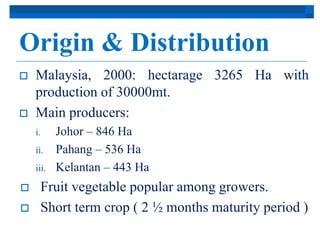
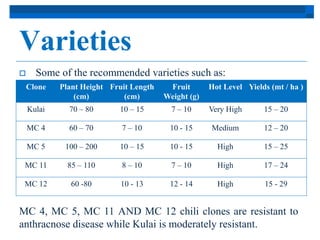
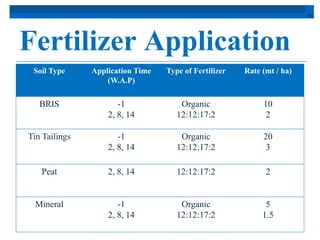
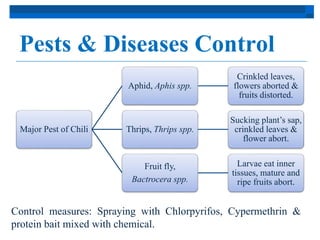
Chili originated in Mexico and South America and was spread by Spain to Asia, where it was incorporated into local cuisines. In Malaysia, chili is popular among growers as a short-term crop, with the main producing states being Johor, Pahang, and Kelantan. Chili varieties like Kulai, MC4, MC5, MC11, and MC12 are recommended for their yields and disease resistance. Chili is grown through seed propagation and transplanting seedlings, with regular maintenance including fertilizing, pest and disease control, and harvesting based on maturity levels.