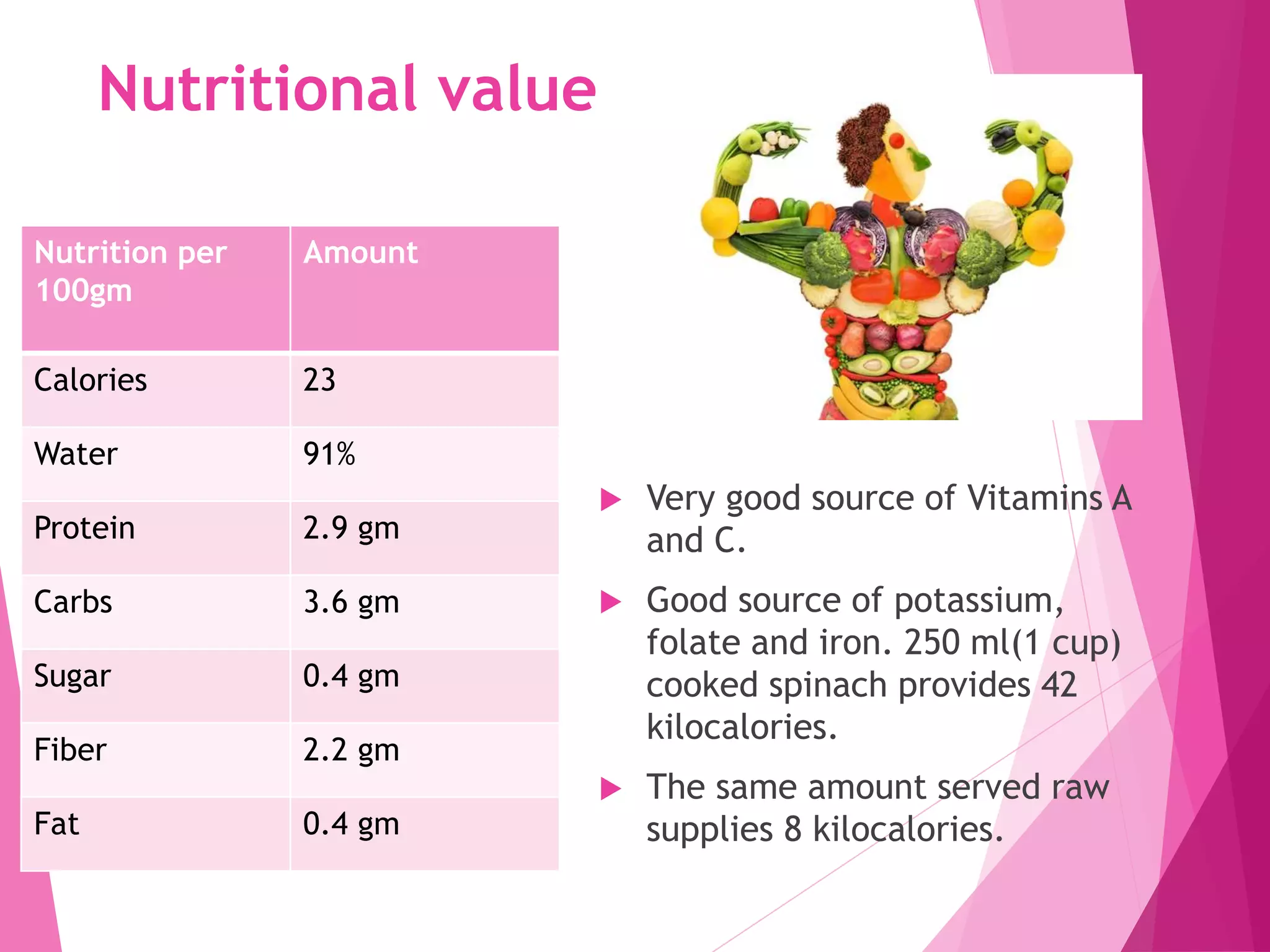
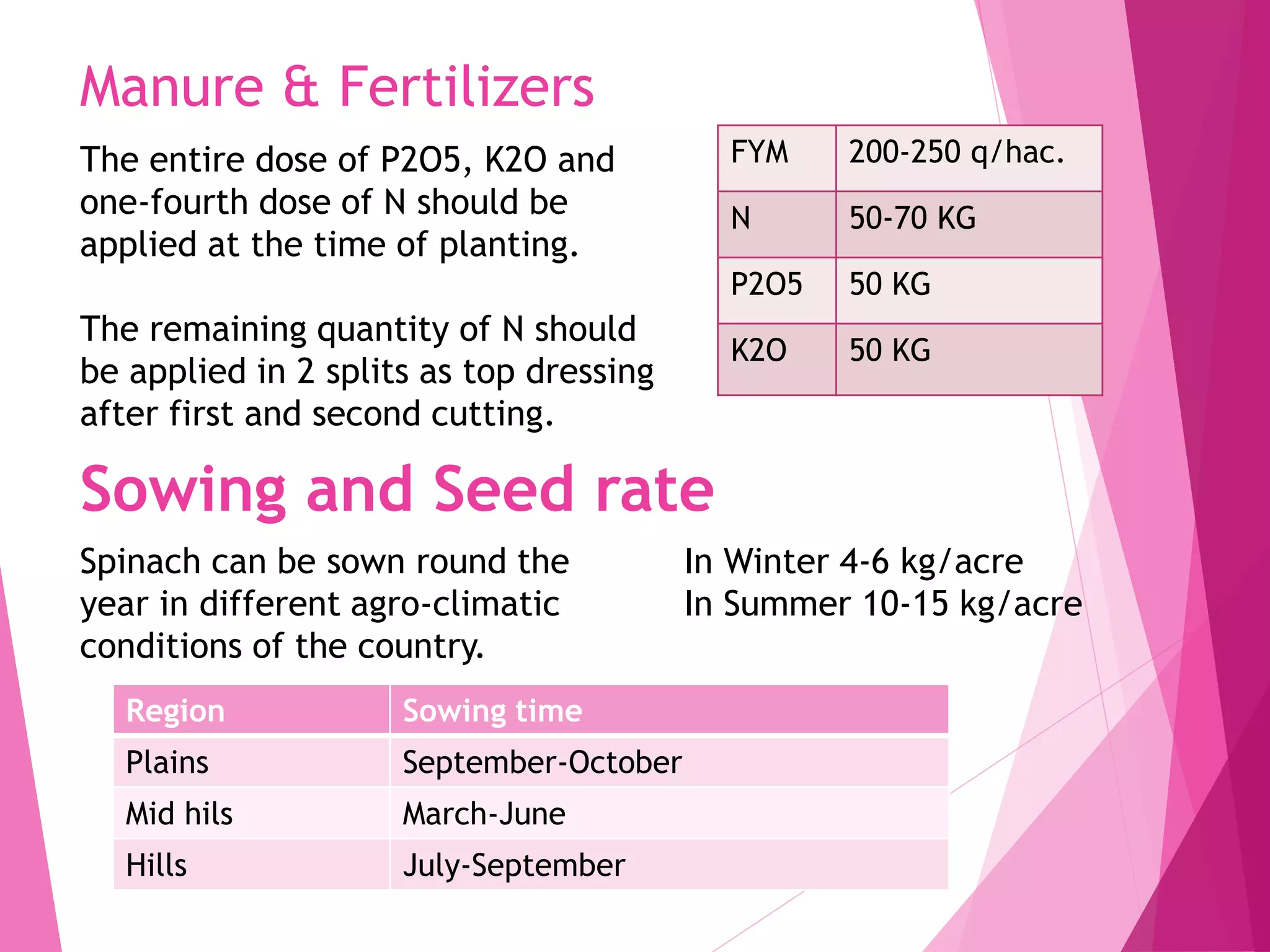
Spinach is a cool season vegetable crop that originated in Iran and was spread to Europe by Arabs and North America in the 1800s. It is a good source of vitamins A and C, potassium, folate, and iron. There are two main varieties - Virginia Savoy which has large, blistered dark green leaves and Early Smooth Leaf with thin yellowish-green leaves. Spinach grows best in temperatures between 15-25°C and requires well-drained soil, frequent irrigation, and weed control. It can be harvested 3-4 weeks after sowing and yields 4-5 cuttings before bolting occurs in warmer conditions.