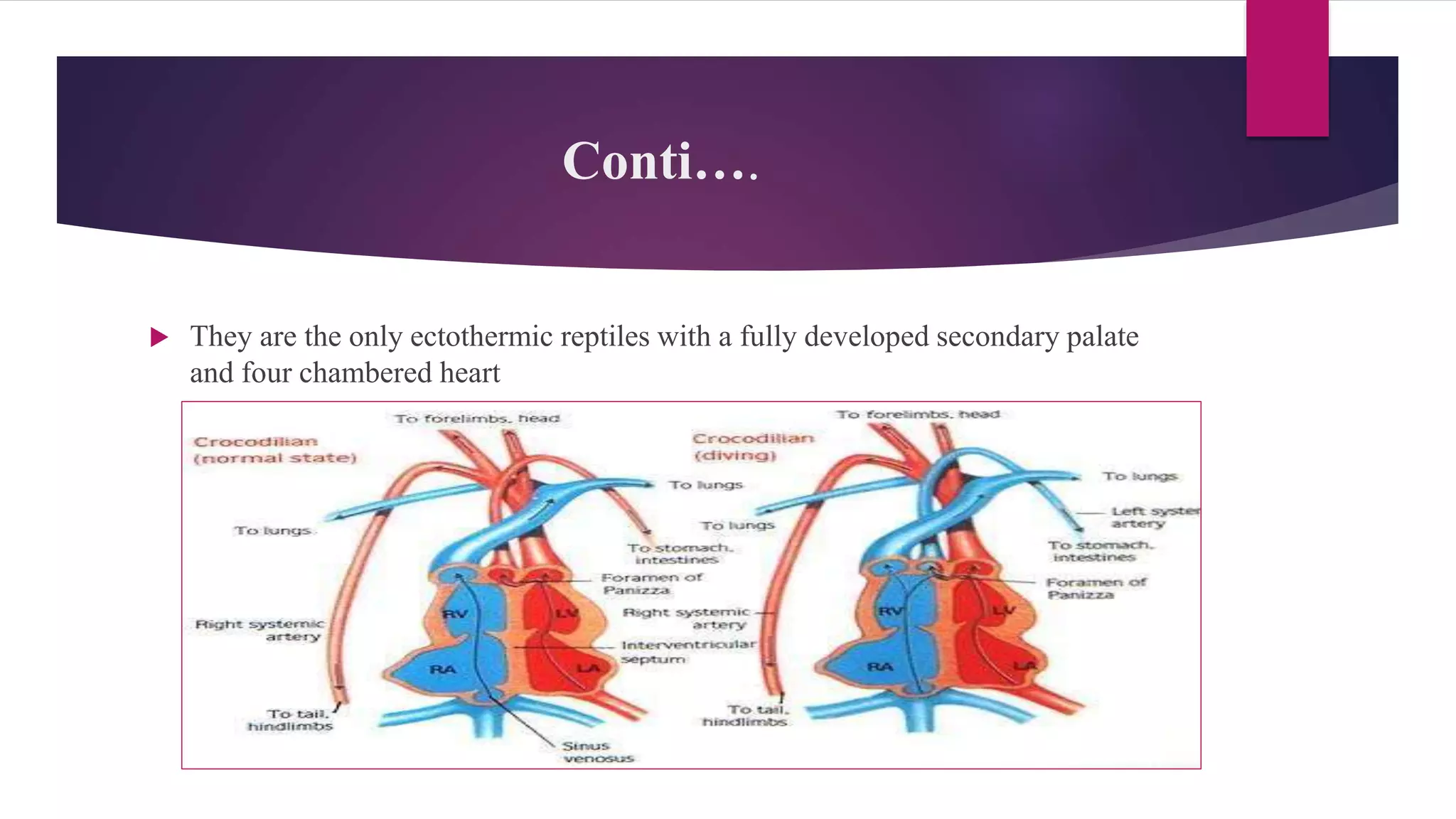
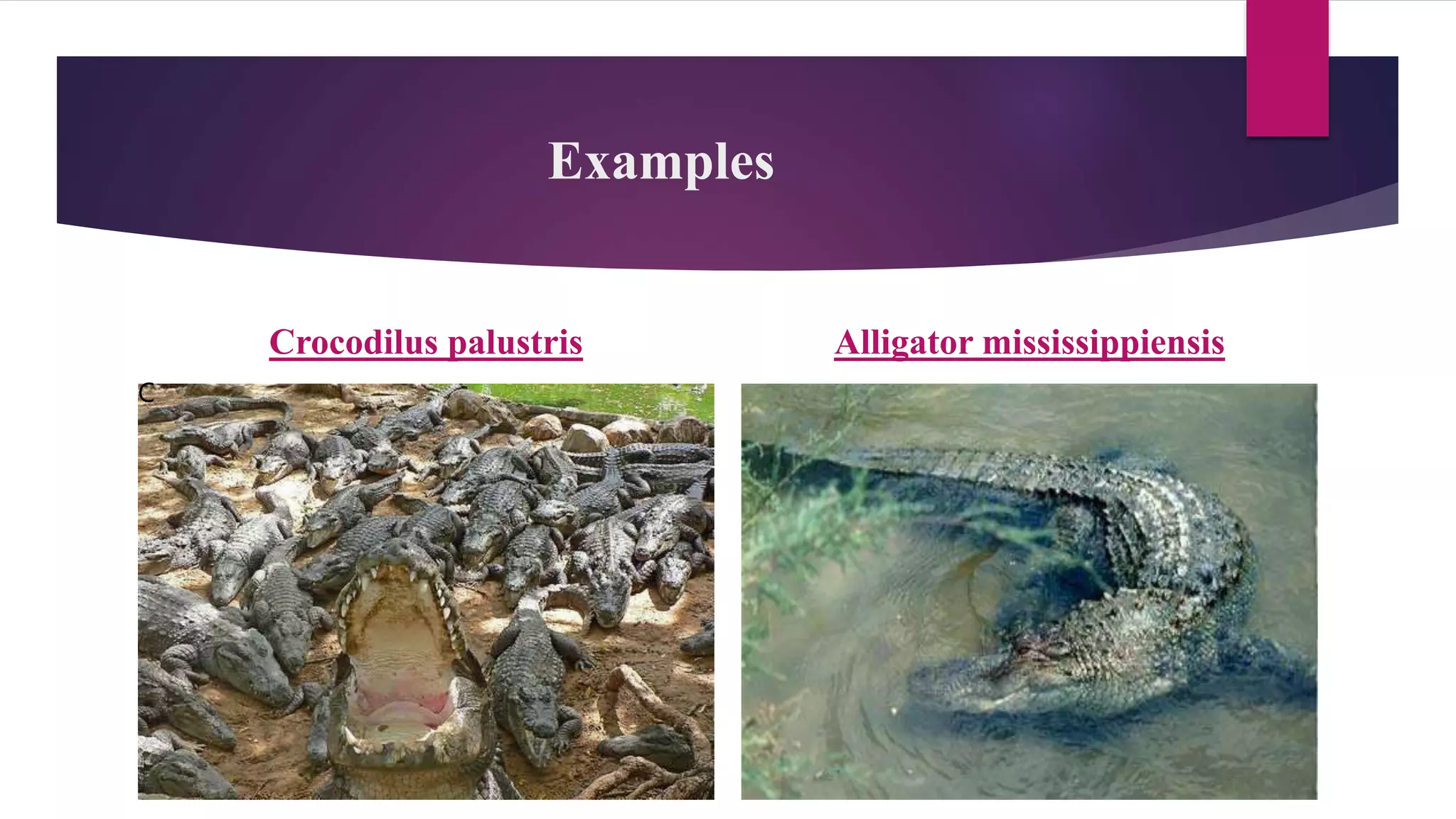
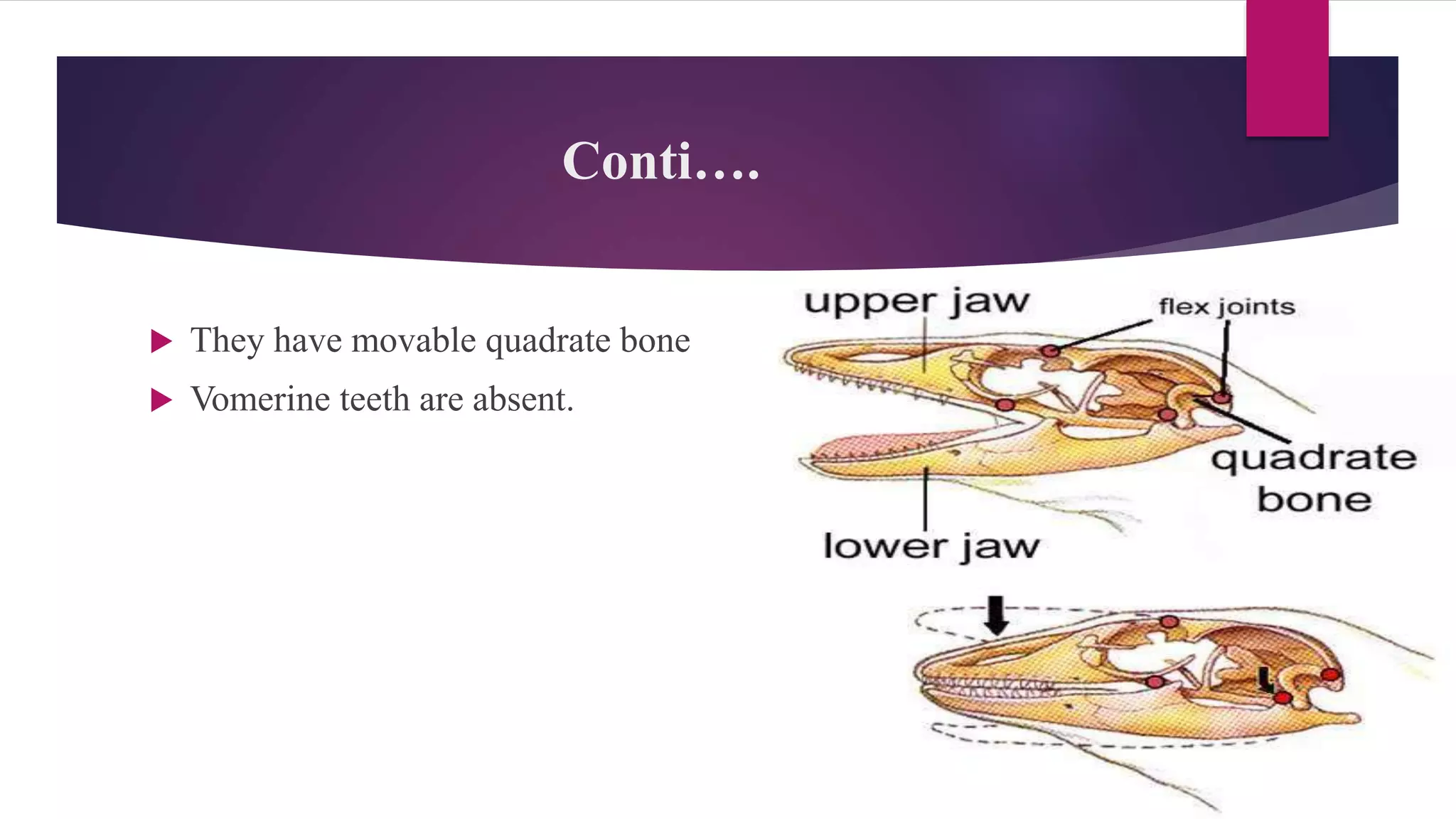
