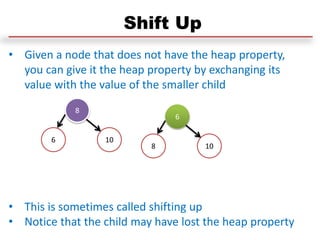
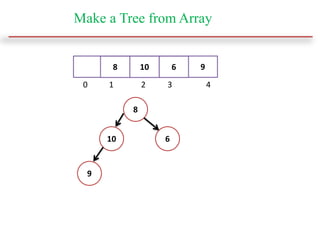
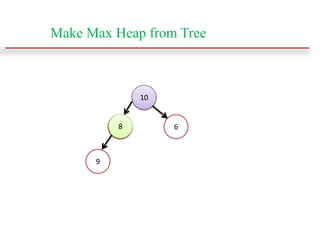
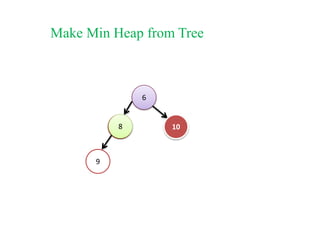
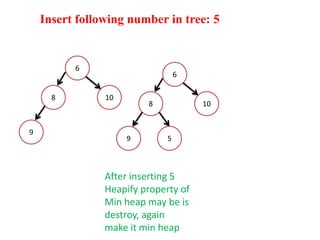
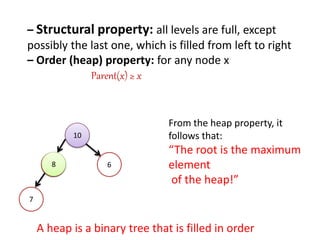
This document discusses heap sort and operations on heaps. It defines max-heaps and min-heaps, and how a heap can be represented as a binary tree and array. It explains that heap sort works by building a max-heap from an array, swapping the root with the last element and reducing the heap size, then sifting the new root down repeatedly until one element remains. Common heap operations like insertion, deletion, and heapify are also covered, along with time complexities of heap operations.


![Def : A heap is a nearly complete binary tree
TYPES:
•Max-heaps (largest element at root), have the max-
heap
property:
– for all nodes i, excluding the root: A[PARENT(i)] ≥
A[i]
•Min-heaps (smallest element at root), have the
min-heap
property:
– for all nodes i, excluding the root: A[PARENT(i)] ≤
A[i]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/musaddiqkhanheapsortpresentation-181129093050/85/Heap-Sort-Algorithm-3-320.jpg)



![Array Representation of Heaps
• A heap can be stored as an
array A.
– Root of tree is A[1]
– Left child of A[i] = A[2i]
– Right child of A[i] = A[2i + 1]
– Parent of A[i] = A[ i/2 ]
The elements in the sub array
A[( n/2 +1) ….. n] are leaves](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/musaddiqkhanheapsortpresentation-181129093050/85/Heap-Sort-Algorithm-8-320.jpg)