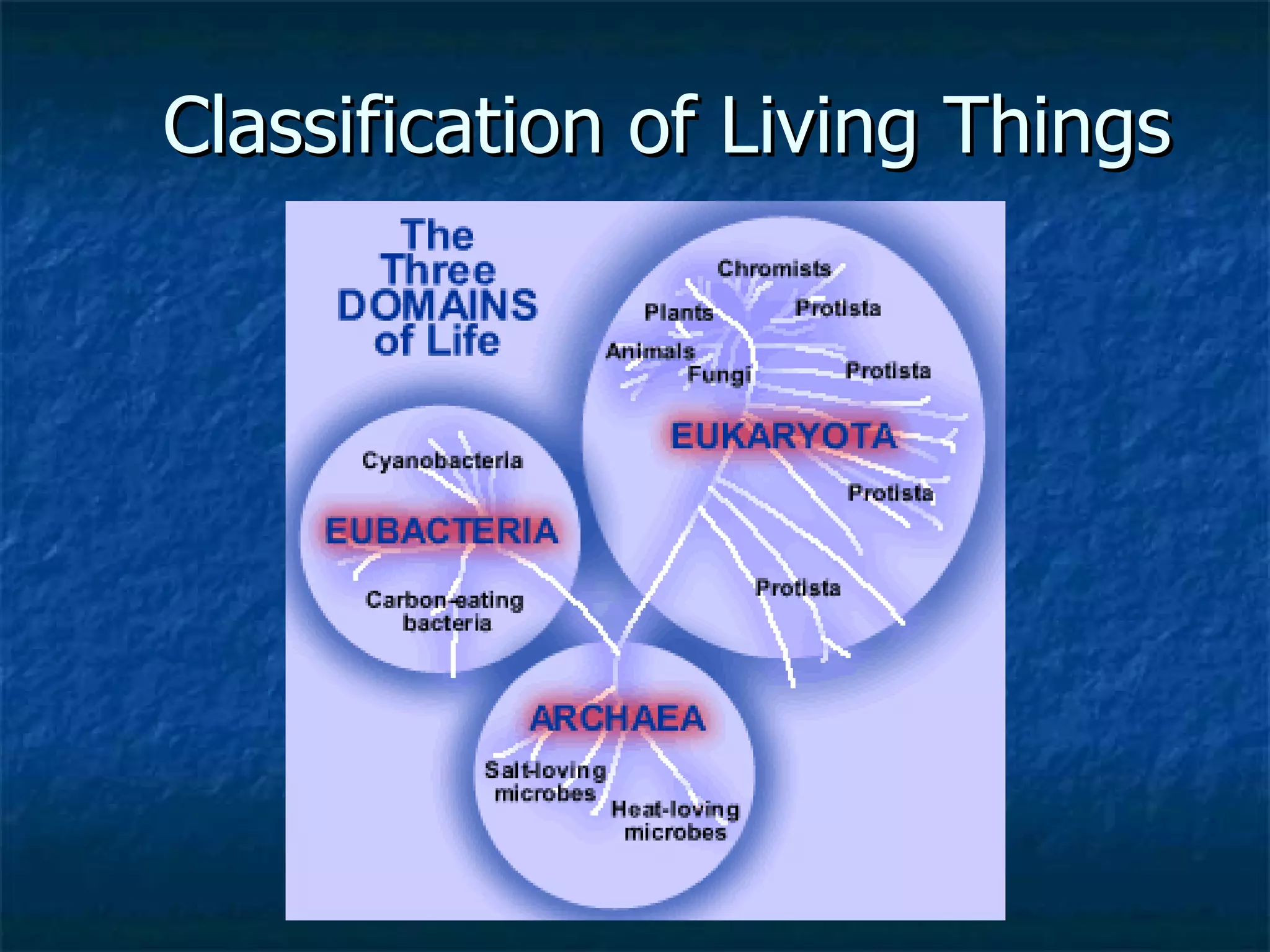
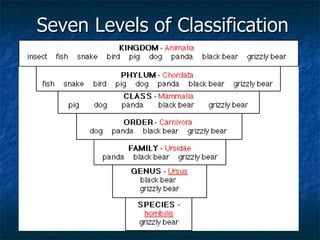
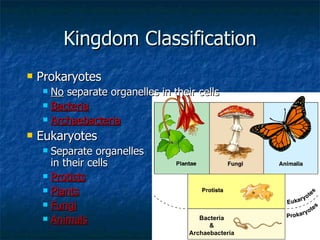
This document summarizes the classification of living things into six kingdoms - Plants, Animals, Protists, Fungi, Archaebacteria, and Eubacteria. It explains the hierarchical system of classification with seven levels from kingdom to species. Key details include that animals are multicellular and heterotrophs, plants are multicellular autotrophs that produce their own food, fungi obtain food from decaying plants, and protists include unicellular organisms not classified as bacteria, plants, animals or fungi.