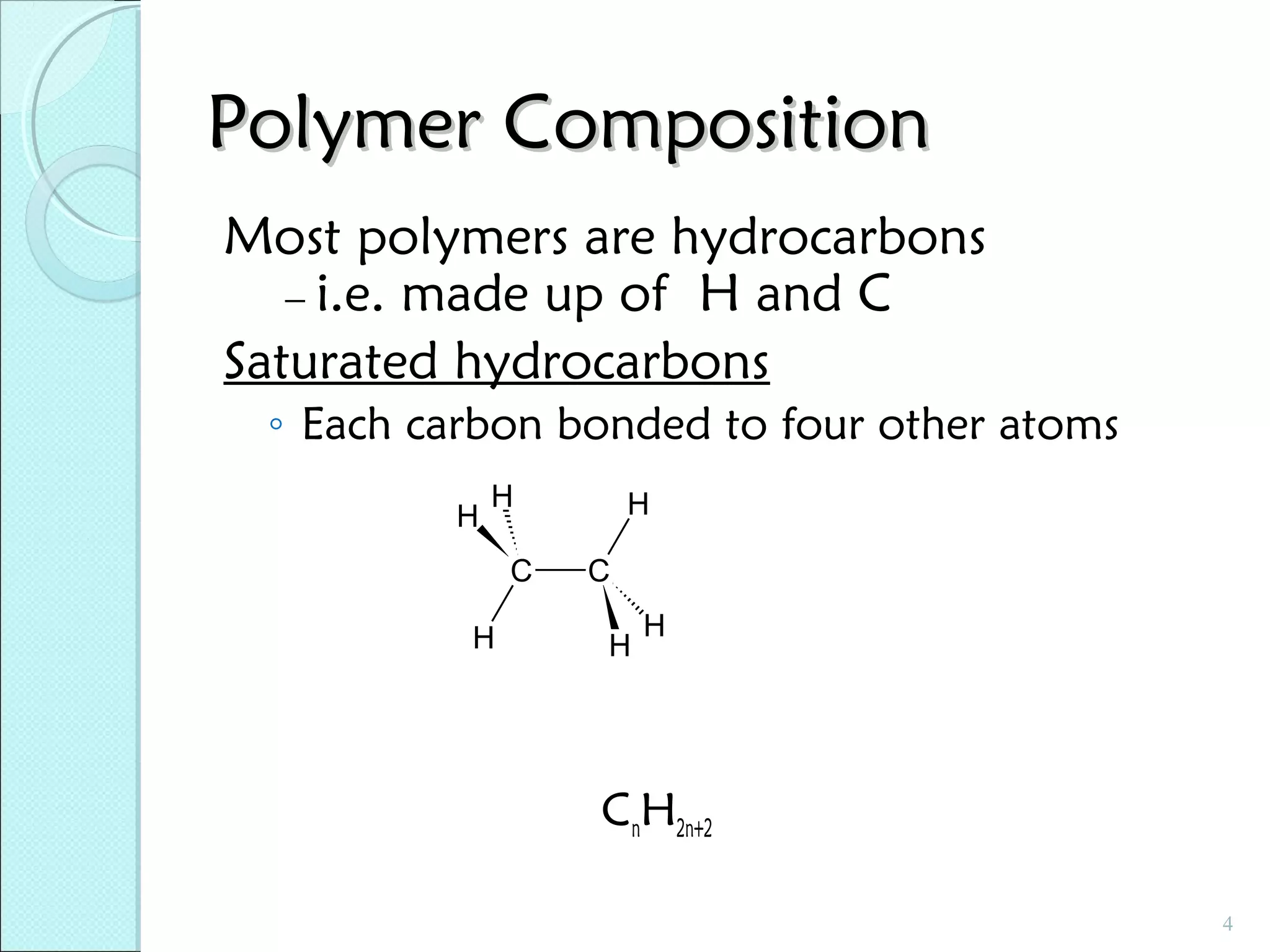
