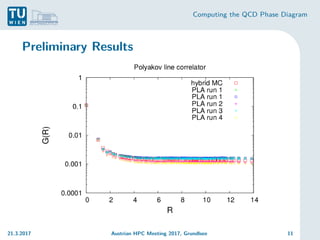
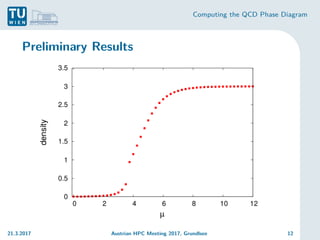
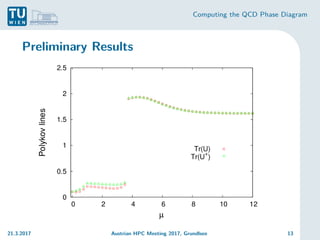
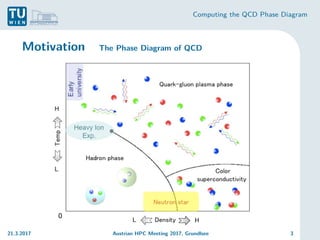
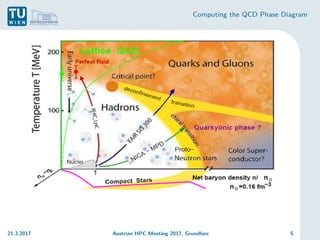
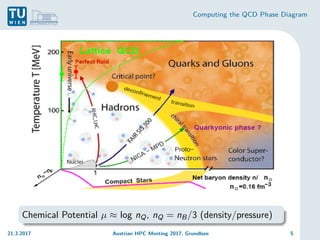
The document discusses the computation of the Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD) phase diagram using effective Polyakov line actions and methods to address the sign problem in lattice QCD. It details the motivations, methodologies, preliminary results, and conclusions drawn from a study conducted during an Austrian HPC meeting in 2017. The work contributes to the understanding of QCD by solving the sign problem and determining effective actions, which may influence future research on quark masses and finite chemical potentials.









![Computing the QCD Phase Diagram
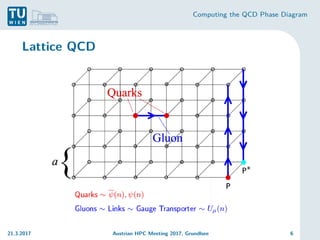
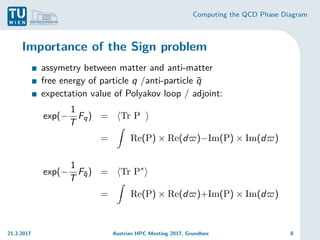
Lattice QCD and the Sign problem
Z =
R
DUDψ̄Dψ e−SYM(U)−SF(U;µ)
SF(U; µ) = −
R
d4x ψ̄ M(U; µ) ψ
Z =
R
DU e−SYM(U) det M(U; µ)
numerical evaluation of bosonic integral with importance
sampling, Metropolis, HMC Algorithms, MILC
observable hOi =
R
DU e−SYM det M O
R
DU e−SYM det M
lack of γ5-hermiticity, γ5M(µ)γ5 = M†(−µ∗) 6= M†(µ)
determinant is complex and satisfies
[det M(µ)]∗ = det M(−µ∗)
21.3.2017 Austrian HPC Meeting 2017, Grundlsee 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ahpc17-230313223046-75a29b49/85/QCD-Phase-Diagram-15-320.jpg)











![Computing the QCD Phase Diagram
Effective Polyakov Line Action
Indirect approach: Polyakov line action (SU(3) spin) model
fix Polyakov line holonomies U0(~
x, 0) = Ux (temporal
gauge) and integrate out all other d.o.f.
eSP (Ux ) =
R
DU0(~
x, 0)DUkDψ
Q
x δ[Ux − U0(~
x, 0)]eSL
21.3.2017 Austrian HPC Meeting 2017, Grundlsee 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ahpc17-230313223046-75a29b49/85/QCD-Phase-Diagram-28-320.jpg)
![Computing the QCD Phase Diagram
Effective Polyakov Line Action
Indirect approach: Polyakov line action (SU(3) spin) model
fix Polyakov line holonomies U0(~
x, 0) = Ux (temporal
gauge) and integrate out all other d.o.f.
eSP (Ux ) =
R
DU0(~
x, 0)DUkDψ
Q
x δ[Ux − U0(~
x, 0)]eSL
derive SP at µ = 0, for µ > 0 we have (true to all orders of
strong coupling/hopping parameter expansion)
21.3.2017 Austrian HPC Meeting 2017, Grundlsee 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ahpc17-230313223046-75a29b49/85/QCD-Phase-Diagram-29-320.jpg)
![Computing the QCD Phase Diagram
Effective Polyakov Line Action
Indirect approach: Polyakov line action (SU(3) spin) model
fix Polyakov line holonomies U0(~
x, 0) = Ux (temporal
gauge) and integrate out all other d.o.f.
eSP (Ux ) =
R
DU0(~
x, 0)DUkDψ
Q
x δ[Ux − U0(~
x, 0)]eSL
derive SP at µ = 0, for µ > 0 we have (true to all orders of
strong coupling/hopping parameter expansion)
Sµ
P(Ux , U†
x ) = Sµ=0
P [eNt µUx , e−Nt µU†
x ]
21.3.2017 Austrian HPC Meeting 2017, Grundlsee 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ahpc17-230313223046-75a29b49/85/QCD-Phase-Diagram-30-320.jpg)
![Computing the QCD Phase Diagram
Effective Polyakov Line Action
Indirect approach: Polyakov line action (SU(3) spin) model
fix Polyakov line holonomies U0(~
x, 0) = Ux (temporal
gauge) and integrate out all other d.o.f.
eSP (Ux ) =
R
DU0(~
x, 0)DUkDψ
Q
x δ[Ux − U0(~
x, 0)]eSL
derive SP at µ = 0, for µ > 0 we have (true to all orders of
strong coupling/hopping parameter expansion)
Sµ
P(Ux , U†
x ) = Sµ=0
P [eNt µUx , e−Nt µU†
x ]
hard to compute exp[SP(Ux )], use relative weights...
21.3.2017 Austrian HPC Meeting 2017, Grundlsee 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ahpc17-230313223046-75a29b49/85/QCD-Phase-Diagram-31-320.jpg)