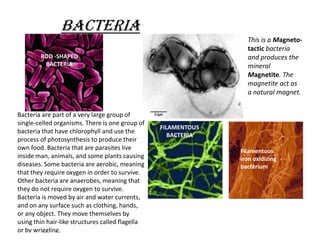
Microorganisms are very small organisms that are not visible to the naked eye. They can live in all environments from cold to hot and in places like air, water, soil, and inside other living things. All ecosystems depend on microorganisms like fungi, cyanobacteria, and lichens that form a layer in soil. Microorganisms can be unicellular like amoebas or multicellular like mold. They are broadly classified as bacteria, algae, protozoa, or fungi.