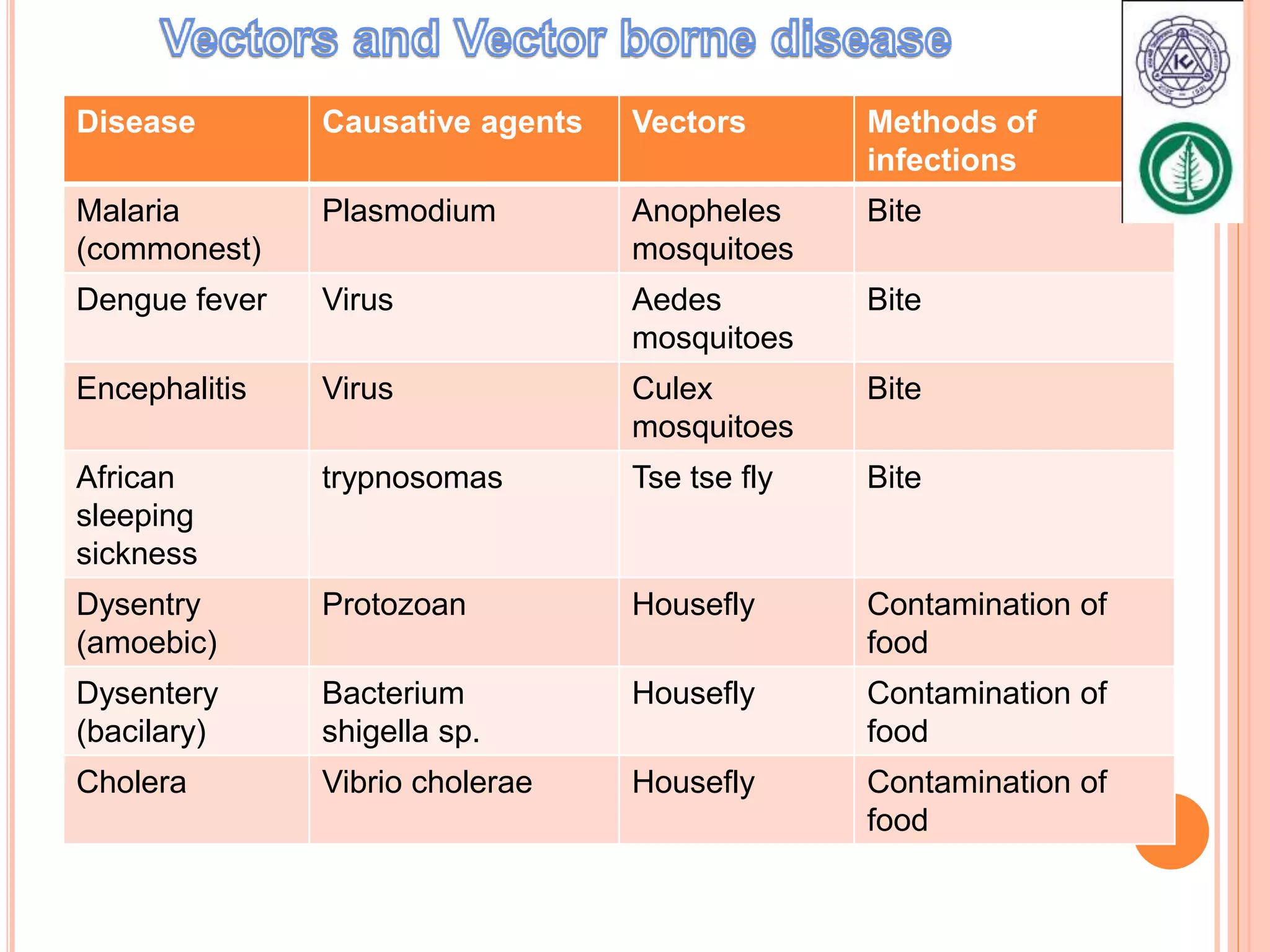
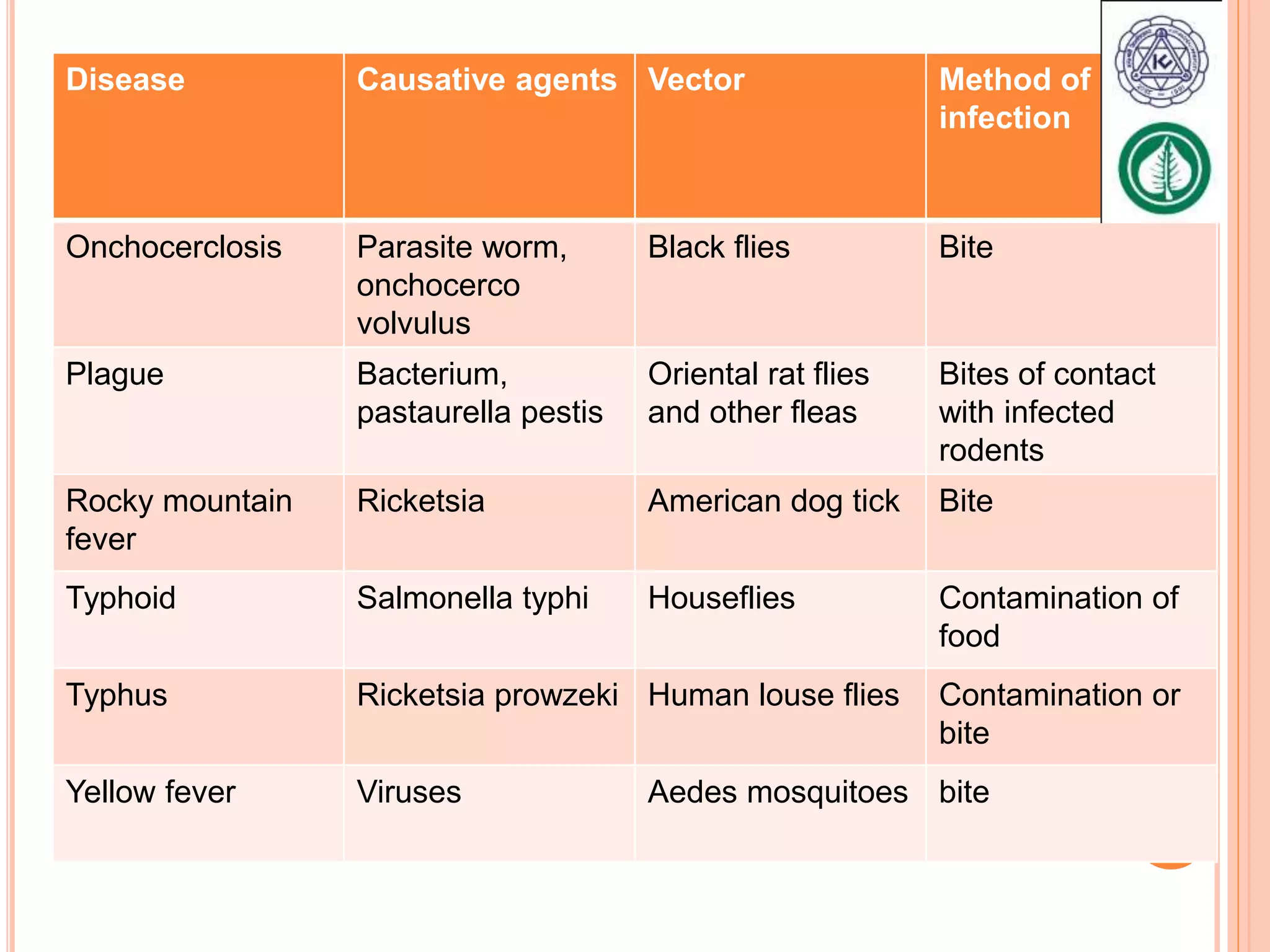
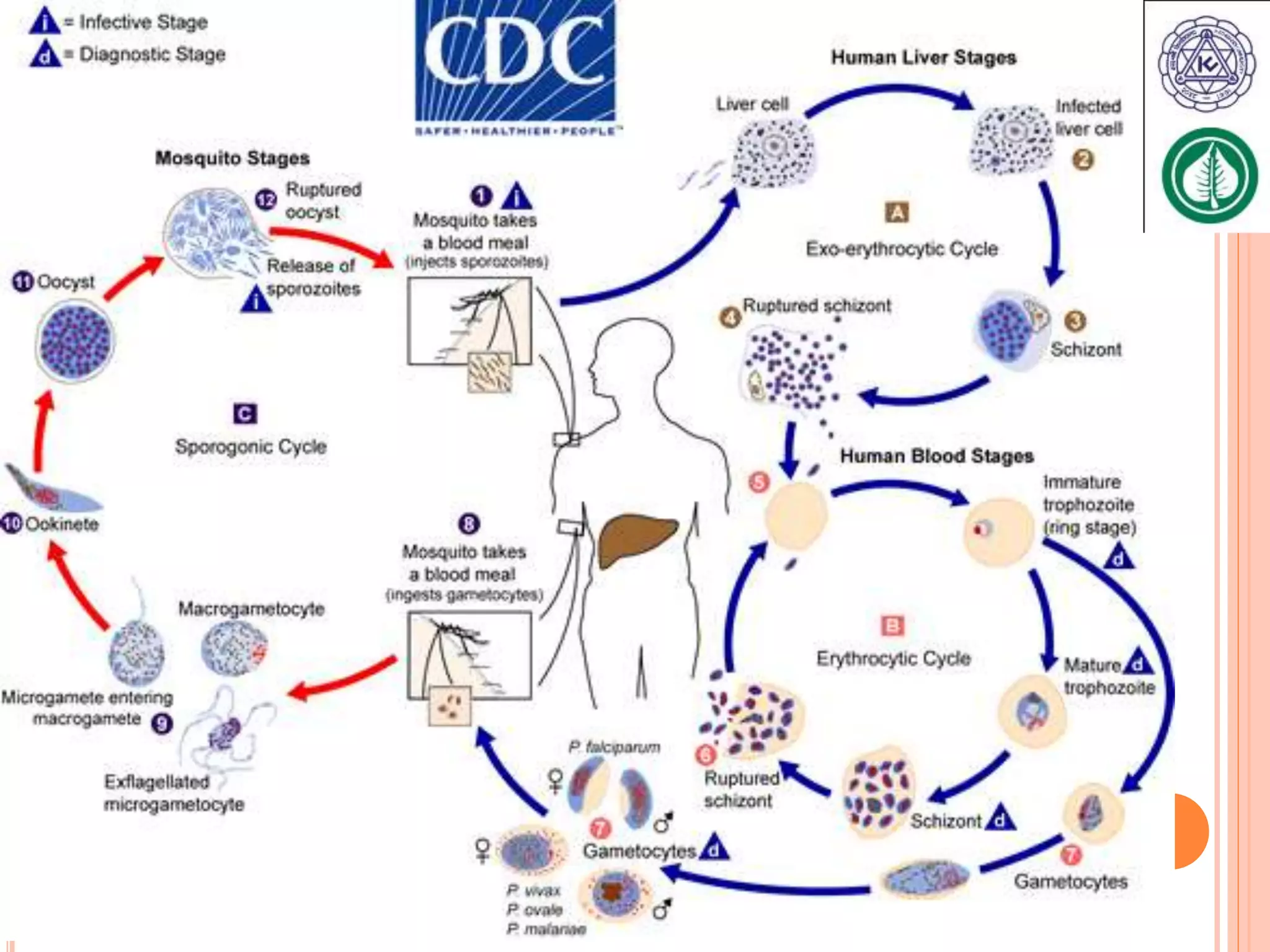
