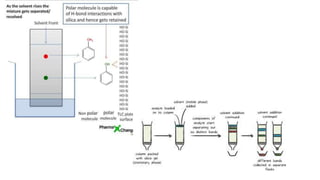
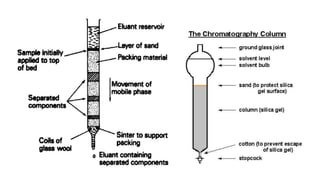
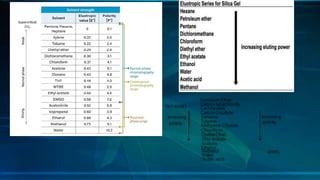
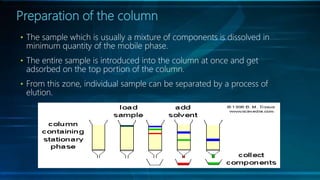
Chromatography is a method of separating mixtures into individual components based on differences in how they interact with and move through stationary and mobile phases. There are various types of chromatography classified by the separation principle used and phases involved, including adsorption, partition, ion exchange, and size exclusion. Column chromatography is commonly used, involving a solid stationary phase packed into a column with a liquid mobile phase passed through to separate components. Factors like choice of stationary phase, mobile phase, development technique affect the separation achieved.