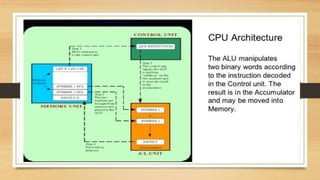
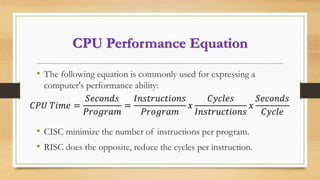
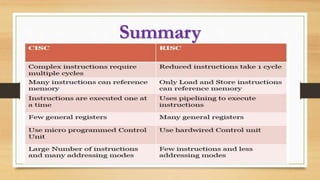
The document discusses CPU architecture and instruction set architecture (ISA), comparing CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computing) and RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) philosophies. CISC aims for fewer lines of code with varying instruction sizes, leading to slower performance, while RISC uses uniform, simple instructions executed in one cycle, enhancing speed but requiring more memory. The CPU performance equation is detailed, highlighting the balance between the number of instructions and cycles per instruction for both architectures.