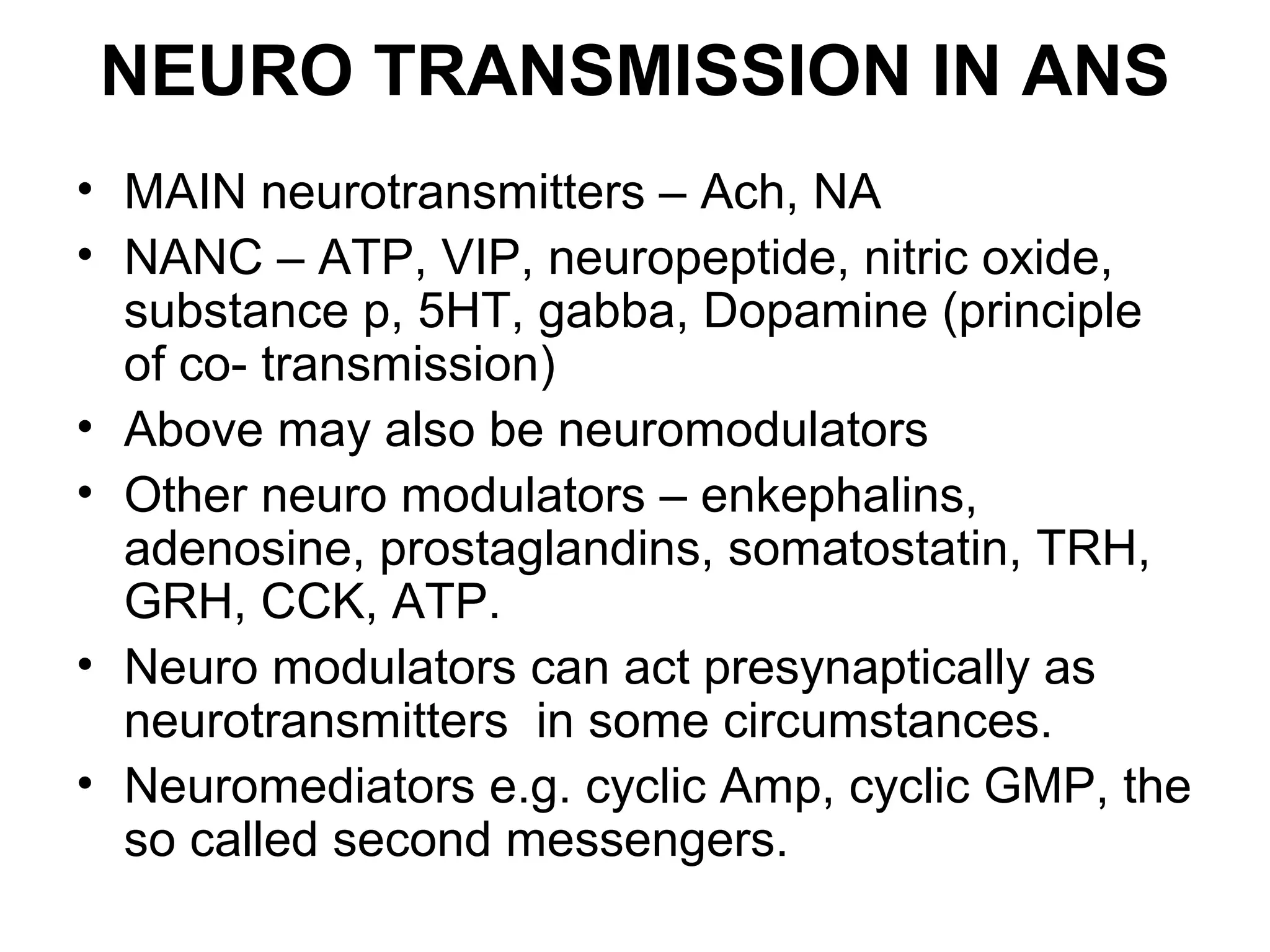
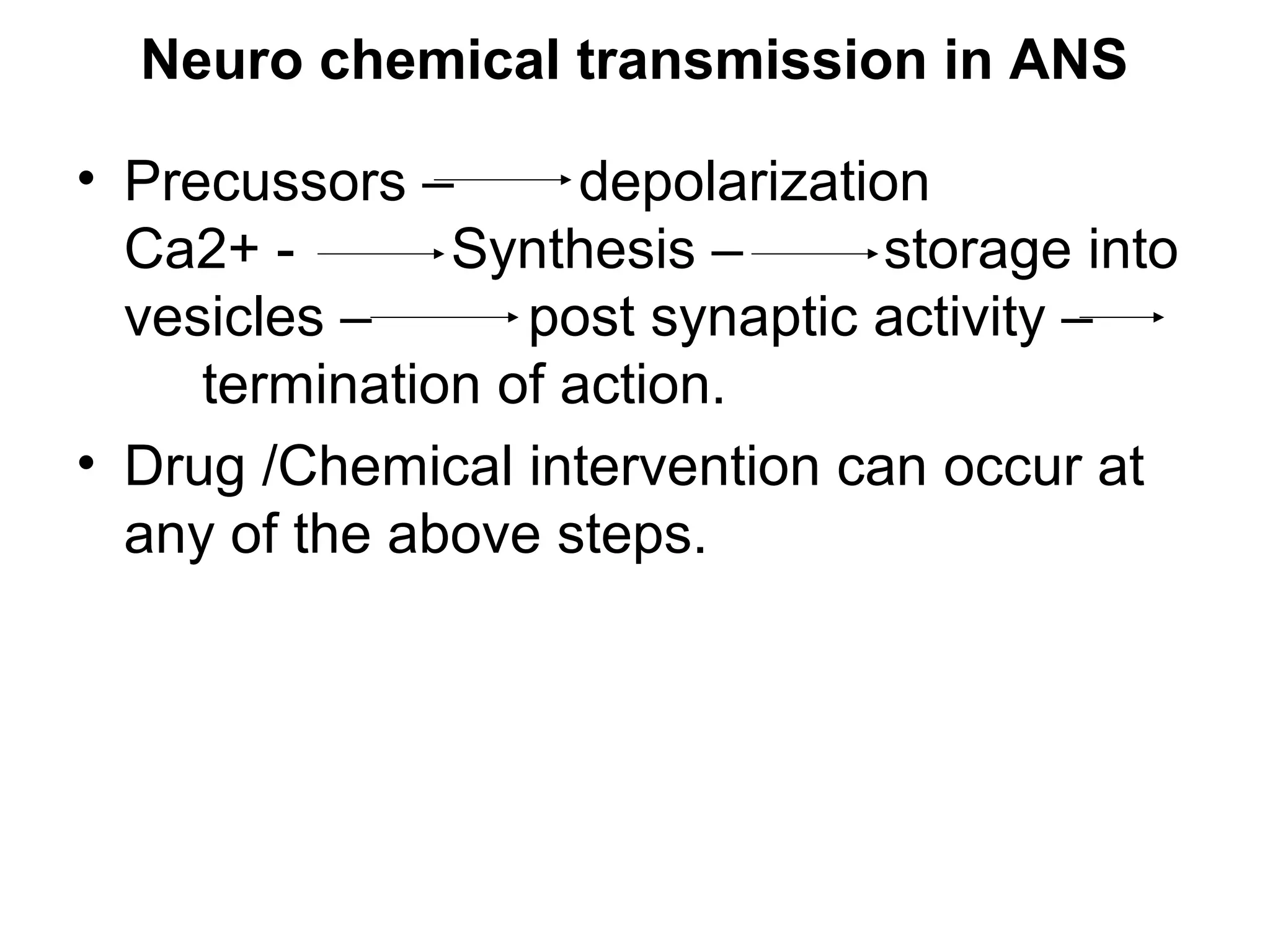
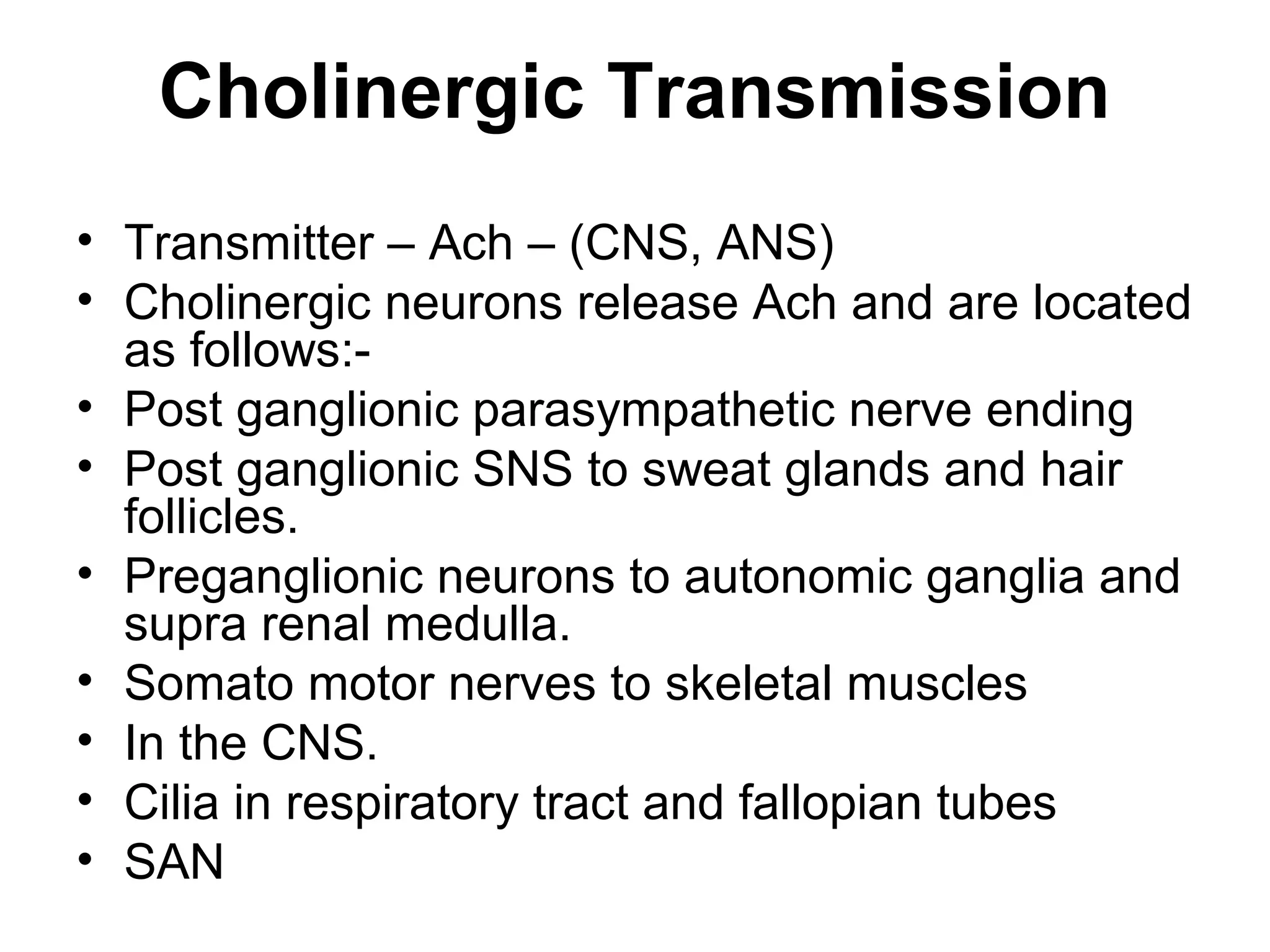
