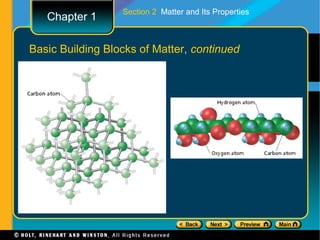
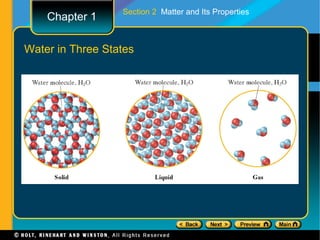
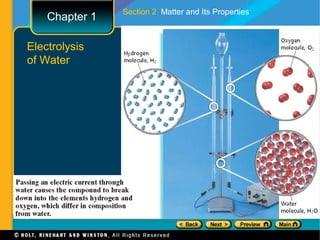
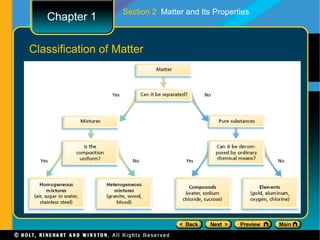
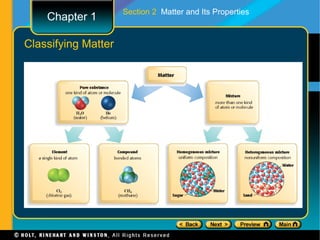
The document covers different topics relating to matter and its properties including the basic building blocks of matter such as atoms and elements, physical and chemical properties, physical and chemical changes, different states of matter, classifying matter as pure substances or mixtures, and energy changes that occur during physical and chemical changes. Key concepts discussed include properties of matter, the structure of atoms and molecules, distinguishing between physical and chemical changes, and classifying different types of mixtures and pure substances.