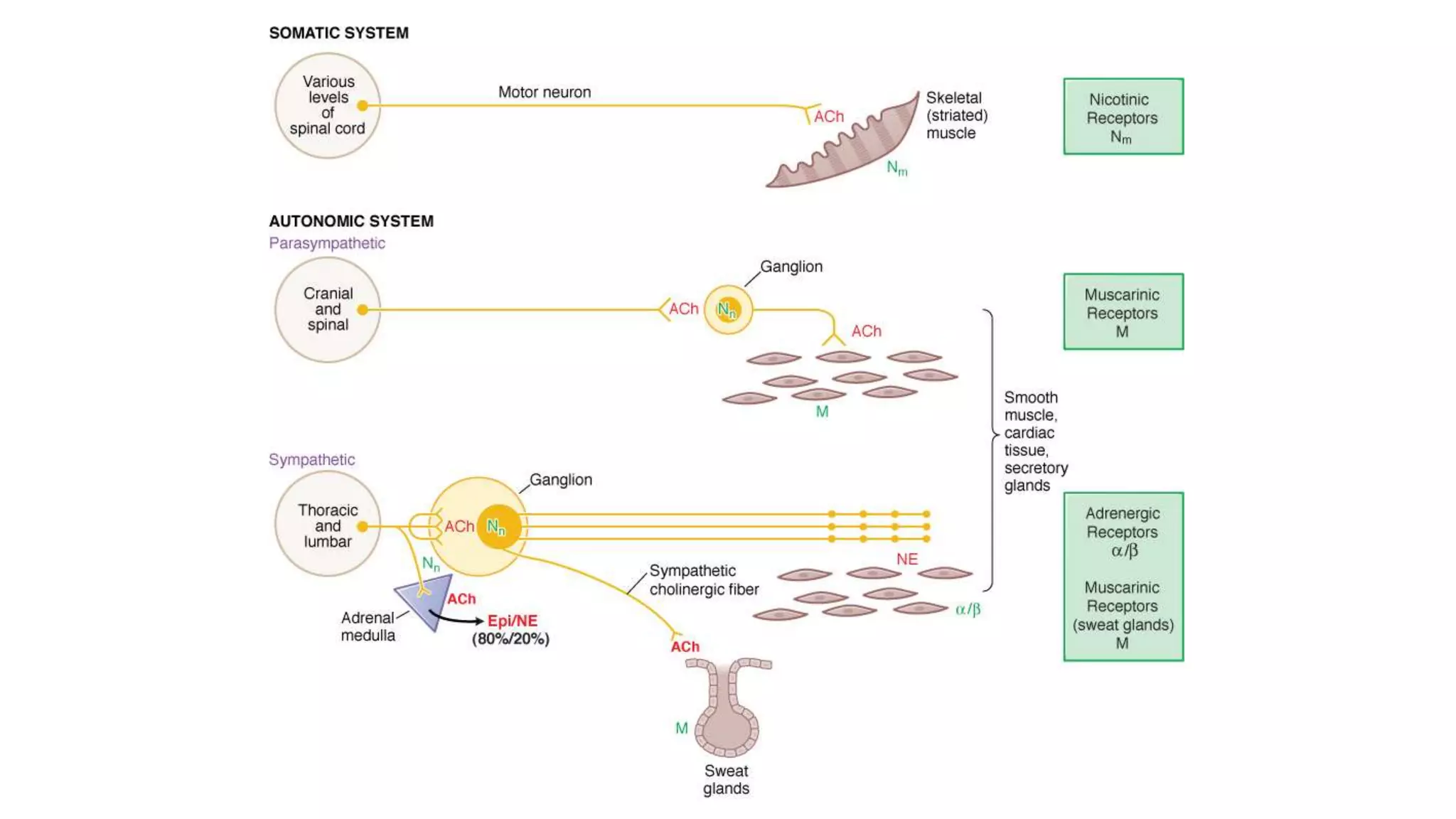
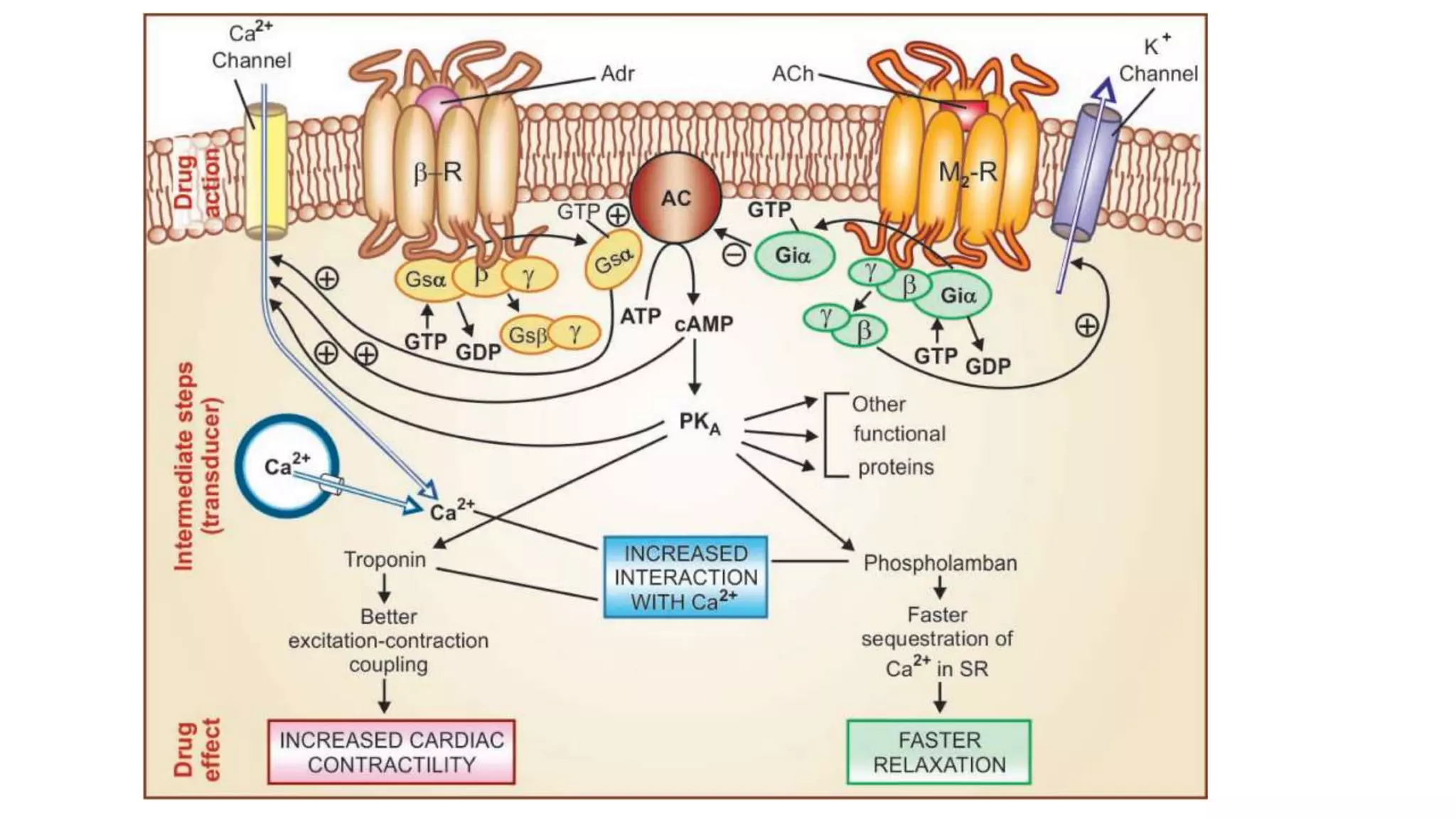
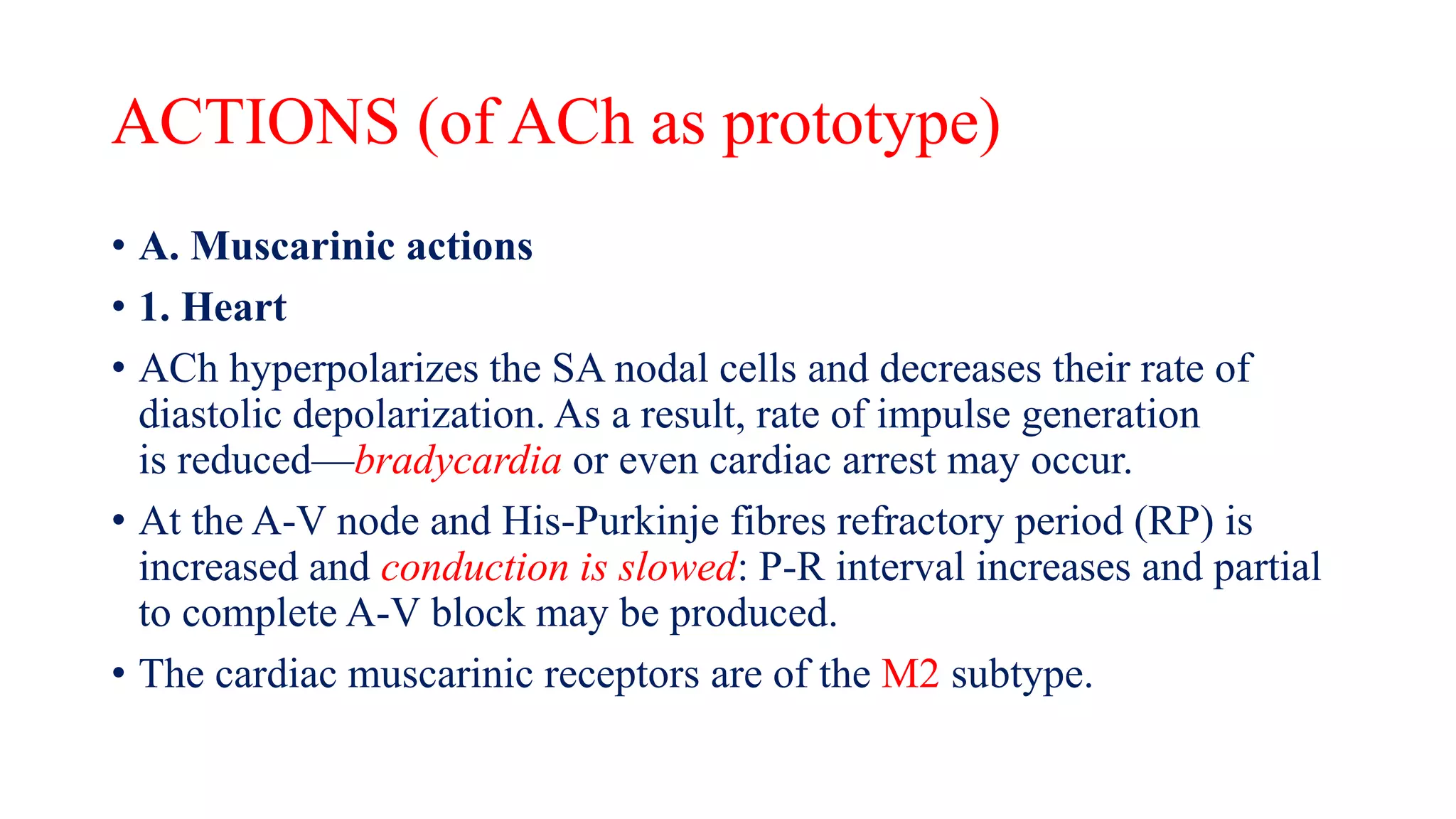
