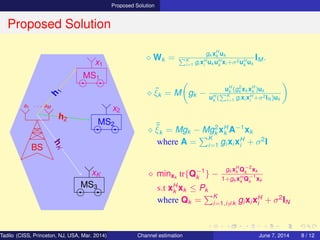
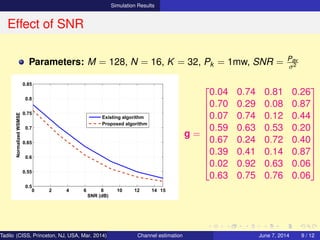
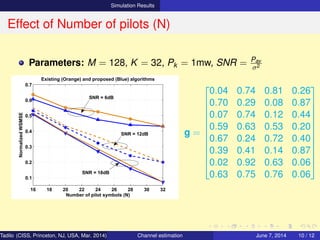
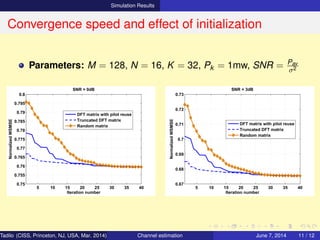
The document presents a new pilot assignment and channel estimation algorithm for multiuser massive MIMO systems, aiming to enhance performance in downlink communication scenarios. It details the system model, problem statement, proposed solutions, and simulation results demonstrating improvements in channel estimation accuracy, particularly with the use of weighted mean squared error (WSMSE) as an objective function. The findings indicate that the algorithm is optimal when the number of users matches the number of pilots.


![Multiuser Block Diagram
Communication Scenario and Objective
BS
a1 · · · aM
MS1
MS2
MSK
h
1
h2
hK
Scenario
• MS1, MS2, MSK are separated in space
and no coordination between them
⇒ Downlink Multiuser system
• MS1, MS2, MSK have single antennas
⇒ Downlink Multiuser MISO system
• Channel between Tx and Rx is flat fading
• Transmission is TDD
• M >> K (i.e., Massive MIMO system)
General Objective
• To estimate channels H = [h1, h2, · · · hk ]
Tadilo (CISS, Princeton, NJ, USA, Mar. 2014) Channel estimation March 20, 2014 3 / 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciss2014slide4-140607140721-phpapp01/85/Pilot-Optimization-and-Channel-Estimation-for-Multiuser-Massive-MIMO-Systems-3-320.jpg)
![Multiuser Block Diagram
Conventional Channel Estimation (Orthogonal)
BS
a1 · · · aM
MS1
MS2
MS3
h
1
h2
h3
x1
x2
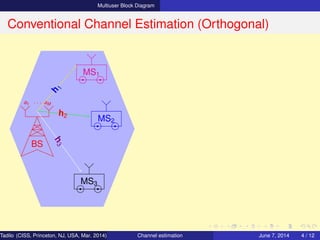
x3
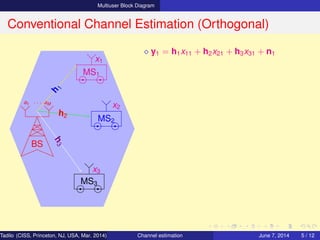
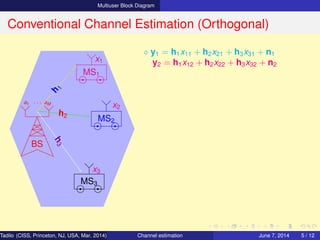
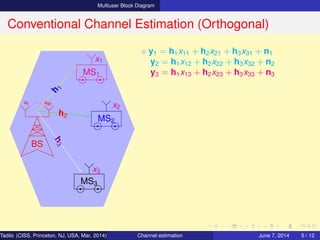
⋄ y1 = h1x11 + h2x21 + h3x31 + n1
y2 = h1x12 + h2x22 + h3x32 + n2
y3 = h1x13 + h2x23 + h3x33 + n3
⇒ Y = HX + N
where X = [x1 x2 x3]
N = [n1 n2 n3]
Tadilo (CISS, Princeton, NJ, USA, Mar. 2014) Channel estimation March 20, 2014 5 / 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciss2014slide4-140607140721-phpapp01/85/Pilot-Optimization-and-Channel-Estimation-for-Multiuser-Massive-MIMO-Systems-8-320.jpg)
