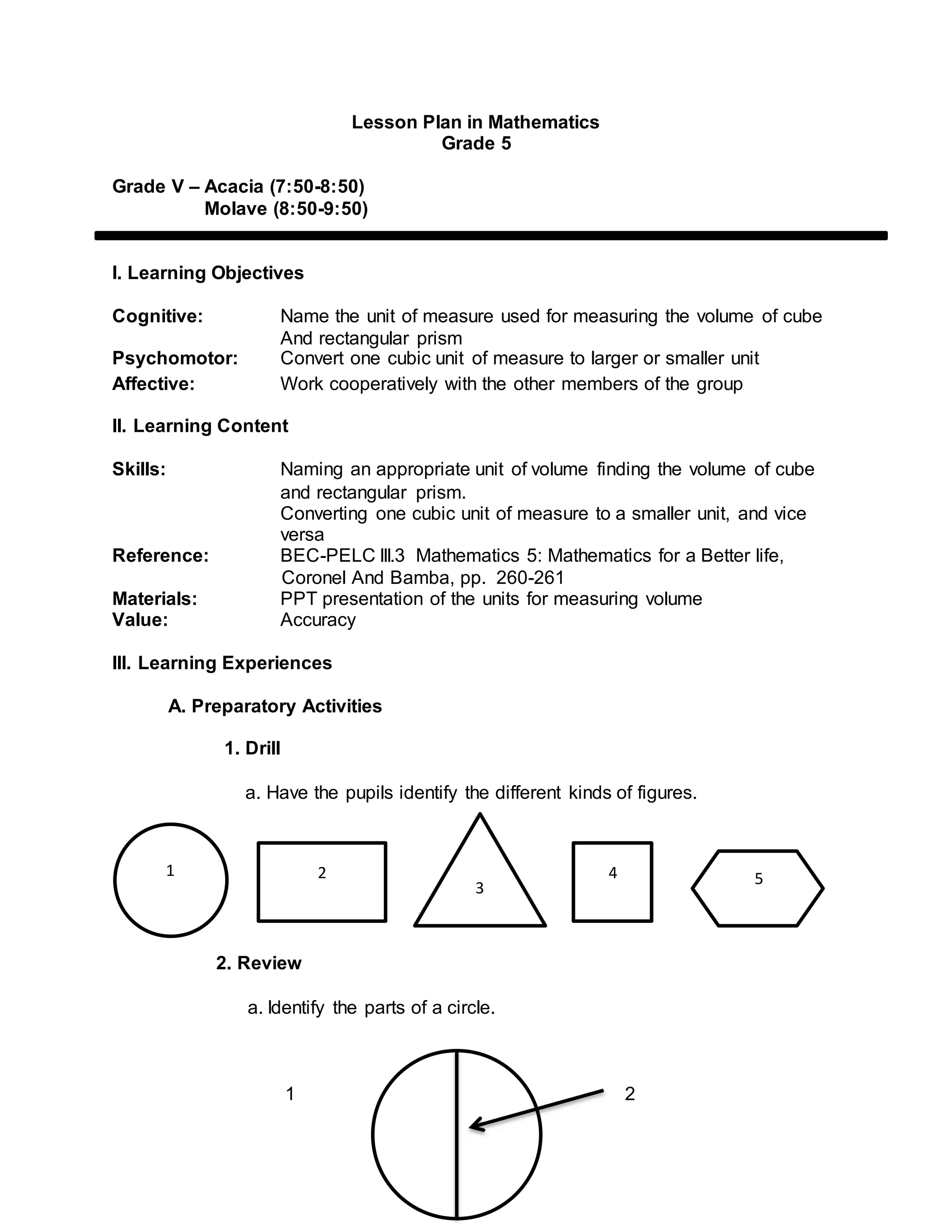
1) The lesson plan is for grade 5 mathematics and covers measuring the volume of cubes and rectangular prisms. It aims to teach students to name appropriate volume units, find the volume of basic 3D shapes, and convert between units.
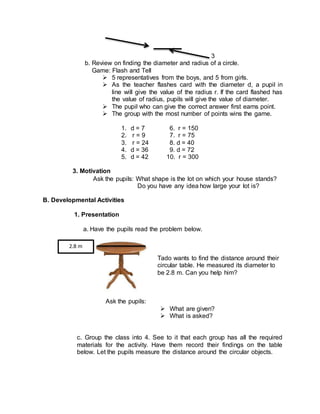
2) The lesson will include interactive activities like games and group work to reinforce concepts of finding diameters, radii, and using formulas to calculate circumferences of circles.
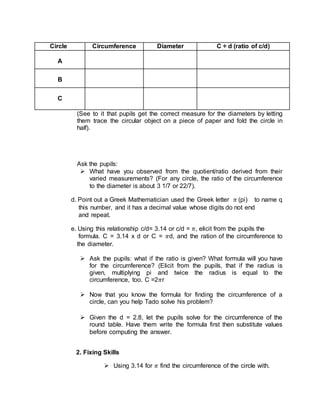
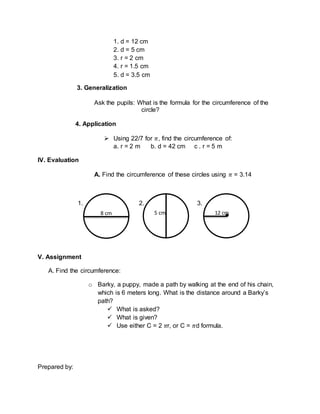
3) Students will practice using pi to calculate circumferences of various circles with different diameters or radii. They will also apply these formulas to word problems involving circular paths.