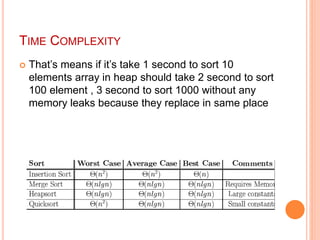
The document discusses heaps, a type of data structure used in heapsort, which organizes data into a binary tree format. It outlines two types of heaps—max-heaps and min-heaps—along with their properties, time complexity, and operational methods such as insertion and deletion. Additionally, it highlights the advantages of the heapsort algorithm and provides references for further reading.


![INTRODUCTION
Heapsort : A sorting algorithm that works by first
organizing the data to be sorted into a special type
of binary tree called a heap.
Heap: is an array object that we can view in special
form of complete binary tree e.g A[]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mohamedfawzy-heap-141222102235-conversion-gate01/85/Heapsort-using-Heap-3-320.jpg)
![HEAP TYPES
Max-Heap-root node has the largest value: A max
full complete binary tree where is root the largest
value for example A[Parent(i)] >= A[i]
Min-Heap root node has the smallest value : A Min
full complete binary tree where is root the smallest
value for example A[Parent(i)] <= A[i]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mohamedfawzy-heap-141222102235-conversion-gate01/85/Heapsort-using-Heap-4-320.jpg)
![HEAP TYPES (CONT)
Parent(i)
return [i/2]
Left(i)
Return 2i
Right(i)
Return 2i+1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mohamedfawzy-heap-141222102235-conversion-gate01/85/Heapsort-using-Heap-5-320.jpg)




![HOW TO USE IT ? INSERTION INTO A MAX
HEAP
void insert_max_heap(int item, int *n)
{
int i;
if (HEAP_FULL(*n)) {
printf(“the heap is full.n”);
exit(1);
}
i = ++(*n);
while ((i!=1)&&(item.key>heap[i/2].key))
{
heap[i] = heap[i/2];
i /= 2;
}
heap[i]= item;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mohamedfawzy-heap-141222102235-conversion-gate01/85/Heapsort-using-Heap-11-320.jpg)
![APPLICATIONS ON HEAP
See an illustration first
Array interpreted as a binary tree
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
26 5 77 1 61 11 59 15 48 19
26[1]
5[2] 77[3]
1[4] 61[5] 11[6] 59[7]
15[8] 48[9] 19[10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mohamedfawzy-heap-141222102235-conversion-gate01/85/Heapsort-using-Heap-12-320.jpg)
![APPLICATIONS ON HEAP
Adjust it to a Max-Heap
77[1]
61[2] 59[3]
48[4] 19[5] 11[6] 26[7]
15[8] 1[9] 5[10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mohamedfawzy-heap-141222102235-conversion-gate01/85/Heapsort-using-Heap-13-320.jpg)

