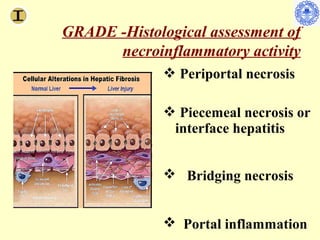
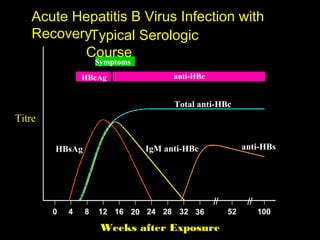
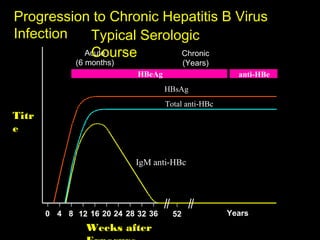
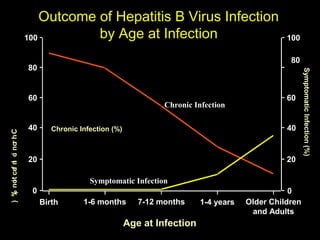
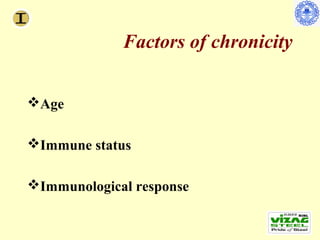
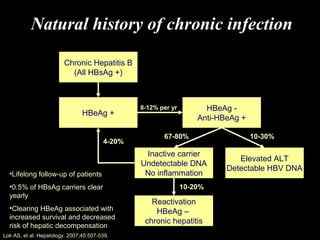
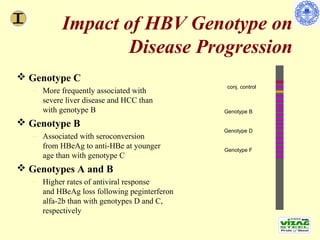
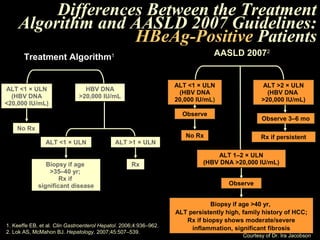
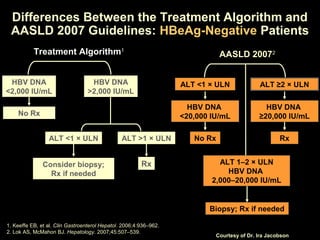
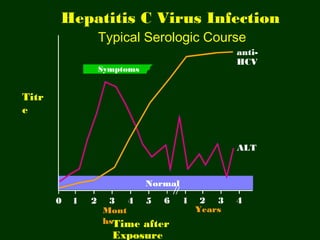
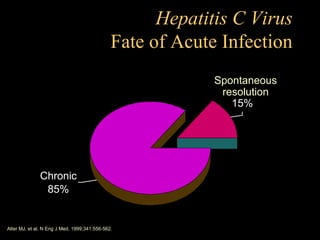
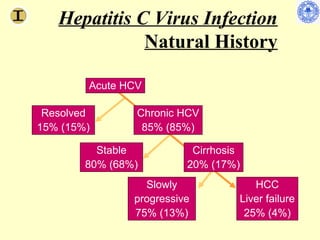
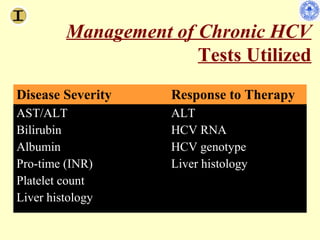
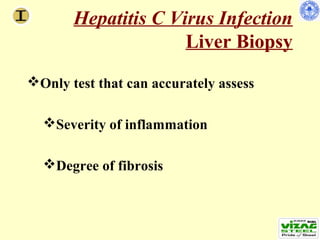
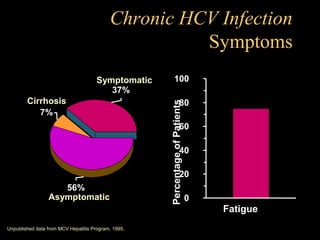
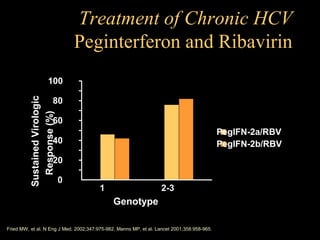
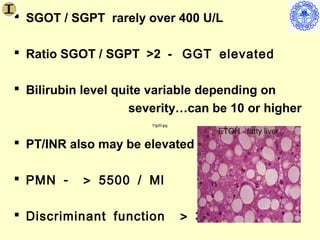
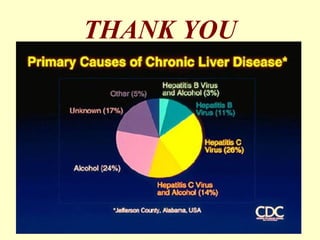
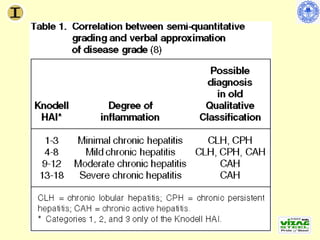
Chronic hepatitis refers to ongoing liver inflammation that persists for over 6 months. It can be caused by hepatitis B or C viruses, autoimmune conditions, drugs, alcohol, or genetic disorders. Diagnosis involves blood tests showing elevated liver enzymes and dysfunction. Histopathological grading assesses necrosis and staging evaluates fibrosis progression which can lead to cirrhosis. Chronic hepatitis B infection may be HBeAg positive or negative and natural history depends on factors like viral genotype and host immunity. Treatment algorithms consider liver enzyme levels and biopsy findings to determine if antiviral therapy is needed.