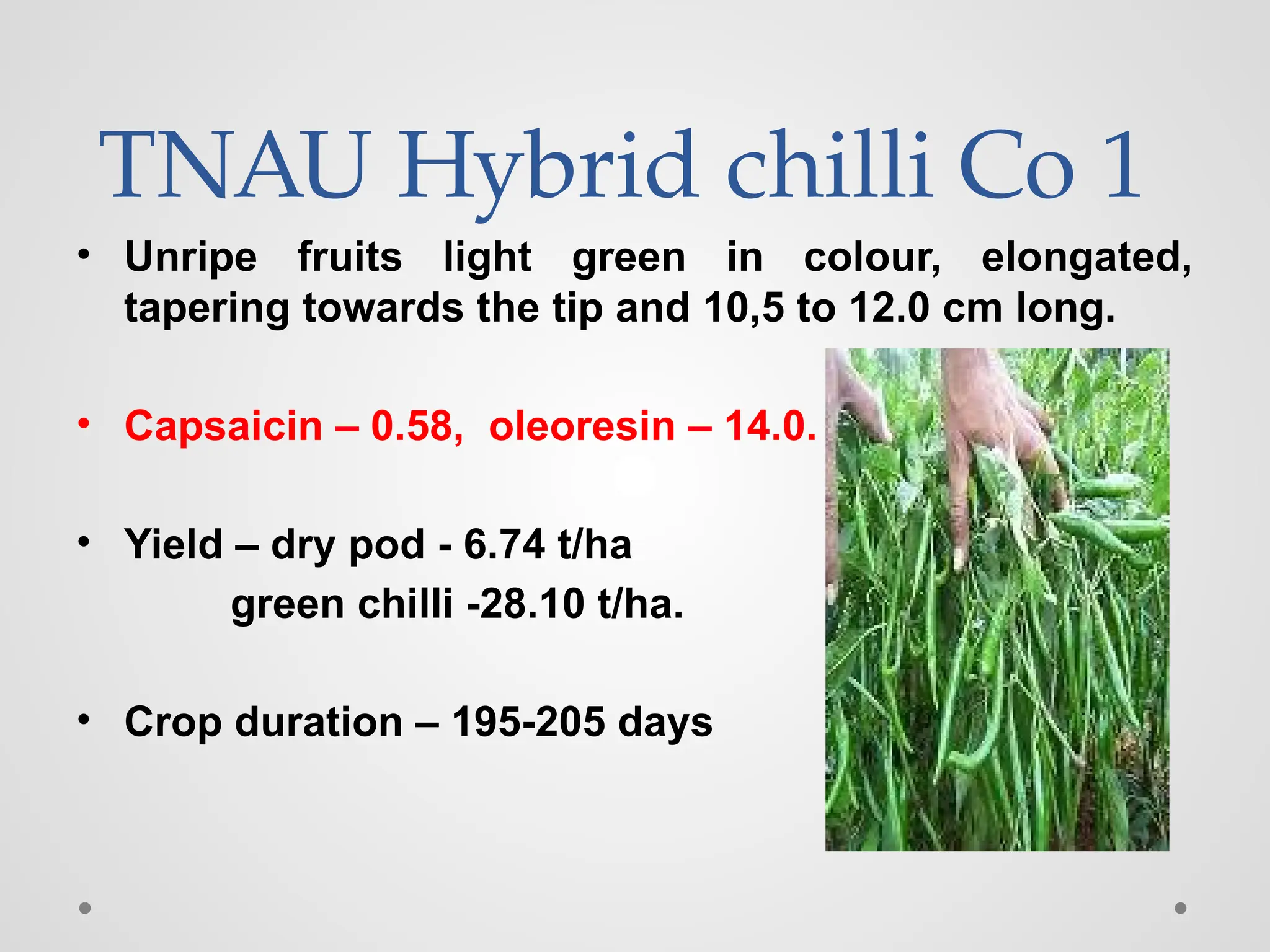
The document discusses the production technology of chilli (Capsicum annum L.), highlighting its origin, significance in kitchens, and the increasing demand in the pharmaceutical industry. It covers various cultivars in India, their characteristics, management practices from sowing to harvest, and pest and disease control measures. Additionally, it includes guidance on soil preparation, planting, irrigation, and fertilization to optimize yield.