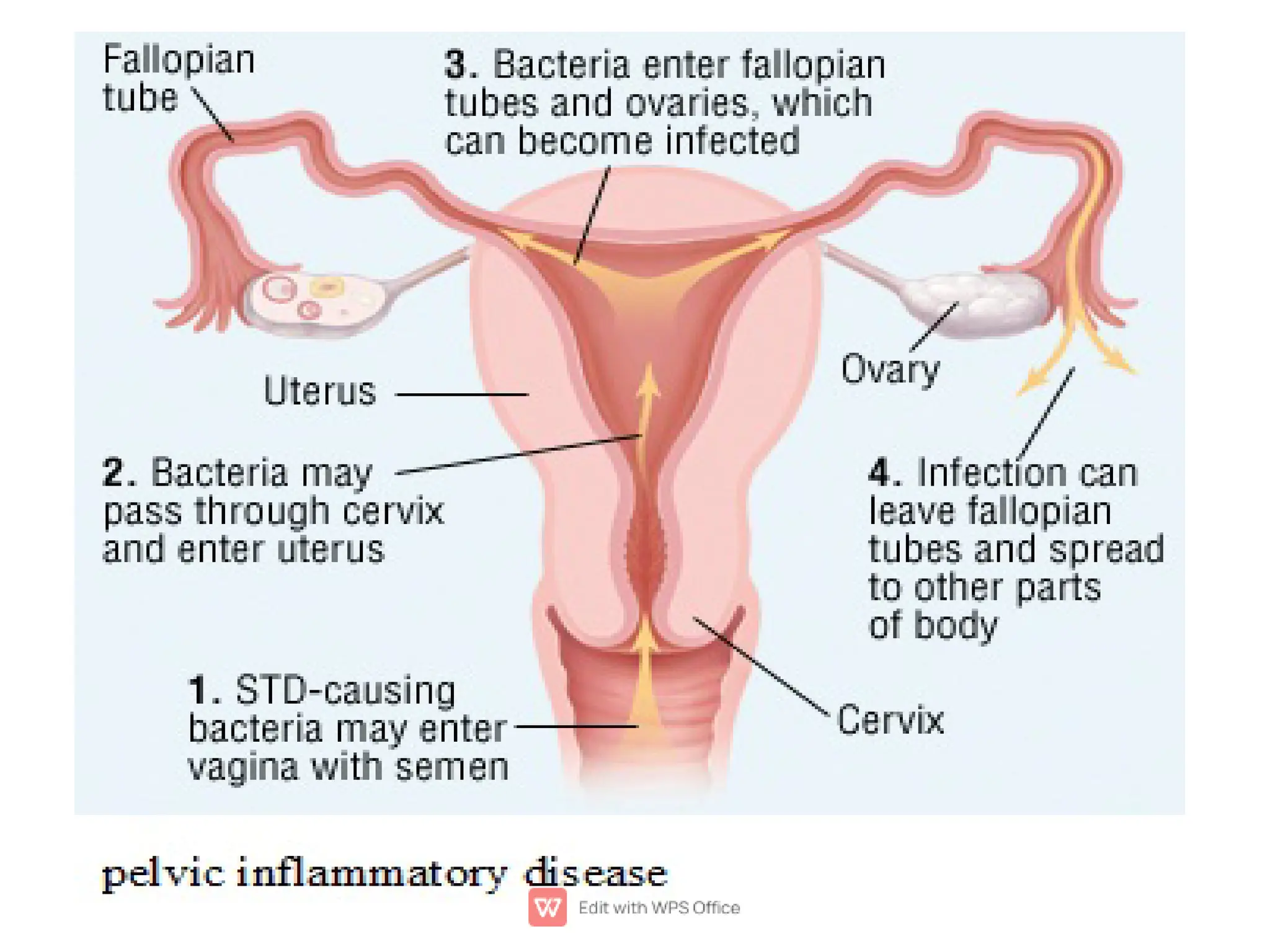
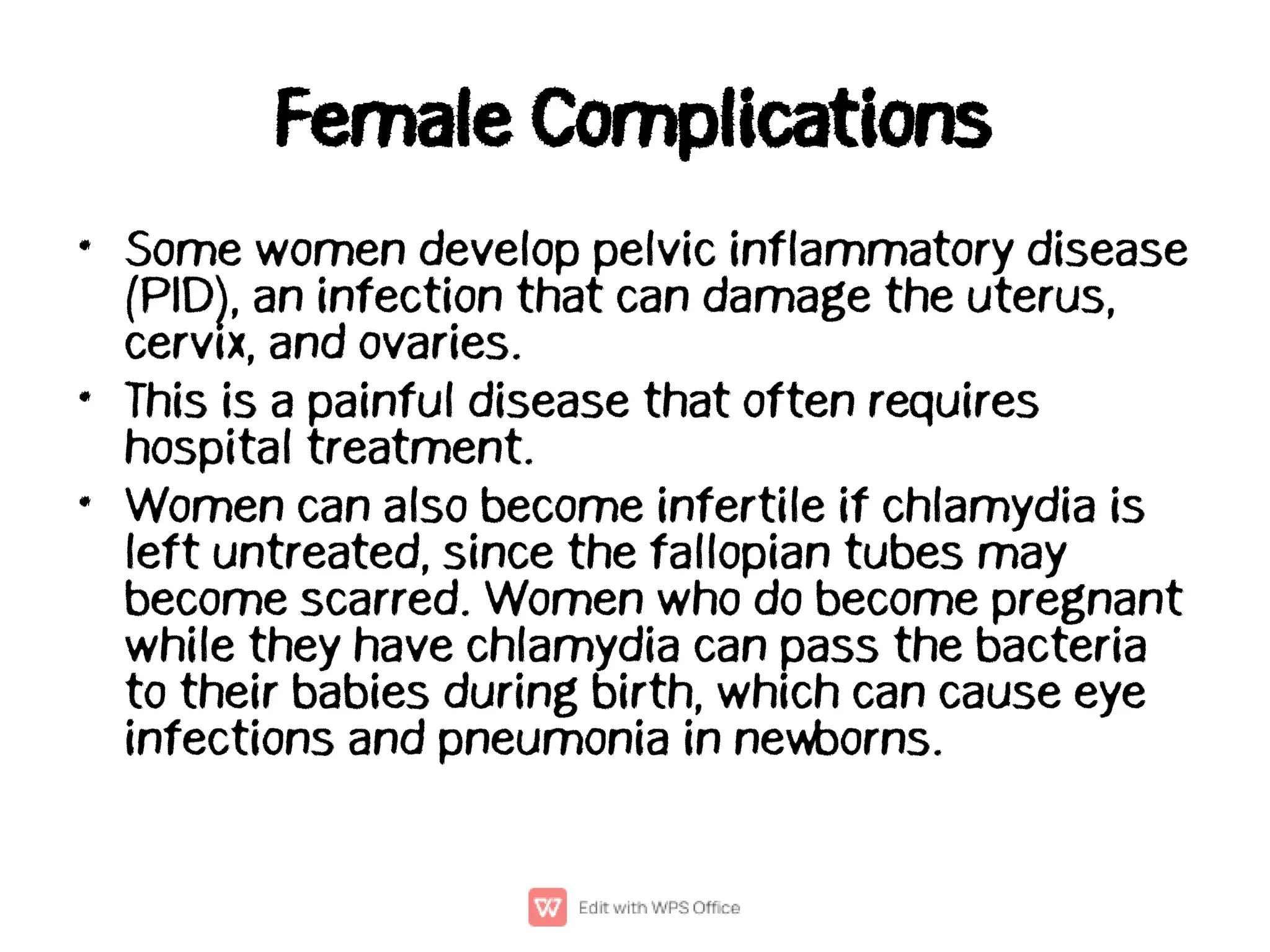
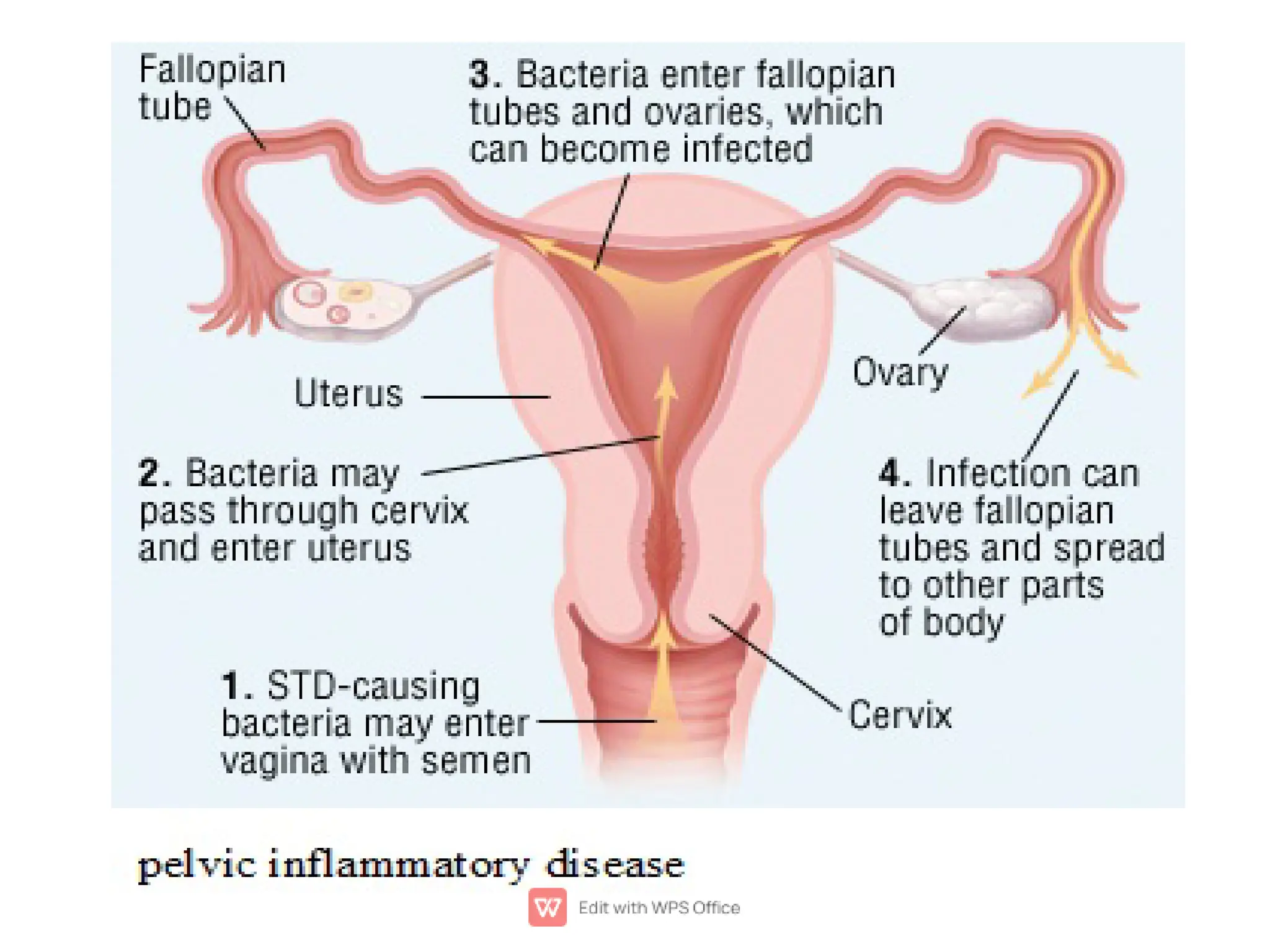
Chlamydia, caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis, is a common sexually transmitted infection affecting millions, particularly women under 25. Many infected individuals may not exhibit symptoms, making timely testing and treatment crucial to prevent complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility in women or epididymitis in men. Prevention strategies include limiting sexual partners and using condoms during intercourse.