![Multiuser Block Diagram
Conventional Channel Estimation (Orthogonal)
BS
a1 · · · aM
MS1
MS2
MS3
h
1
h2
h3
x1
x2
x3
⋄ y1 = h1x11 + h2x21 + h3x31 + n1
y2 = h1x12 + h2x22 + h3x32 + n2
y3 = h1x13 + h2x23 + h3x33 + n3
⇒ Y = HX + N
where X = [x1 x2 x3]
N = [n1 n2 n3]
⇒ YXH
= H + NXH
ˆhk = hk + NxH
k
⇒ Requires N ≥ K
Tadilo (CISS, Princeton, NJ, USA, Mar. 2014) Channel estimation March 20, 2014 5 / 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciss2014slide4-140607140721-phpapp01/85/Pilot-Optimization-and-Channel-Estimation-for-Multiuser-Massive-MIMO-Systems-9-320.jpg)

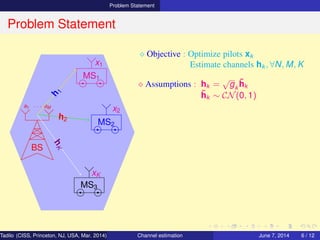
![Problem Statement
Problem Statement
BS
a1 · · · aM
MS1
MS2
MS3
h
1
h2
hK
x1
x2
xK
⋄ Objective : Optimize pilots xk
Estimate channels hk , ∀N, M, K
⋄ Assumptions : hk =
√
gk
˜hk
˜hk ∼ CN(0, 1)
⋄ Problem : Y = HXH
+ N
where H = [h1, · · · , hK ]
X = [x1, · · · , xN ]
N = [n1, · · · , nN]
Tadilo (CISS, Princeton, NJ, USA, Mar. 2014) Channel estimation March 20, 2014 6 / 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciss2014slide4-140607140721-phpapp01/85/Pilot-Optimization-and-Channel-Estimation-for-Multiuser-Massive-MIMO-Systems-12-320.jpg)
![Problem Statement
Problem Statement
BS
a1 · · · aM
MS1
MS2
MS3
h
1
h2
hK
x1
x2
xK
⋄ Objective : Optimize pilots xk
Estimate channels hk , ∀N, M, K
⋄ Assumptions : hk =
√
gk
˜hk
˜hk ∼ CN(0, 1)
⋄ Problem : Y = HXH
+ N
where H = [h1, · · · , hK ]
X = [x1, · · · , xN ]
N = [n1, · · · , nN]
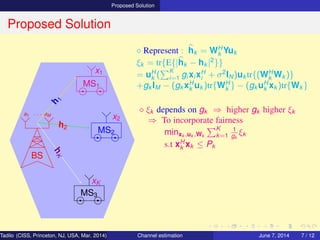
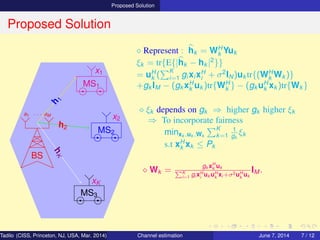
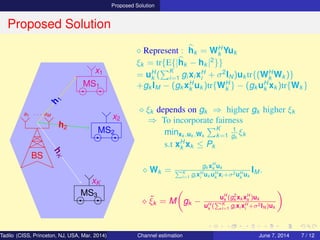
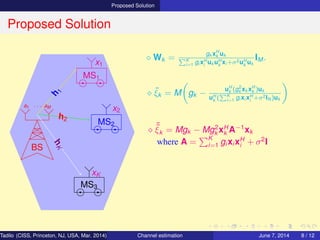
⋄ Represent : hk = WH
k Yuk
ξk = tr{E{|hk − hk |2
}}
= uH
k (
K
i=1 gi xi xH
i + σ2
IN)uk tr{(WH
k Wk )}
+gk IM − (gk xH
k uk )tr{WH
k } − (gk uH
k xk )tr{Wk }
Tadilo (CISS, Princeton, NJ, USA, Mar. 2014) Channel estimation March 20, 2014 6 / 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciss2014slide4-140607140721-phpapp01/85/Pilot-Optimization-and-Channel-Estimation-for-Multiuser-Massive-MIMO-Systems-13-320.jpg)