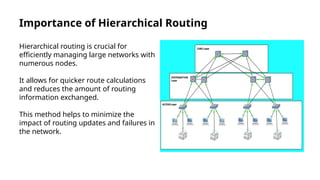
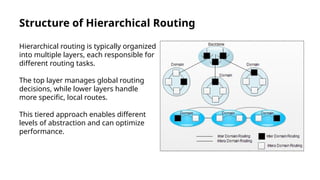
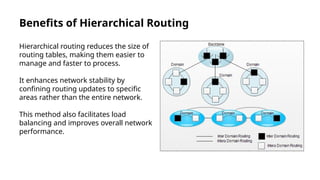
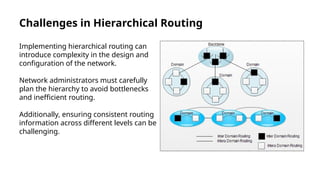
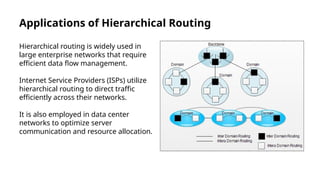
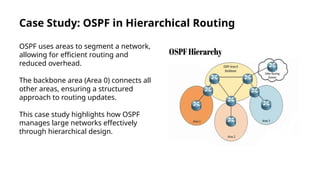
Hierarchical routing is an effective method for managing large-scale networks by dividing them into smaller segments, reducing routing table sizes and improving scalability. Common protocols like OSPF and EIGRP enable efficient routing through structured layers, but implementing such systems can introduce complexities. The approach is essential for modern networking, particularly as IoT and cloud computing rise, necessitating adaptation in routing strategies.