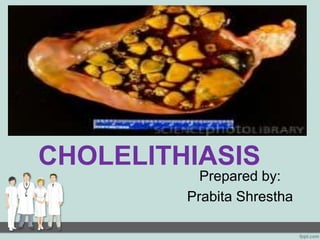
Cholelithiasis
- 2. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF GALL BLADDER: • Gallbladder is a muscular organ that serves as a reservoir for bile, present in most vertebrates. • In humans, it is a pear-shaped membranous sac on the undersurface of the right lobe of the liver just below the lower ribs. • It is generally about 7.5 cm (about 3 inch) long and 2.5 cm (1 inch) in diameter at its thickest part; it has a capacity varying from 1 to 1.5 fluid ounces. • The body (corpus) and neck (collum) of the gallbladder extend backward, upward, and to the left. The wide end (fundus) points downward and forward, sometimes extending slightly beyond the edge of the liver.
- 3. Contd… • Structurally, the gallbladder consists of an outer peritoneal coat (tunica serosa); a middle coat of fibrous tissue and unstriped muscle (tunica muscularis); and an inner mucous membrane coat (tunica mucosa). • The function of the gallbladder is to store bile, secreted by the liver and transmitted from that organ via the cystic and hepatic ducts, until it is needed in the digestive process. • The gallbladder, when functioning normally, empties through the biliary ducts into the duodenum to aid digestion by promoting peristalsis and absorption, preventing putrefaction, and emulsifying fat.
- 4. Introduction of cholelithiasis: • Cholelithiasis is the process of stone formation in the gall bladder. • Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gall bladder which can be acute and chronic and usually precipitated by gall stone impacted in the cystic duct, causing distension of the gall bladder. • Stones are made up of cholesterol, calcium bilirubinate, or a mixture caused by changes in the bile composition. • Gall stones can develop in the common bile duct, cystic duct, hepatic duct, small bile duct and pancreatic duct. Crystals can also form in the submucosa of the gall bladder causing widespread inflammation.
- 6. Contd… • Digestion of fat occurs mainly in the small intestine, by pancreatic enzymes called lipases. • The purpose of bile is to help the lipases to work, by emulsifying fat into smaller droplets to increase access for the enzymes, enable intake of fat, including fat-soluble vitamins: Vitamin A, D, E, and K, rid the body of surpluses and metabolic wastes cholesterol and bilirubin.
- 7. Contd: • Cholelithiasis is one of the very common health problems in Nepal and all over the world. • It is four times more common in women than in men. • It occurs frequently in middle ages or in old age group. • It is the most common disorder of the biliary tract. • It is more common in obese person, those who have diabetes mellitus and other endocrine problem.
- 8. Aetiology : Hereditary Diet pattern – especially excessive fatty consumption Obese person may be due to impaired fat metabolism Birth control period-alters hormone levels Multiple pregnancy Inflammation of biliary tract Stagnant bile in gall bladder
- 9. The following are more likely to develop gallstones: • Bone marrow or solid organ transplant • Diabetes • Failure of the gallbladder to empty bile properly (this is more likely to happen during pregnancy) • Liver cirrhosis and biliary tract infections (pigmented stones) • Medical conditions that cause the liver to make too much bilirubin, such as chronic hemolytic anemia, including sickle cell anemia • Rapid weight loss from eating a very low-calorie diet, or after bariatric surgery • Receiving nutrition through a vein for a long period of time.
- 10. Pathophysiology: • Gallstones are composed of cholesterol, bile salts, calcium, bilirubin and proteins. • However, the exact cause of gallstone formation is not clearly understood. • There are 3 specific factors which appear to contribute to the formation of gall stones.
- 11. metabolic disorders increased serum cholesterol cholesterol stones bilirubin stones calcium stones biliary stasis bile stagnates in gall bladder leading to excessive absorption of water causing precipitation of salts forms mixed stones of various sizes inflammation of biliary system causing bile constituents altered inflammed gall bladder mucosa absorbs more of bile acids resulting in reduced solubility of cholesterol CHOLELITHIASIS
- 12. Clinical features: Acute abdominal pain in right hypochondric region. Tachycardia Diaphoresis Nausea / vomiting Chills and rigor Jaundice Stool will be clay colored due to loss of urobilinogen. Dyspepsia Bilirubin will be excreted in urine. Sometimes a sausage – shaped mass may be felt when abdomen is palpated.