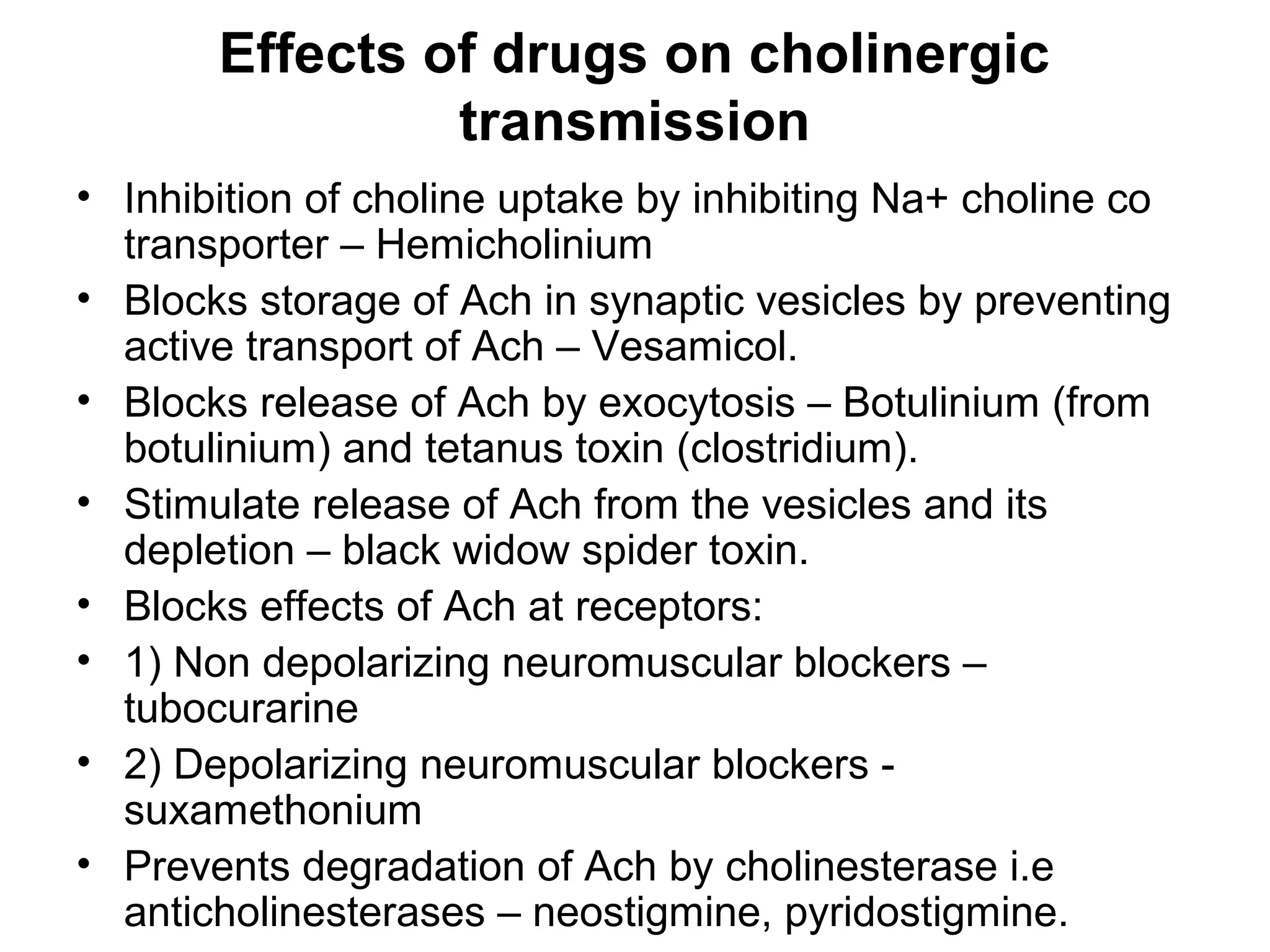
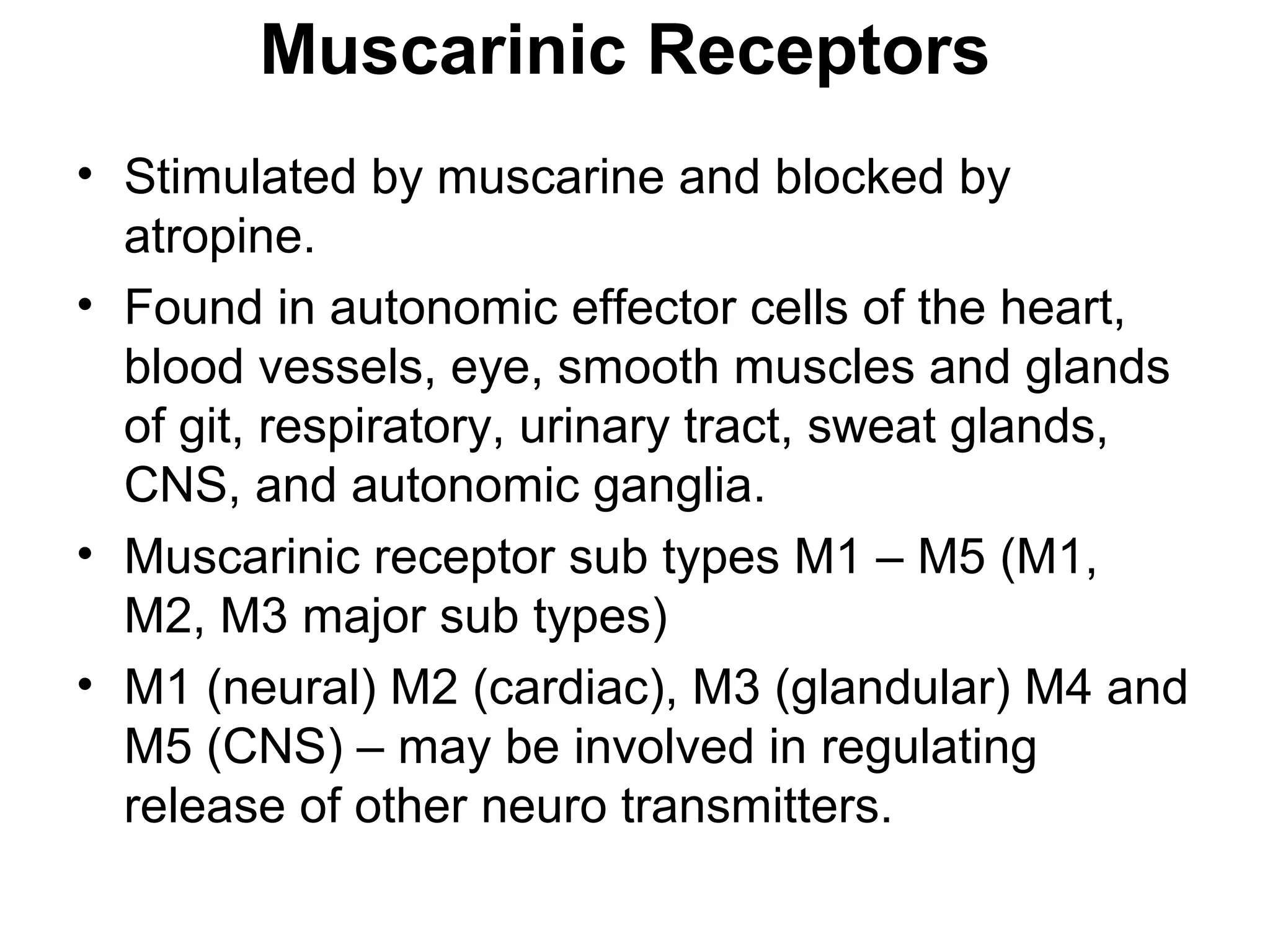
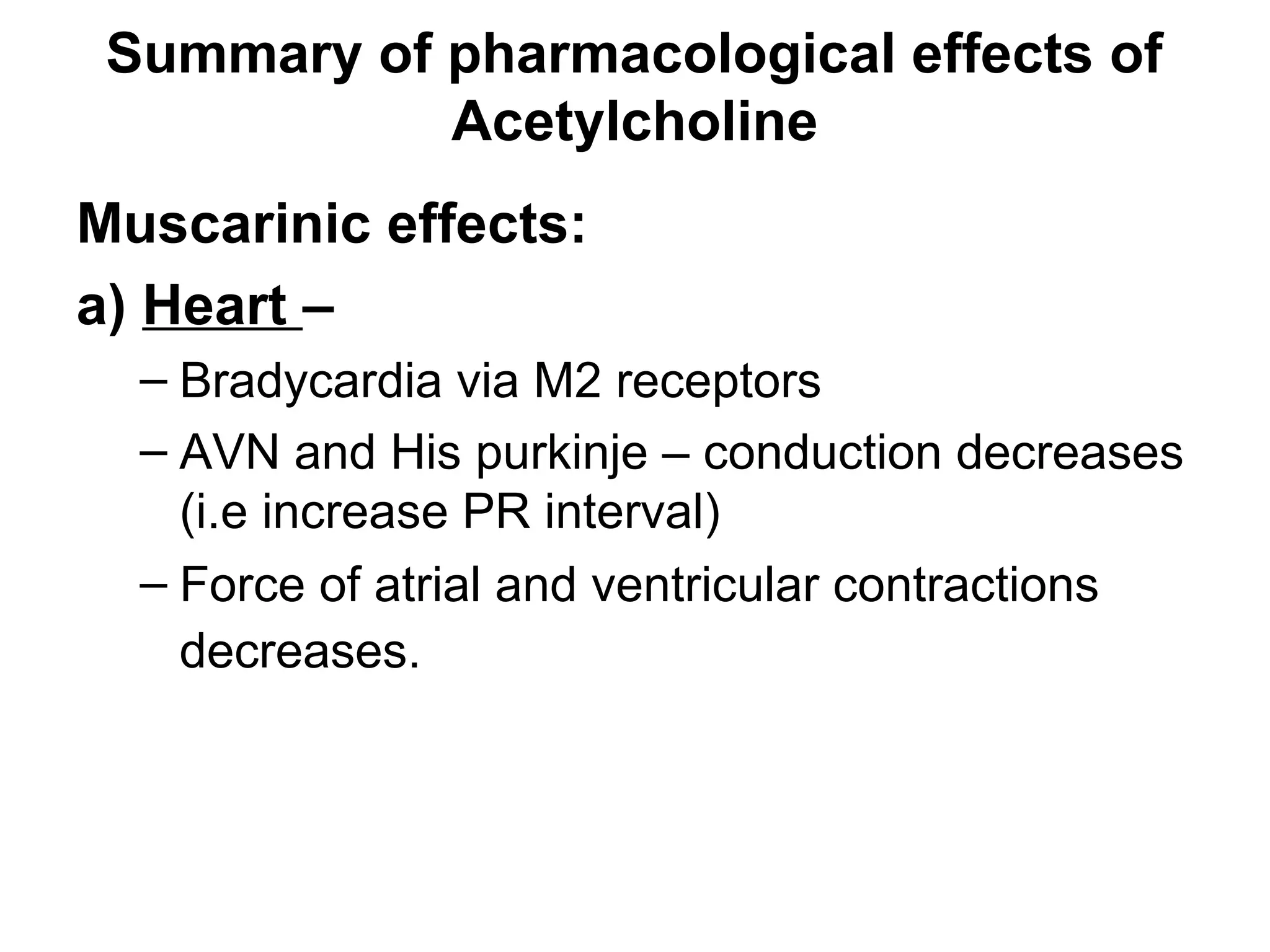
