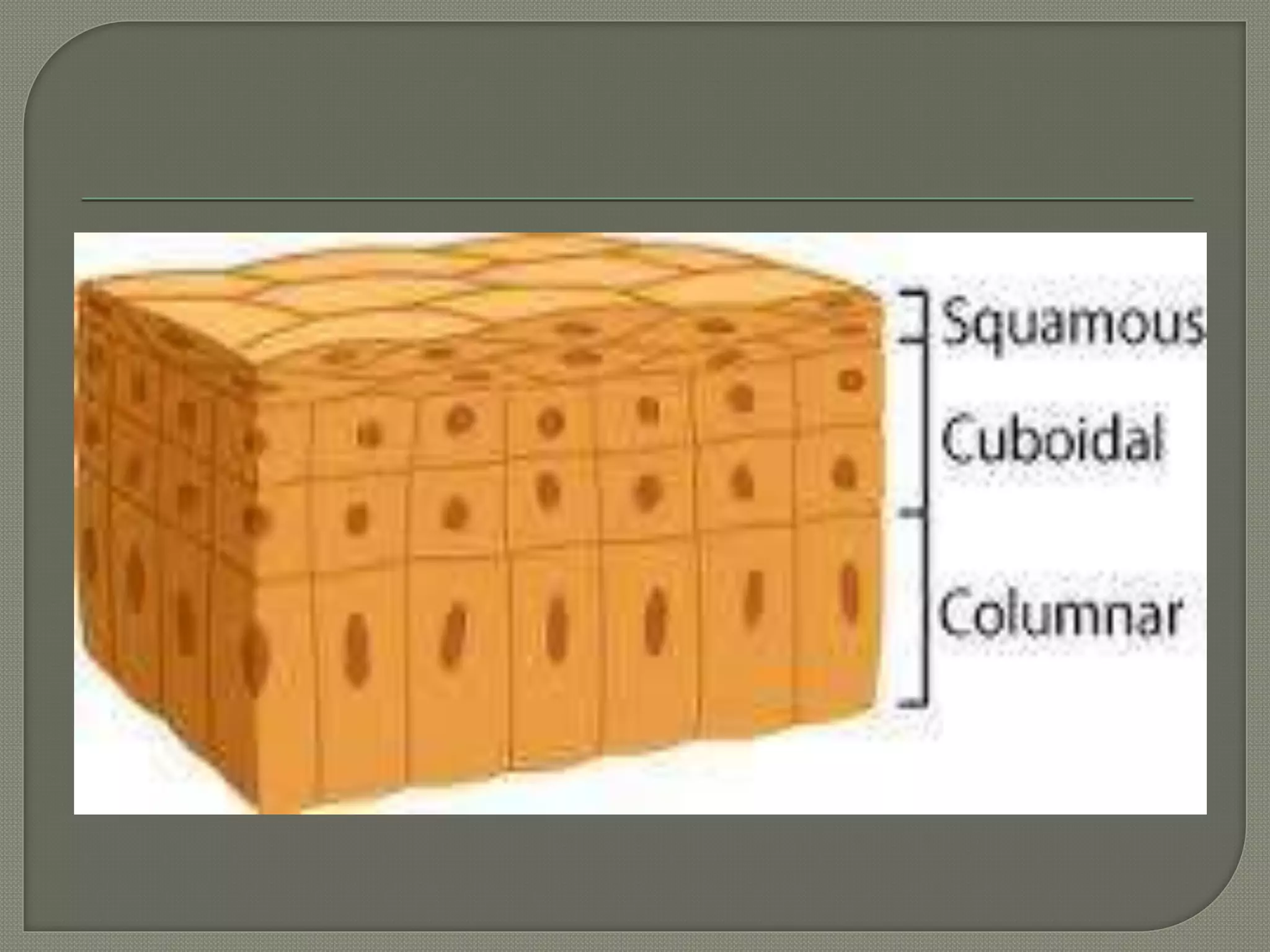
Chlamydia is a highly transmissible infection caused by chlamydia bacteria, primarily affecting the cervix, urethra, vagina, and rectum, often remaining asymptomatic. Transmission occurs through sexual contact, and screening is recommended for sexually active women under 25 and pregnant women, with antibiotics such as azithromycin or doxycycline used for treatment. Testing methods include nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) for greater sensitivity, though some traditional methods like culture are still referenced.