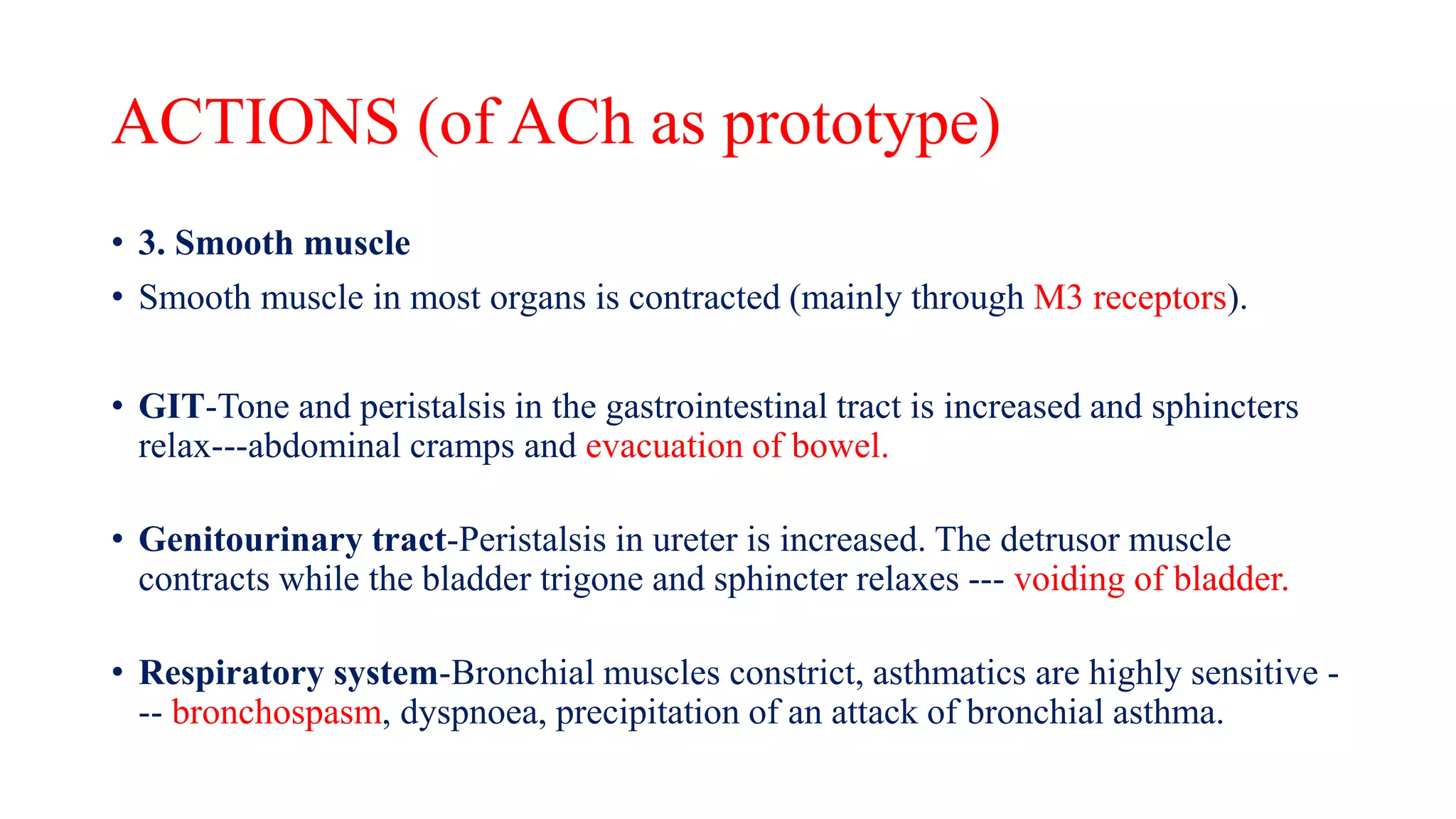
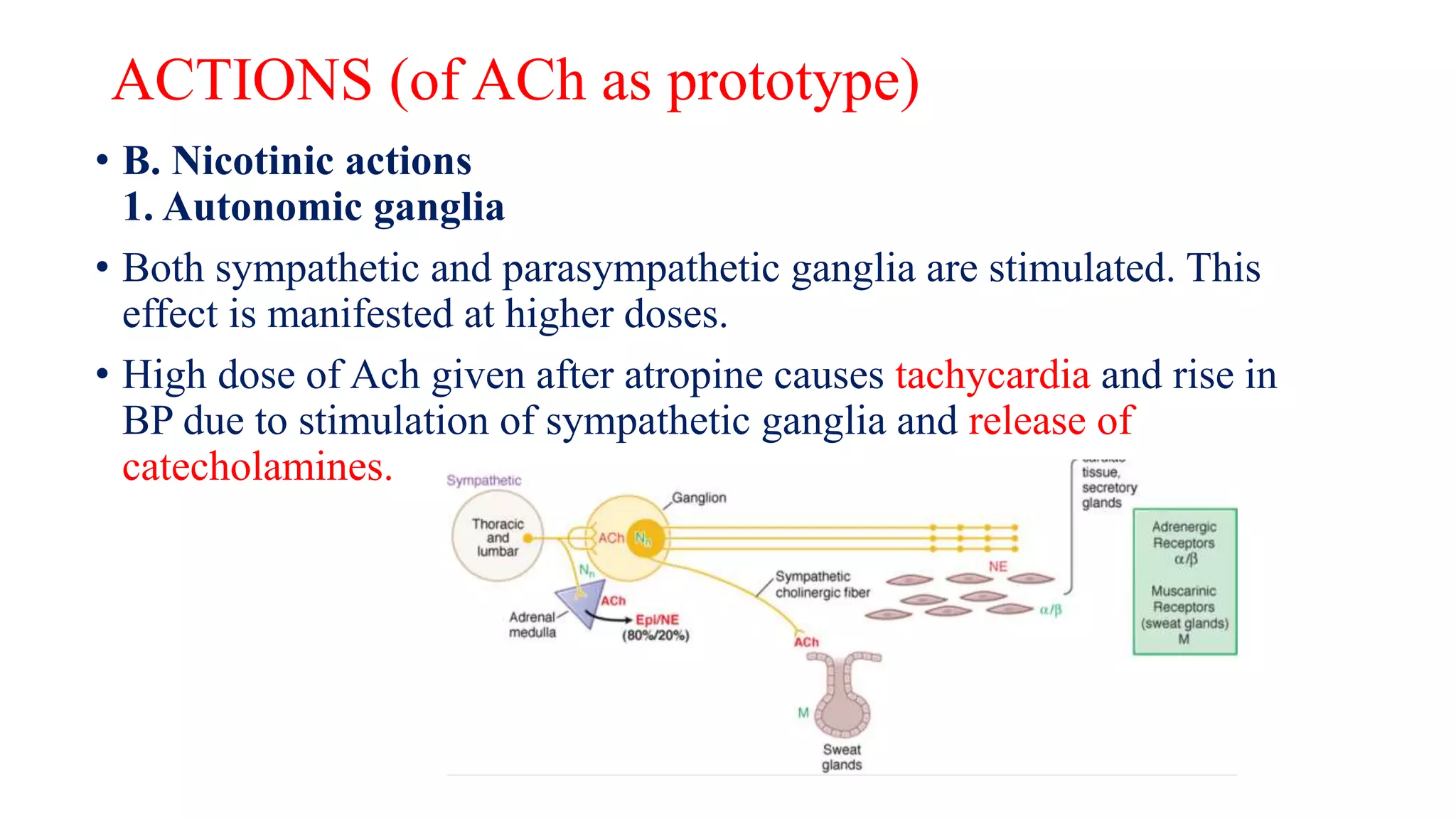
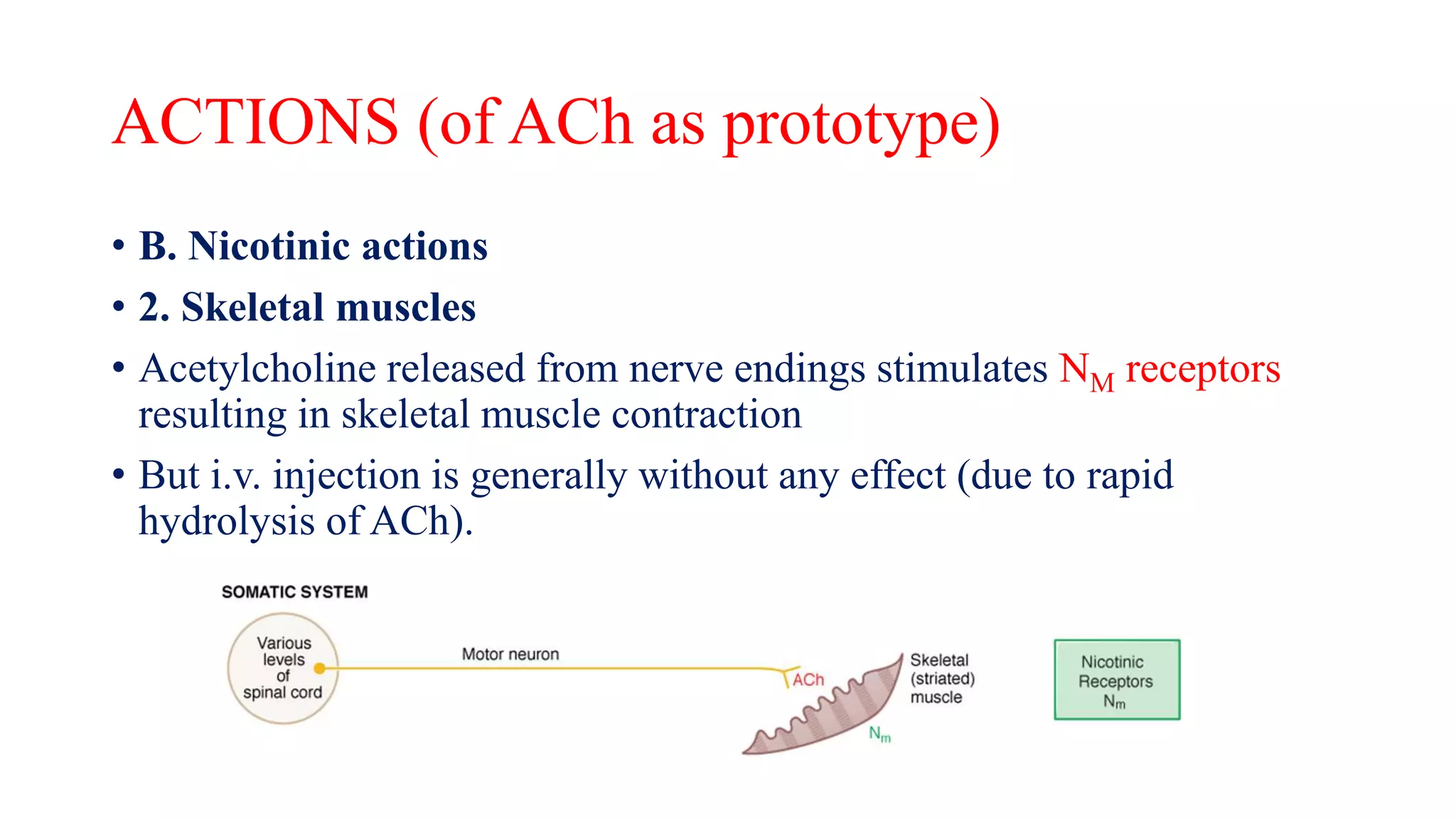
