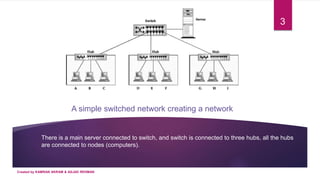
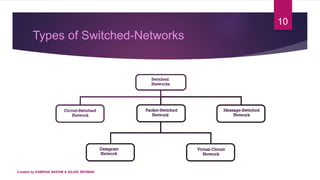
1) A switched network consists of interconnected switches that create temporary connections between devices linked to the switch. Multiple cables can connect devices to a switch to enable communication.
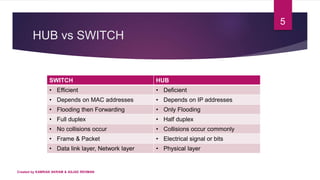
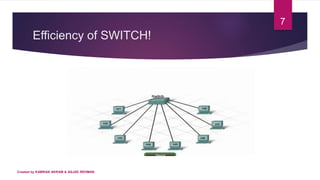
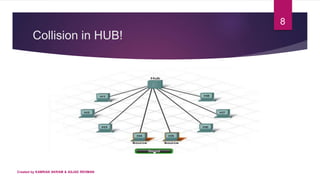
2) A switch works by flooding frames to all ports initially, then learning MAC addresses of devices and forwarding subsequent frames only to the relevant port, avoiding collisions. In contrast, a hub only floods frames.
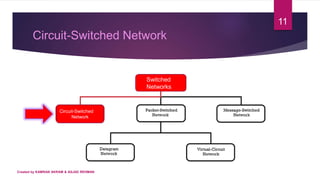
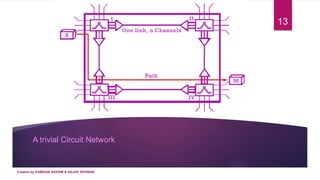
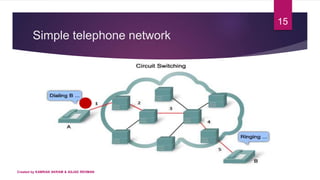
3) A circuit-switched network is a set of switches connected by physical links, where each link is divided into channels. It establishes a dedicated connection between stations using one or more links and channels. The connection remains for the duration until one party signals teardown.