- 13. Investigations: A complete blood count is obtained routinely in patients suspected of cholelithiasis. CBC might serve as a preoperative lab test normally obtained in patients undergoing major surgery, such as laparoscopic cholecystectomy. An elevated white blood cell count alerts the clinician to the possibility of acute cholecystitis, a condition requiring more urgent treatment.
- 15. USG
- 20. Contd… CT Scan of Hepatobiliary system Cholecystography
- 21. Nutritional and supportive therapy Rest, IV fluids, NG suction, analgesic and antibiotic agents. Diet Pharmacological therapy Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) Chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) Non-surgical removal of gallstones Contact dissolution therapy Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy Medical management:
- 22. Surgical management: 1. Cholecystectomy: Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. It is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. Surgical options include the standard procedure, called laparoscopic cholecystectomy, and an older more invasive procedure, called open cholecystectomy. Its indications are: cholecystitis, biliary colic, risk factors for gall bladder cancer, and pancreatitis caused by gall stones. The most serious complication of cholecystectomy is damage to the common bile duct. This occurs in about 0.25% of cases.
- 24. 2. Intraoperative cholangiography and choledochoscopy: Intraoperative cholangiography is an examination of the bile ducts following administration of a radiopaque contrast medium during operation. Choledochoscopy is the direct visualization of the biliary tract with an endoscope through a t-tube or incision into the common bile duct. Small calculi can be removed from the common bile duct during this procedure. .
- 25. 3. Placement of a T-tube: In this procedure, T tube is placed in the common bile duct to decompress the biliary tree and allow access into the biliary tree postoperatively After an open cholecystectomy, a wopund drain removes exudates from the area formerly occupied by the gallbladder, and a T-tube diverts bile, which is still forming.
- 26. Nursing management: Assessment: Obtain history and demographic data that may indicate risk factors for biliary disease. Assess patient’s pain for location, description, intensity, relieving and exacerbating factors. Assess for signs of dehydration: dry mucous membranes, poor skin turgor, low urine output with elevated specific gravity. Assess sclera and skin for jaundice Monitor temparature and WBC for indications of infection.
- 27. Nursing diagnosis: 1. Acute Pain related to: biological trauma obstruction / spasm tract inflammatory processes, ischemia / tissue necrosis. 2. Risk for Deficient Fluid Volume related to: Increase in gastric fluid loss: vomiting, gastric distention Treatment has the effect of reducing the fluid. The freezing process
- 28. 3. Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements related to: Risk factors that affect: Imposed on themselves and given limited food, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, pain. Loss of nutrients, affect digestion due to disturbance / narrowing of the bile duct. 4. Deficient Knowledge: about prognosis and treatment needs related to: Re asking about information. Information misinterpretation. Have not / do not know the source of information
- 29. Nursing Interventions • Place the patient in low Fowler’s position. • Provide intravenous fluids and nasogastric suction. • Provide water and other fluids and soft diet, after bowel sounds return. • Instruct the patient to use a pillow to splint incision. • Administer analgesic agents as ordered. • Remind patient to expand lungs fully to prevent atelectasis. • Promote early ambulation. • Monitor elderly and obese patients most closely for respiratory problems,
- 30. • Place drainage bag in patient’s pocket when ambulating. • Observe for indications of infection, leakage of bile, or obstruction of bile drainage. • Observe for jaundice. • Note and report right upper quadrant pain, nausea, and vomiting. • Change dressing frequently, using ointment to protect skin from irritation
- 31. Evaluation: expected outcomes • Verbalizes reduced pain level • Tolerate oral fluids and solid fluids; adequate urine output
- 32. References: 1. Lippincott, Manual Of Nursing Practice, 8th Edition, Page No. : 709-712 2. Lippincott, Atlas Of Pathophysiology, 2nd Edition, Page No. : 162- 163 3. HLMC, Textbook of Adult Nursing, 1st Edition, Page No. : 7-9, Page No. : 97-100 4. Brunner and Suddarth’s, Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10th Edition, Page No. :1115-1119 5. Dr. Sudeep K. Yadav, A Book On Pathophysiology, 2nd Edition, Page No. : 130-135 6. http://spareyourtummy.wordpress.com/2012/05/23/cholelithi asis/
