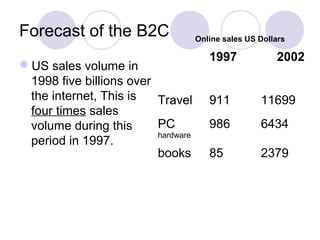
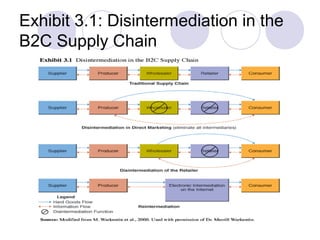
The document discusses various topics related to electronic retailing and business models. It describes retailers as intermediaries between manufacturers and customers. Amazon is discussed as the biggest online retailer with low prices, easy browsing, product information, and order features. Direct marketing is described where manufacturers sell directly to customers without intermediaries. Dell is used as an example of a direct marketer that sells computers through its website. The document also discusses electronic intermediaries like online stores and malls, as well as different business models for electronic markets including direct vs indirect marketing and global vs regional approaches.