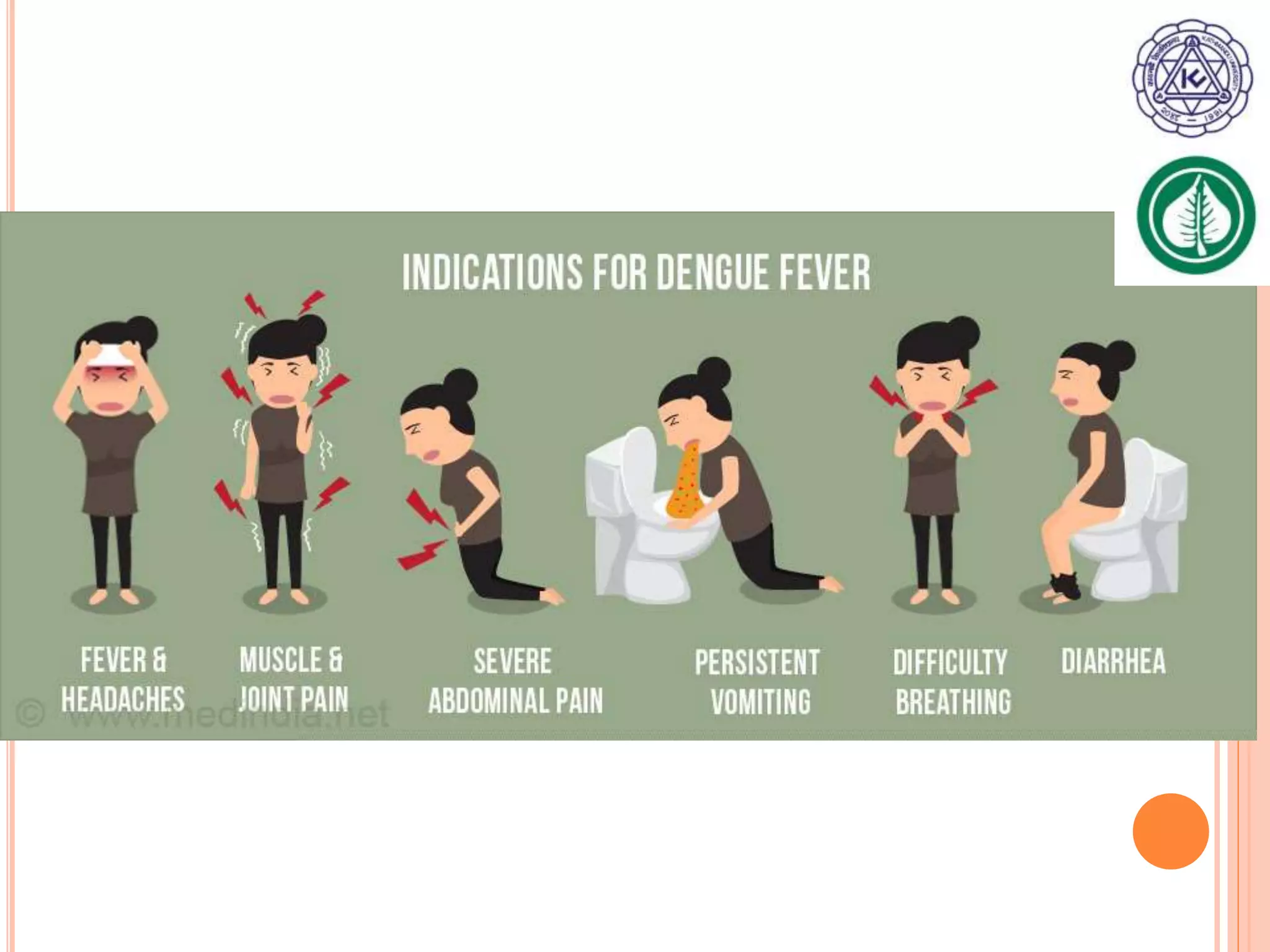
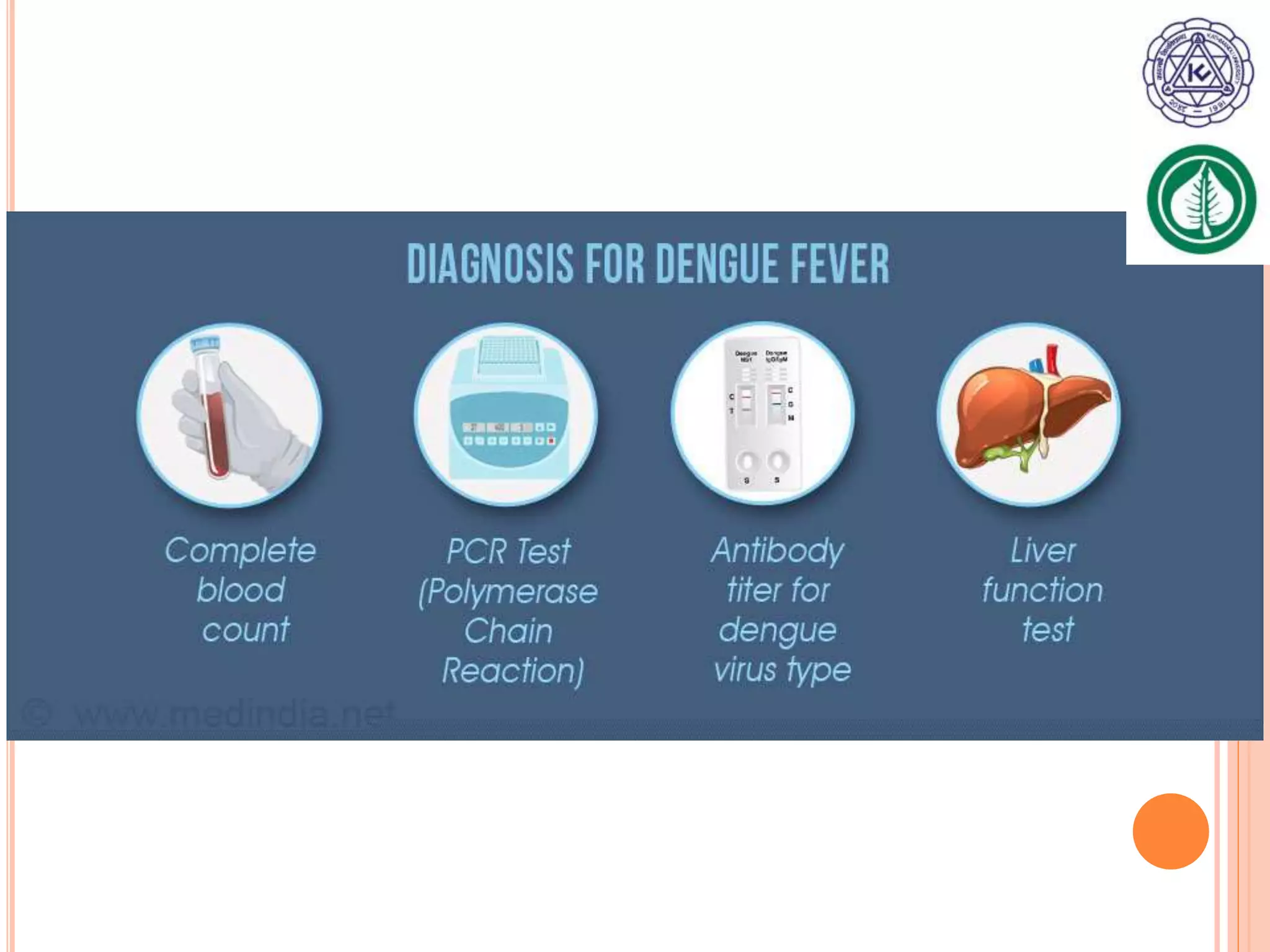
