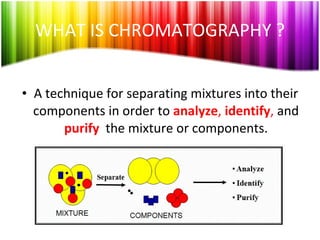
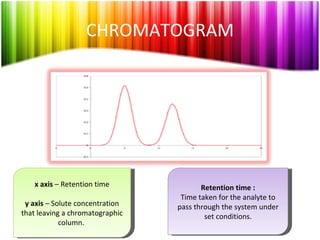
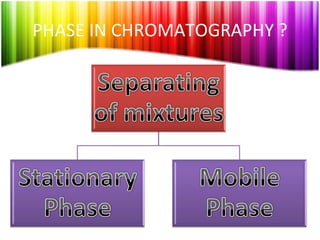
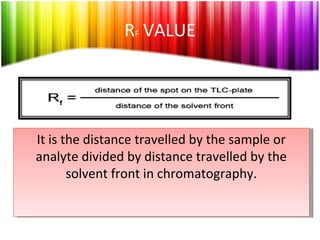
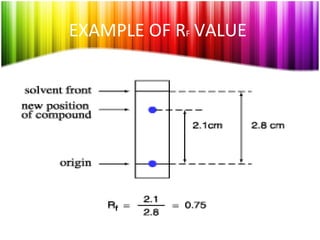
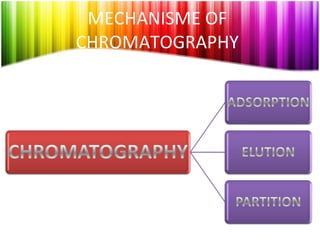
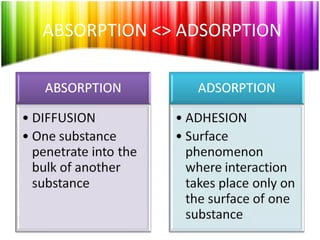
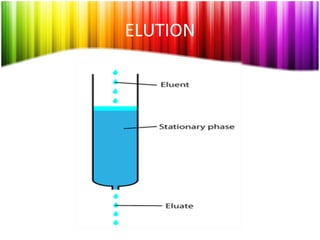
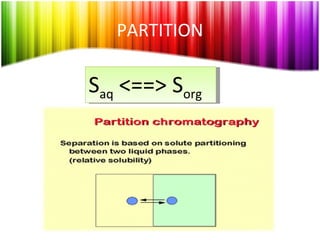
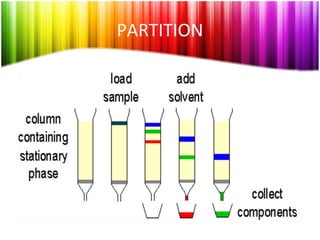
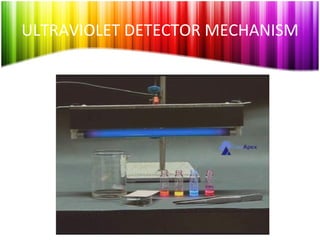
Chromatography is a technique used to separate mixtures into individual components and analyze, identify, and purify substances. It works by distributing components between a stationary and mobile phase as they travel through a chromatographic system. The visual output, or chromatogram, shows different patterns corresponding to different mixture components based on their retention times and concentrations. Common stationary phases include adsorbents like liquids or solids, while mobile phases are usually solvents or supercritical fluids that carry analytes through the system.