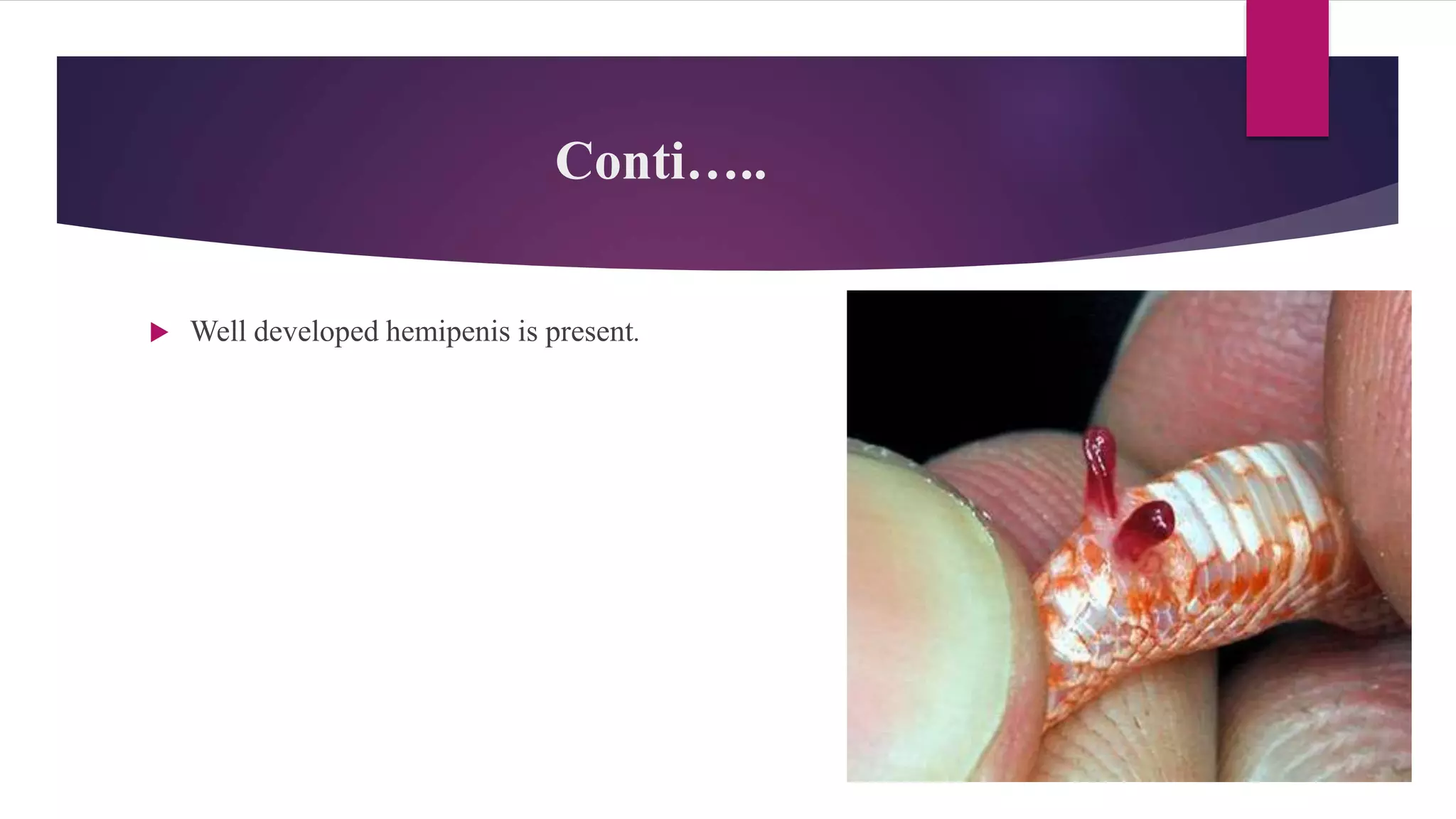
The document classifies reptiles into four orders: Testudines (turtles and tortoises), Rhynochophalia (tuataras), Crocodilia (crocodiles and alligators), and Squamata (lizards and snakes). It provides details on the characteristics of each order, such as their skin, limbs, teeth, eggs, and examples of species. The orders are distinguished from each other by these anatomical features and characteristics.