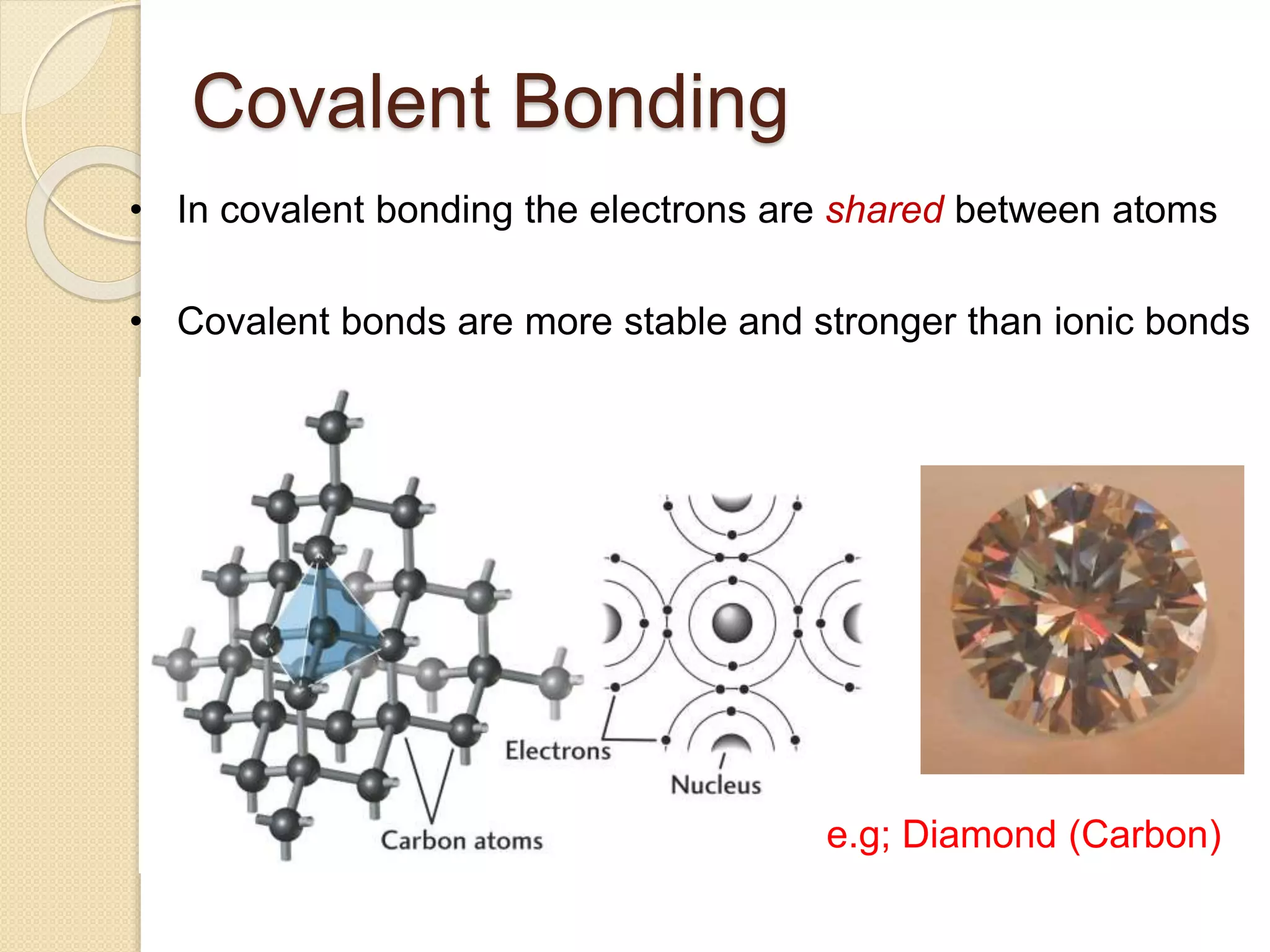
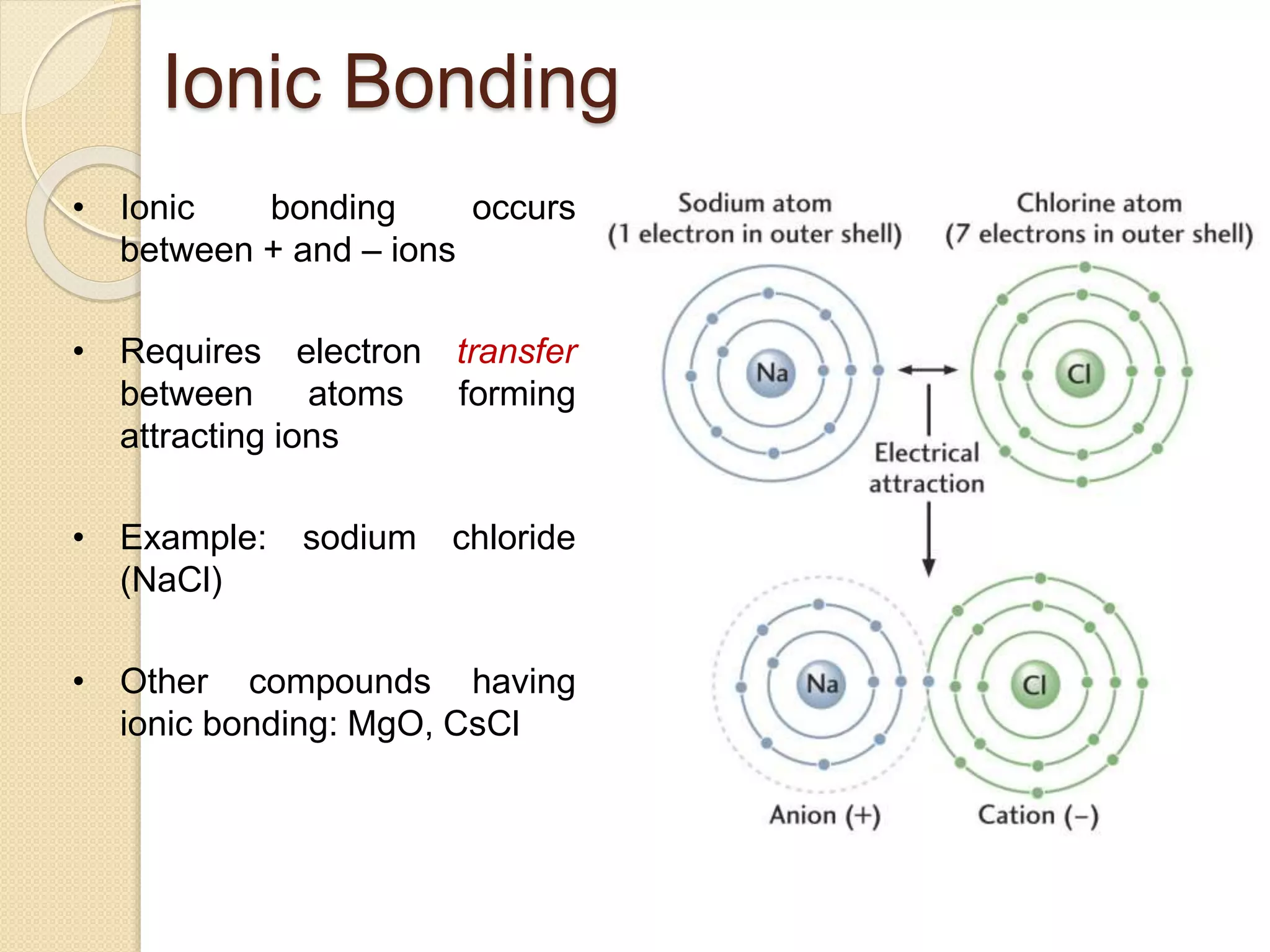
This document provides information about Material Technology 1 course offered by PN. Norhazlina Bte Amon. The course covers topics like material structure, binary alloy systems, ferrous materials, metal working processes, corrosion and non-ferrous metals over 18 weeks. Students will be assessed through quizzes, theory tests and other tasks like end of chapter exercises and presentations.