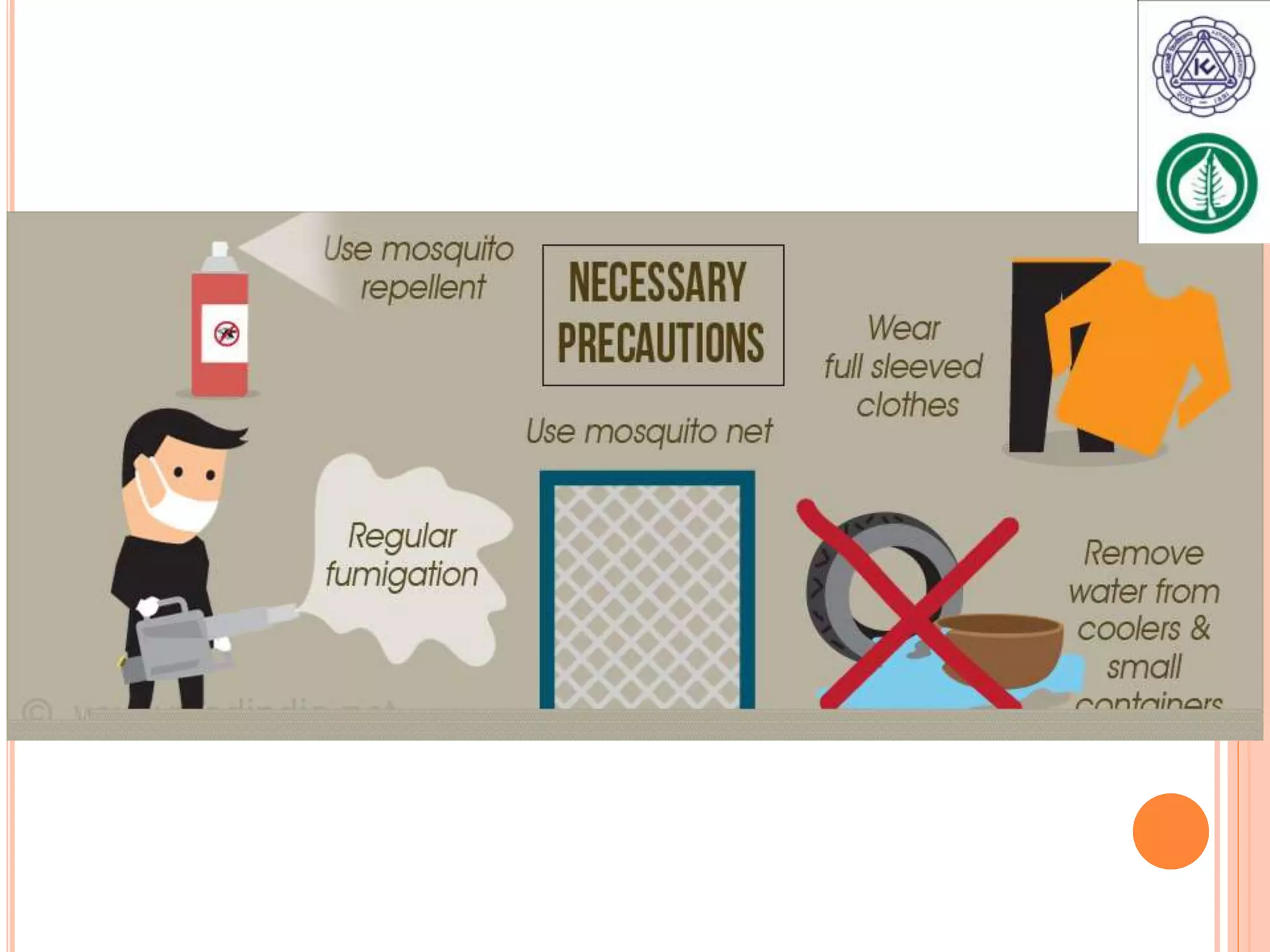
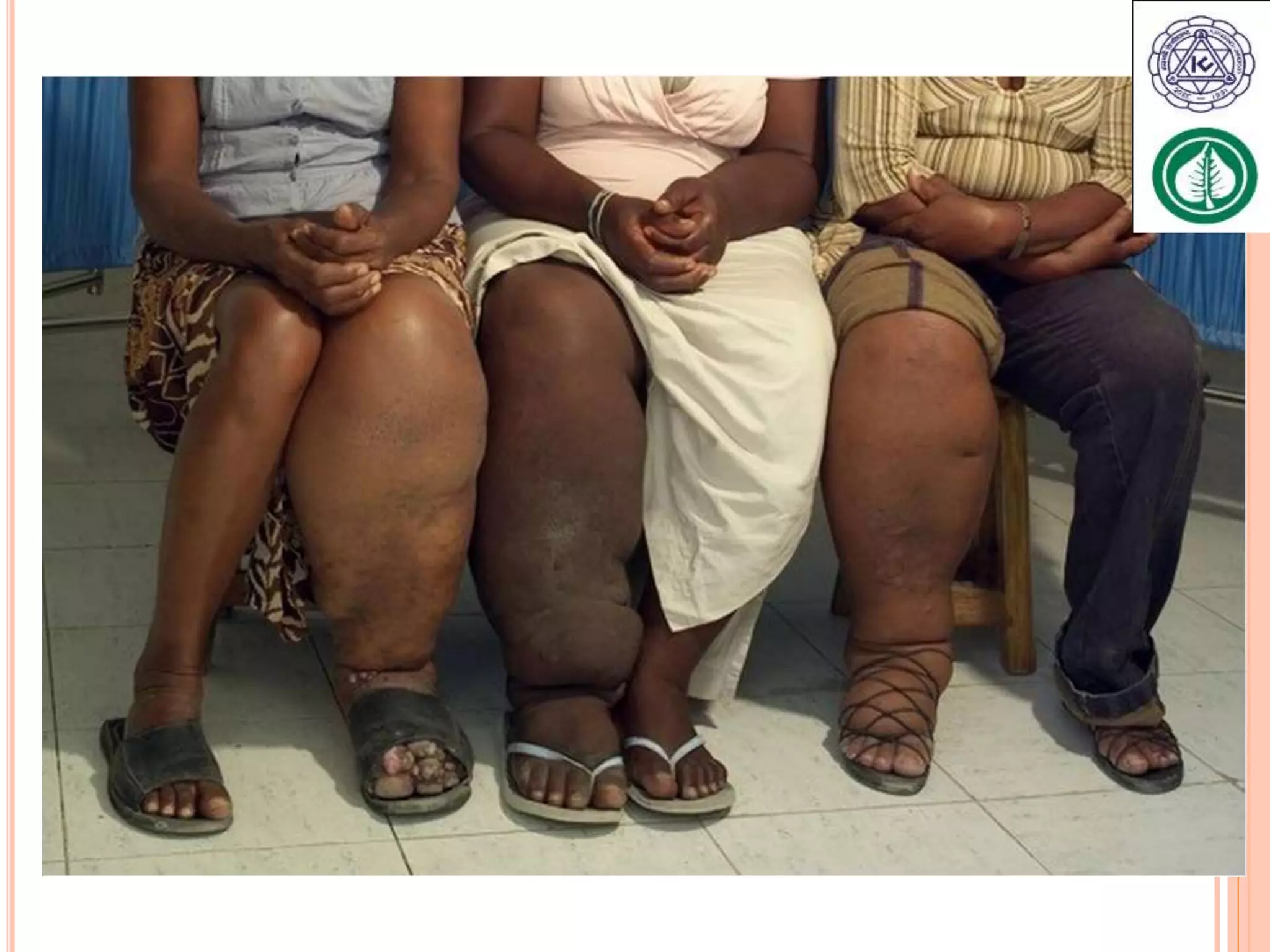
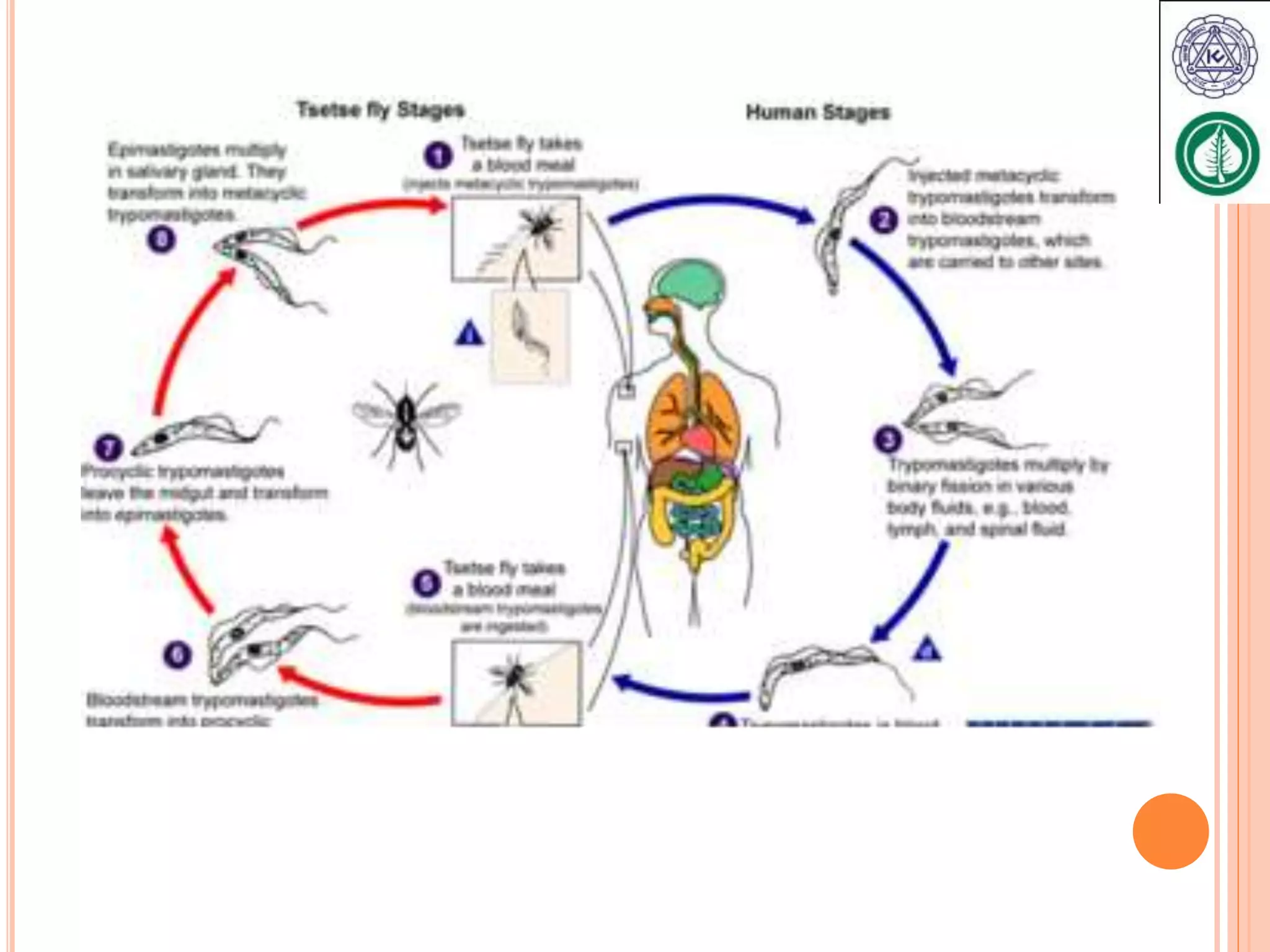
Vector borne diseases are caused by pathogens transmitted via the bite or contact with arthropods like insects and arachnids. The document outlines the major vector borne diseases according to the type of vector, including mosquito-borne diseases like malaria and dengue, fly-borne diseases such as African sleeping sickness, lice-borne typhus, flea-borne plague, and tick-borne Rocky Mountain spotted fever and Lyme disease. It provides details on the causative agents, hosts, methods of transmission, symptoms, and control measures for many of these important diseases.