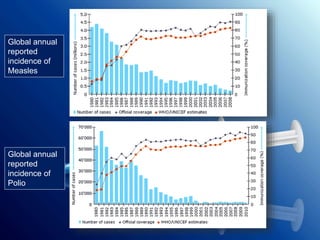
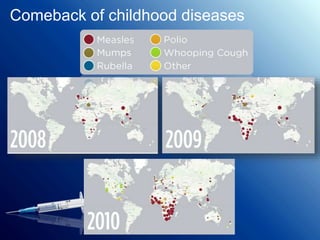
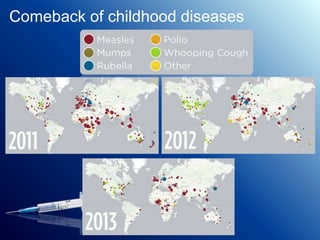
Immunization protects children from deadly diseases by making their immune systems resistant. It has saved millions of lives through vaccines for diseases like smallpox, polio, measles and more. Vaccines work by exposing the body to a weakened or dead form of the disease so the immune system can build defenses. While very safe, they come with minor side effects like soreness or fever in some cases. Maintaining high global vaccination rates keeps diseases from returning and spreading to new populations.




![Types of Vaccines
Type of Vaccine Description
Live attenuated vaccines
[eg. Mumps, rubella, chickenpox]
• Contain modified version of the living microbe
that has been weakened in the lab so it can’t
cause disease
Inactivated Viral or Bacterial vaccine
[eg. ]
• More stable and safer than live vaccines
• Stimulate weaker immune system response
Subunit vaccines • Include only the antigens that best stimulate
the immune system
• Adverse reactions to the vaccine lower
Toxoid vaccines • Used when a bacterial toxin is main cause of
illness
Conjugate vaccines • Used to get around problem of polysaccharide
coatings
DNA vaccines • Take vaccines to a new technological level
• Dispense with both the whole organism and
its parts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/744fff47-eda5-4c42-9a83-26605c6ccb07-160904064620/85/Childhood-Immunization-7-320.jpg)






![Influenza [flu] throughout History
• Spanish Influenza: 1918 – 1919
• Illness and mortality rates high among young adults
• Waves of infection spread fast through nations and continents
• Killed approx. 50 million people worldwide
• Asian Influenza: 1957 -1958
• Surfaced in China
• Killed approx. 2 million
• Hong Kong Flu: 1968 – 1969
• Spread from Asia to North America
• Vaccine made but not produced early enough
• Avian Flu Threat 1997 – present
• Virus passed from birds to humans
• Number of people did die
• H1N1 Influenza: 2009
• First appeared in Mexico and spread to US
• Virus origin from pigs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/744fff47-eda5-4c42-9a83-26605c6ccb07-160904064620/85/Childhood-Immunization-18-320.jpg)

![Dubai Health Authority [DHA] –
Immunization Guidelines
• Routes of Administrating Vaccines
– Intradermal injections
• Delivered into dermis (top layer of skin)
– Subcutaneous injections
• needle given in top layers of skin
• area of insertion does not need to be rubbed or moved
– Intramuscular injections
• given in muscle tissue below the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of skin
• area of insertion does need to be rubbed and moved to make sure the liquid
does not stay in one area](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/744fff47-eda5-4c42-9a83-26605c6ccb07-160904064620/85/Childhood-Immunization-20-320.jpg)