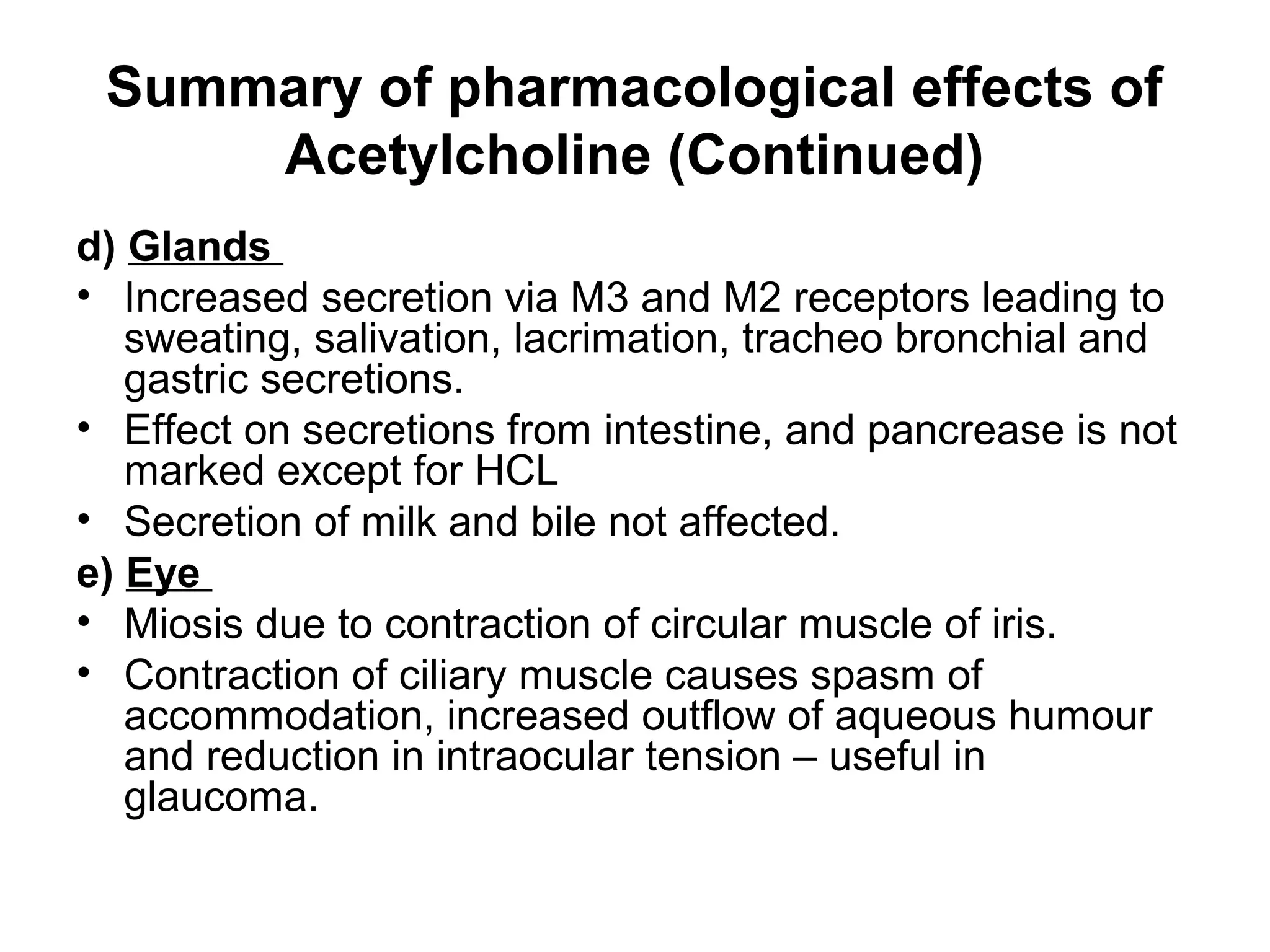
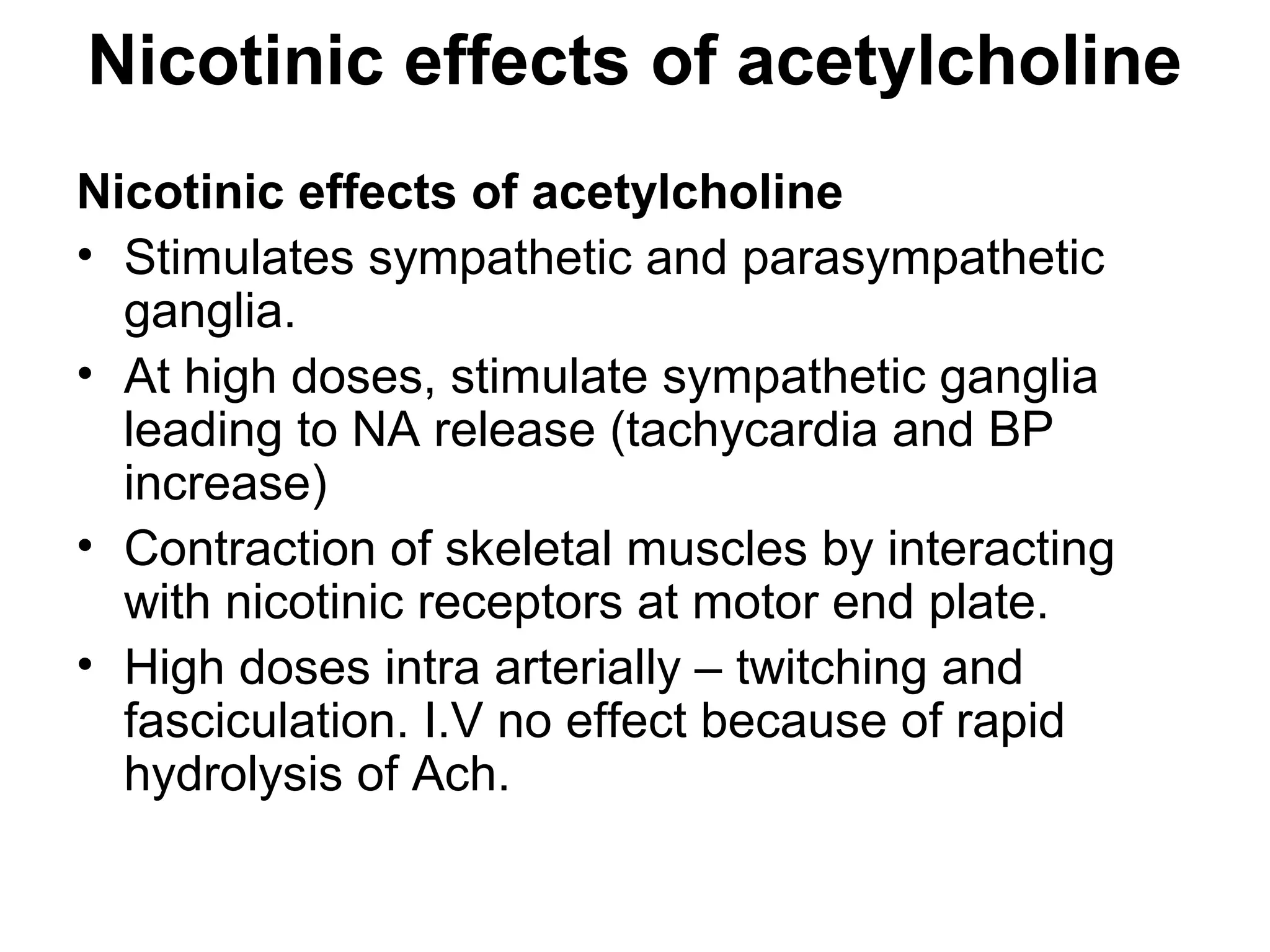
The document discusses the autonomic nervous system (ANS) and acetylcholine (Ach) neurotransmission. The ANS controls involuntary functions and is divided into the parasympathetic (PSN) and sympathetic (SNS) systems. Ach is the main neurotransmitter of the PSN and SNS. It binds to muscarinic and nicotinic receptors. Cholinergic drugs like anticholinesterases inhibit Ach breakdown, increasing its effects. They are used to treat conditions like myasthenia gravis but have side effects like excessive secretions. The document covers the synthesis, storage, release and effects of Ach in detail.