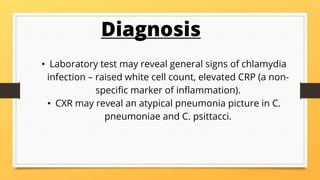
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted bacterial infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis. It is most prevalent in sexually active young men and women aged 15-25. The bacteria have a unique developmental cycle where they exist in both extra- and intracellular forms. While often asymptomatic, chlamydia infections can cause lymphogranuloma venereum, infant pneumonia, and urinary tract infections if left untreated. Diagnosis involves laboratory tests to detect signs of infection. Treatment consists of antibiotics like doxycycline or azithromycin. Abstaining from sex or using condoms can help prevent spreading chlamydia to partners.