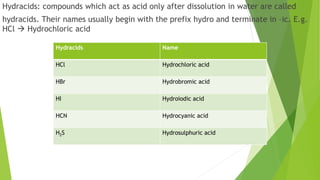
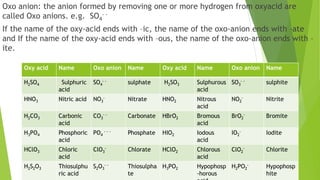
The document serves as an introductory class on chemistry at Trinity College, detailing its importance and scope, including core concepts such as atoms, molecules, and ions. It explains the difference between atomic and molecular mass along with naming compounds, and it provides examples of various chemical compounds and their formulas. Additionally, it includes homework assignments related to calculating atomic and molecular masses and naming different compound types.