Dynamic programming is used to solve optimization problems by breaking them down into overlapping subproblems. It is applicable to problems that exhibit optimal substructure and overlapping subproblems. The matrix chain multiplication problem can be solved using dynamic programming in O(n^3) time by defining the problem recursively, computing the costs of subproblems in a bottom-up manner using dynamic programming, and tracing the optimal solution back from the computed information. Similarly, the longest common subsequence problem exhibits optimal substructure and can be solved using dynamic programming.










![A Recursive Solution
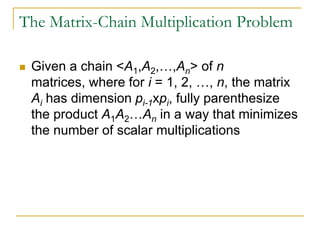
Our subproblem is the problem of
determining the minimum cost of a
parenthesization of Ai,…,Aj, where 1 <= i <= j
<= n
Let m[i,j] be the minimum number of
multiplications needed to compute Ai..j
Lowest cost to compute A1..n is m[1,n]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-140325170008-phpapp02/85/Chapter-16-12-320.jpg)
![A Recursive Solution
How do we recursively define m[i,j]?
If i = j, no multiplications are necessary since we never
have to multiply a matrix by itself
Thus, m[i,i] = 0 for all i
If i < j, we compute as follows:
Assume that there is some optimal parenthesization that splits
the range between k and k+1
m[i,j] = m[i,k]+m[k+1,j]+pi-1pkpj, per our previous discussion
To do this, we must find k
There are j-i possibilities, which can be checked directly](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-140325170008-phpapp02/85/Chapter-16-13-320.jpg)
![A Recursive Solution
Our recursive solution is now:
m[i,j] gives the costs of optimal solutions to
subproblems
Define a second table s[i,j] to help keep track of
how to construct an optimal solution
Each entry contains the value k at which to split the
product
ji
ji
pppjkmkim
jim
jki
jki
if
if
}],1[],[{min
0
],[
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-140325170008-phpapp02/85/Chapter-16-14-320.jpg)


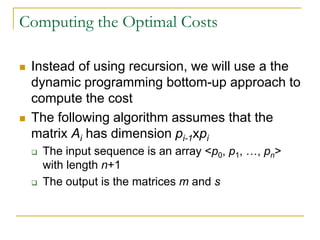
![MatrixChainOrder(const double p[], int size, Matrix
&m, Matrix &s)
{
int n = size-1;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++i )
m(i,i) = 0;
for ( int L = 2 ; L <= n ; ++L ) {
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n-L+1 ; ++i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j <= i+L-1 ; ++j ) {
m(i,j) = MAXDOUBLE;
for ( int k = i ; k <= j-1 ; ++k ) {
int q = m(i,k)+m(k+1,j)+p[i-1]*p[k]*p[j];
if ( q < m(i,j) ) m(i,j) = q;
else s(i,j) = k;
} // for ( k )
} // for ( j )
} // for ( i )
} // for ( L )
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-140325170008-phpapp02/85/Chapter-16-18-320.jpg)


![Constructing an Optimal Solution
So far, we only know the optimal number of scalar
multiplications, not the order in which to multiply the matrices
This information is encoded in the table s
Each entry s[i,j] records the value k such that the optimal
parenthesization of Ai…Aj occurs between matrix k and k+1
To compute the product A1..n, we parenthesize at s[1,n]
Previous matrix multiplications can be computed recursively
E.g., s[1,s[1,n]] contains the optimal split for the left half of the
multiplication](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-140325170008-phpapp02/85/Chapter-16-21-320.jpg)
![Constructing an Optimal Solution
MatrixChainMultiply(const Matrix A[], const Matrix &s, int
i, int j)
{
if ( j > i )
{
Matrix X = MatrixChainMultiply(A, s, i, s(i,j));
Matrix Y = MatrixChainMultiply(A, s, s(i,j)+1, j);
return MatrixMultiply(X,Y);
}
else
return A[i];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-140325170008-phpapp02/85/Chapter-16-22-320.jpg)



![Overlapping Subproblems
From the matrix-chain algorithm, we see earlier
computations being reused to perform later
computations:
What if we replaced this with a recursive
algorithm?
Figure 16.2 on page 311 shows the added
computations
int q = m(i,k)+m(k+1,j)+p[i-1]*p[k]*p[j];
if ( q < m(i,j) )
m(i,j) = q;
else
s(i,j) = k;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-140325170008-phpapp02/85/Chapter-16-26-320.jpg)




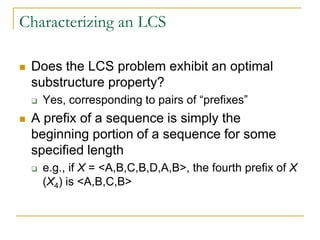



![A Recursive Solution To Subproblems
What is the cost of an optimal solution?
Let c[i,j] be the length of an LCS of Xi & Yj
If i or j = 0, then the LCS for that subsequence has length 0
Otherwise, the cost follows directly from Theorem 16.1:
ji
ji
yxji
yxji
ji
jicjic
jicjic
and0,if
and0,if
0or0if
],1[],1,[max(
1]1,1[
0
],[](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-140325170008-phpapp02/85/Chapter-16-35-320.jpg)

![Computing the Length of an LCS
The following algorithm fills in the cost table c
based on the input sequences X and Y
It also maintains a table b that helps simplify an
optimal solution
Entry b[i,j] points to the table entry corresponding to the
optimal subproblem solution chosen when computing
c[i,j]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-140325170008-phpapp02/85/Chapter-16-37-320.jpg)

![Computing the Length of an LCS
// Fill in tables
for ( int i = 1 ; i < m ; ++i )
for ( int j = 1 ; j < n ; ++j ) {
if ( x[i] == y[j] ) {
c(i,j) = c(i-1,j-1)+1;
b(i,j) = 1; // Subproblem type 1 “ã”
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-140325170008-phpapp02/85/Chapter-16-39-320.jpg)



