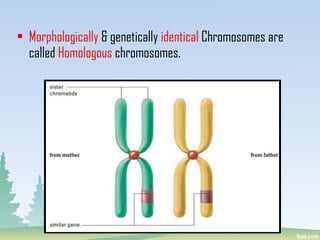
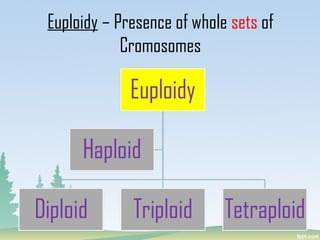
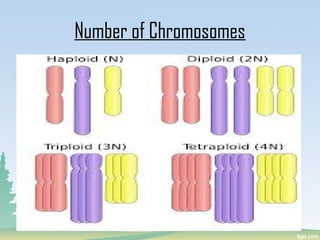
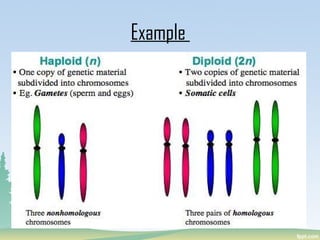
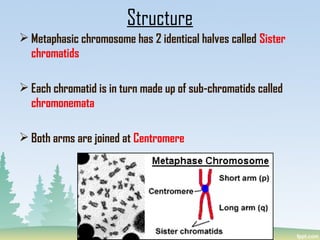
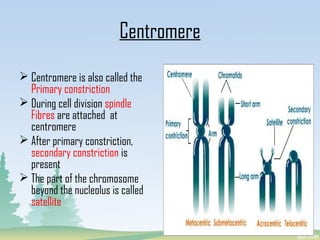
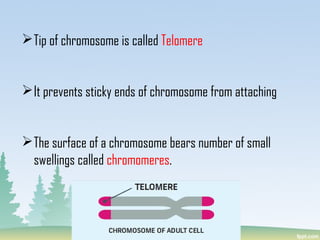
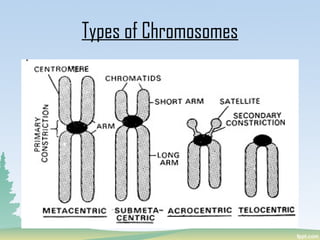
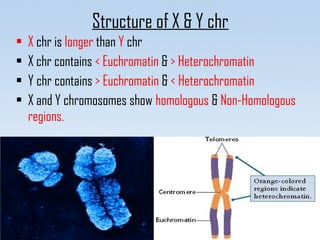
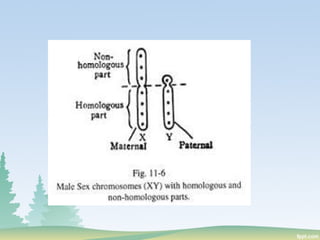
Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of cells and are responsible for heredity, variation, mutation, and evolution. They vary in size from 0.1 to 33 micrometers in length and 0.2 to 2 micrometers in thickness. Chromosomes have a characteristic shape with two identical halves called sister chromatids joined at the centromere. The X chromosome is typically longer than the Y chromosome and contains more euchromatin and less heterochromatin, while the Y chromosome shows the opposite pattern.