Heaps are nearly complete binary trees stored as arrays that satisfy the heap property: for max-heaps a parent node is greater than or equal to its children, and for min-heaps a parent is less than or equal to its children. Heap operations like insert, extract max/min, and increase/decrease key take O(log n) time due to the heap's height. The heapsort algorithm uses a max-heap to sort an array in O(n log n) time by repeatedly extracting and placing the max element in its final position. Priority queues implemented with heaps support insertion, maximum/minimum extraction, and key increases/decreases in O(log n) time.


![Heaps
Heaps are typically stored using arrays
The array is of size length(A)
heapsize(A) elements are currently in use
A[1] is the “root” node of the tree
Any element x has the following properties:
Parent(x) is x/2
Left(x) is 2*x
Right(x) is 2*x+1
16 14 10 8 7 9 3 2 4 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cis435week05-140325170020-phpapp01/85/Cis435-week05-3-320.jpg)
![The Heap Property
Heaps satisfy what is known as the heap
property:
For a max-heap, the heap property is:
A[Parent(x)] >= A[x]
I.e., the root node of the tree or any subtree has a
larger value than any node in its subtrees
This is reversed for min-heaps:
A[Parent(x)] <= A[x]
I.e., the smallest element is at the root](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cis435week05-140325170020-phpapp01/85/Cis435-week05-4-320.jpg)


![MaxHeapify
MaxHeapify(A, x, heapsize)
{
L = Left(x)
R = Right(x)
if ( L < heapsize && A[L] > A[x] )
Largest = L
else
Largest = x
if ( R <= heapsize && A[R] > A[Largest] )
Largest = R
if ( Largest != x )
{
swap(A[x], A[Largest])
MaxHeapify(A, Largest, heapsize)
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cis435week05-140325170020-phpapp01/85/Cis435-week05-7-320.jpg)




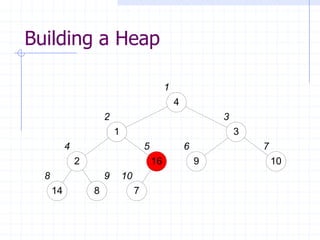
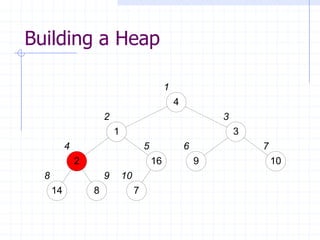
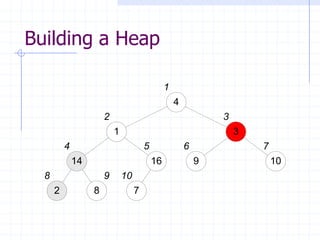
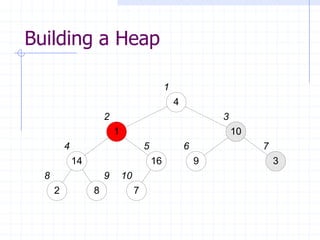
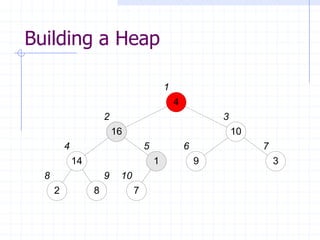
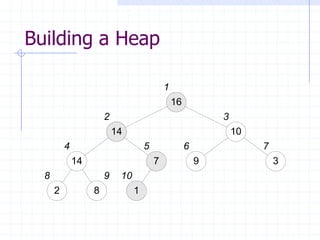

![The HeapSort Algorithm
The HeapSort algorithm sorts an array by
using a max-heap as an intermediate
step
First, a max-heap is built from the input
The max element is exchanged with
A[heapsize], to put it in its final position
The remainder of the array is then re-
heapified, using heapsize - 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cis435week05-140325170020-phpapp01/85/Cis435-week05-19-320.jpg)
![The HeapSort Algorithm
HeapSort(A, size)
{
BuildHeap(A, size)
For ( x = size ; x >= 2 ; --x )
{
swap(A[1], A[x])
--heapsize
Heapify(A, 1, x-1)
}
}
What is the running time of HeapSort?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cis435week05-140325170020-phpapp01/85/Cis435-week05-20-320.jpg)



![Priority Queuess
HeapMaximum(A)
{
return A[1];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cis435week05-140325170020-phpapp01/85/Cis435-week05-24-320.jpg)
![Priority Queues
HeapExtractMax(A, heapsize)
{
if ( heapsize < 1 )
throw HeapUnderflowError();
max = A[1];
A[1] = A[heapsize];
--heapsize;
MaxHeapify(A, 1, heapsize);
return max;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cis435week05-140325170020-phpapp01/85/Cis435-week05-25-320.jpg)
![Priority Queues
HeapIncreaseKey(A, i, key)
{
if ( key < A[i] )
throw HeapKeyError();
A[i] = key;
while ( i > 1 && A[Parent(i) < A[i] )
{
swap(A[i], A[Parent(i)]);
i = Parent(i);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cis435week05-140325170020-phpapp01/85/Cis435-week05-26-320.jpg)
![Priority Queues
MaxHeapInsert(A, key, heapsize)
{
++heapsize;
A[heapsize] = -MAXKEY;
HeapIncreaseKey(A, A[heapsize], key);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cis435week05-140325170020-phpapp01/85/Cis435-week05-27-320.jpg)