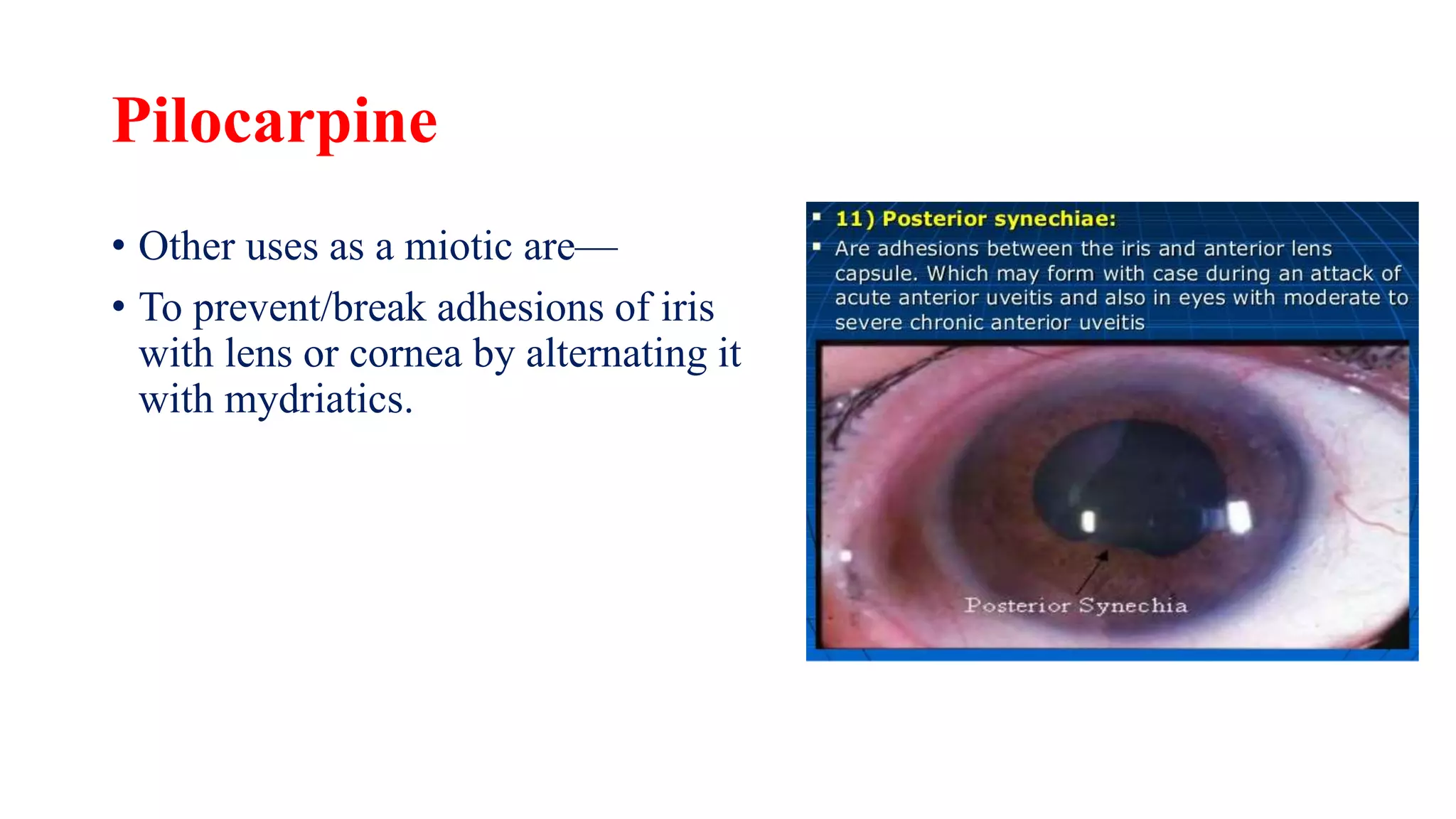
This document discusses cholinergic agonists and their mechanisms of action. It describes how acetylcholine is synthesized and metabolized by cholinesterase. It outlines the two main types of cholinergic receptors - muscarinic and nicotinic receptors. Muscarinic receptors have subtypes that mediate various effects in the heart, blood vessels, smooth muscles and exocrine glands. Nicotinic receptors are located at autonomic ganglia and the neuromuscular junction. Some cholinergic drugs like pilocarpine are used clinically for their effects on muscarinic receptors in the eye.