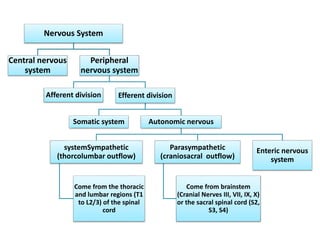
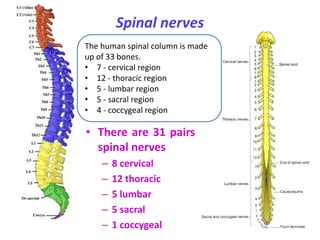
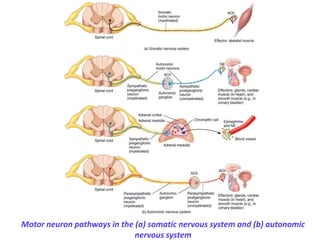
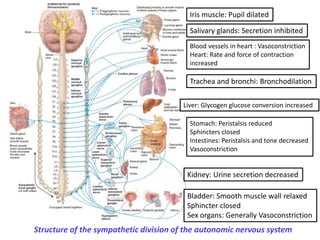
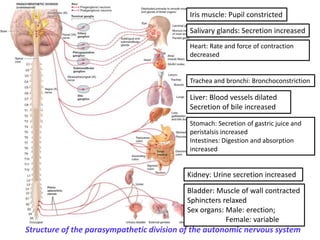
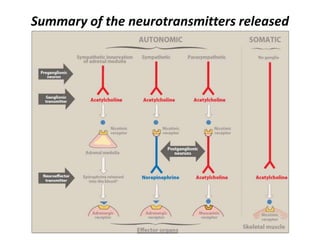
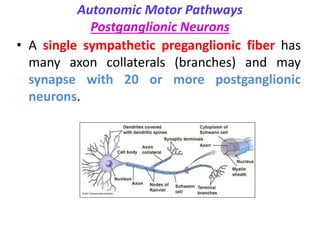
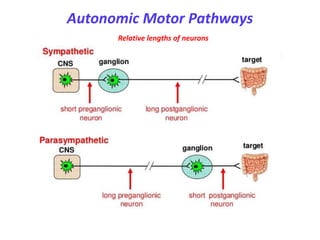
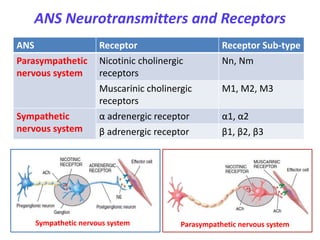
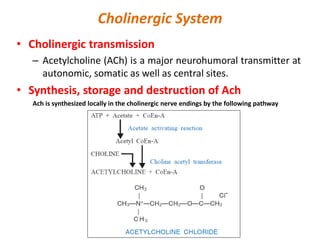
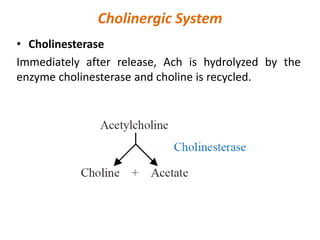
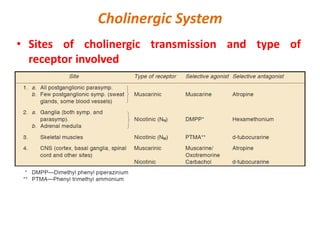
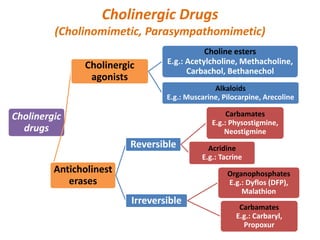
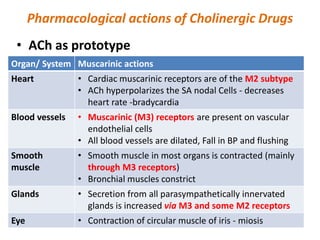
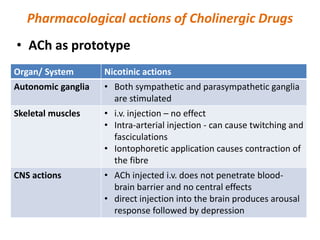
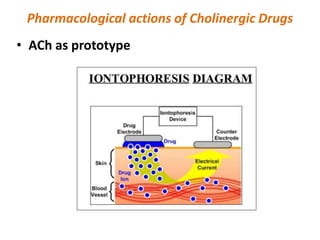
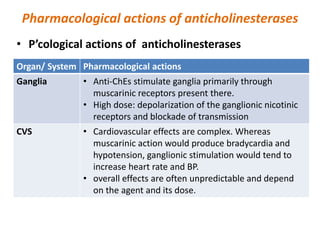
This document provides an introduction to autonomic pharmacology and discusses cholinergic and anticholinergic drugs. It describes the autonomic nervous system, including its sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. Cholinergic transmission is mediated by acetylcholine and hydrolyzed by cholinesterase. Cholinergic drugs such as acetylcholine act on muscarinic and nicotinic receptors to affect various organs. Anticholinesterases inhibit cholinesterase and amplify the effects of endogenous acetylcholine. They are used to treat conditions like glaucoma, myasthenia gravis, and postoperative ileus. Their overdose requires supportive care and antidotes like atropine.