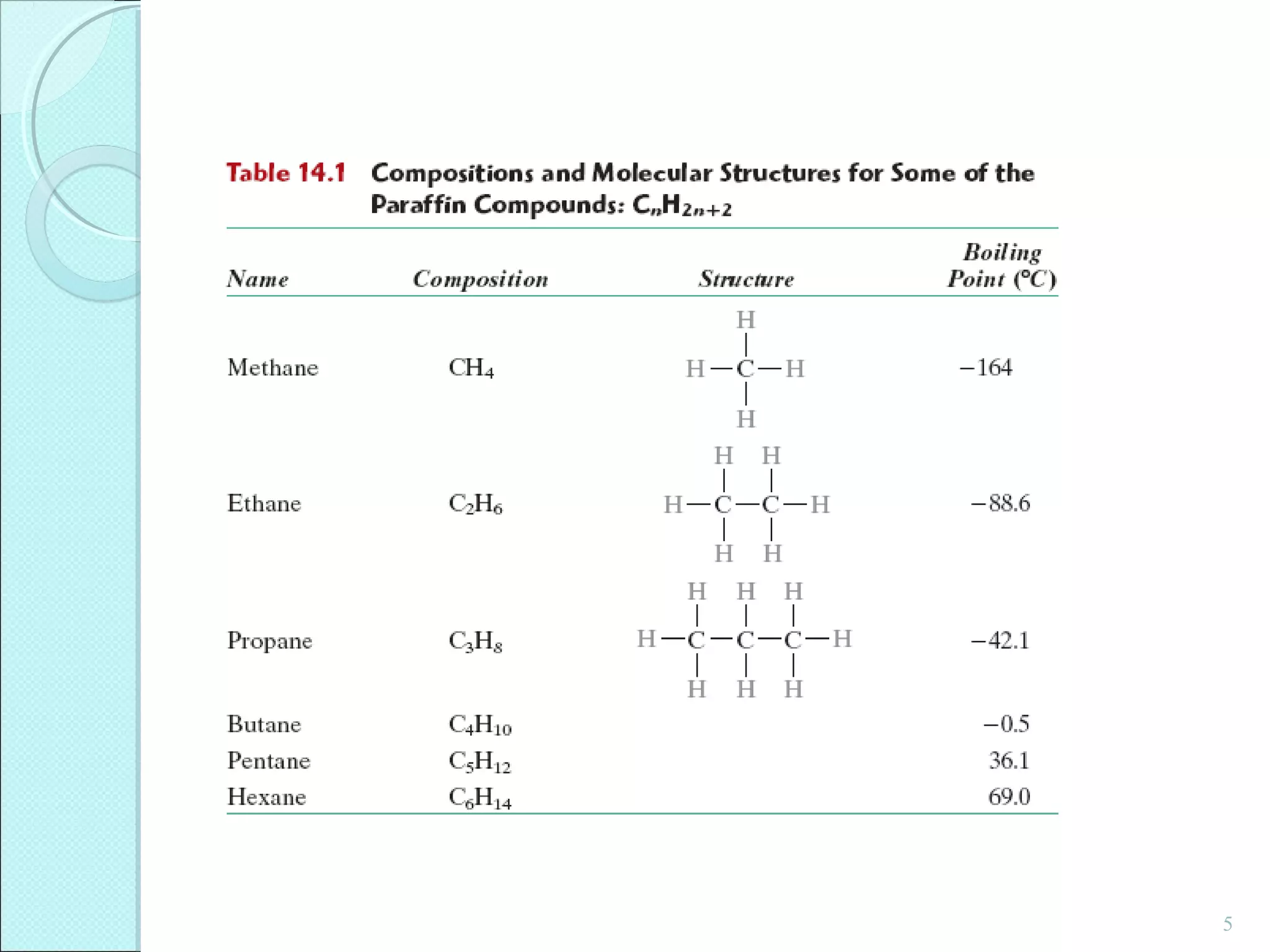
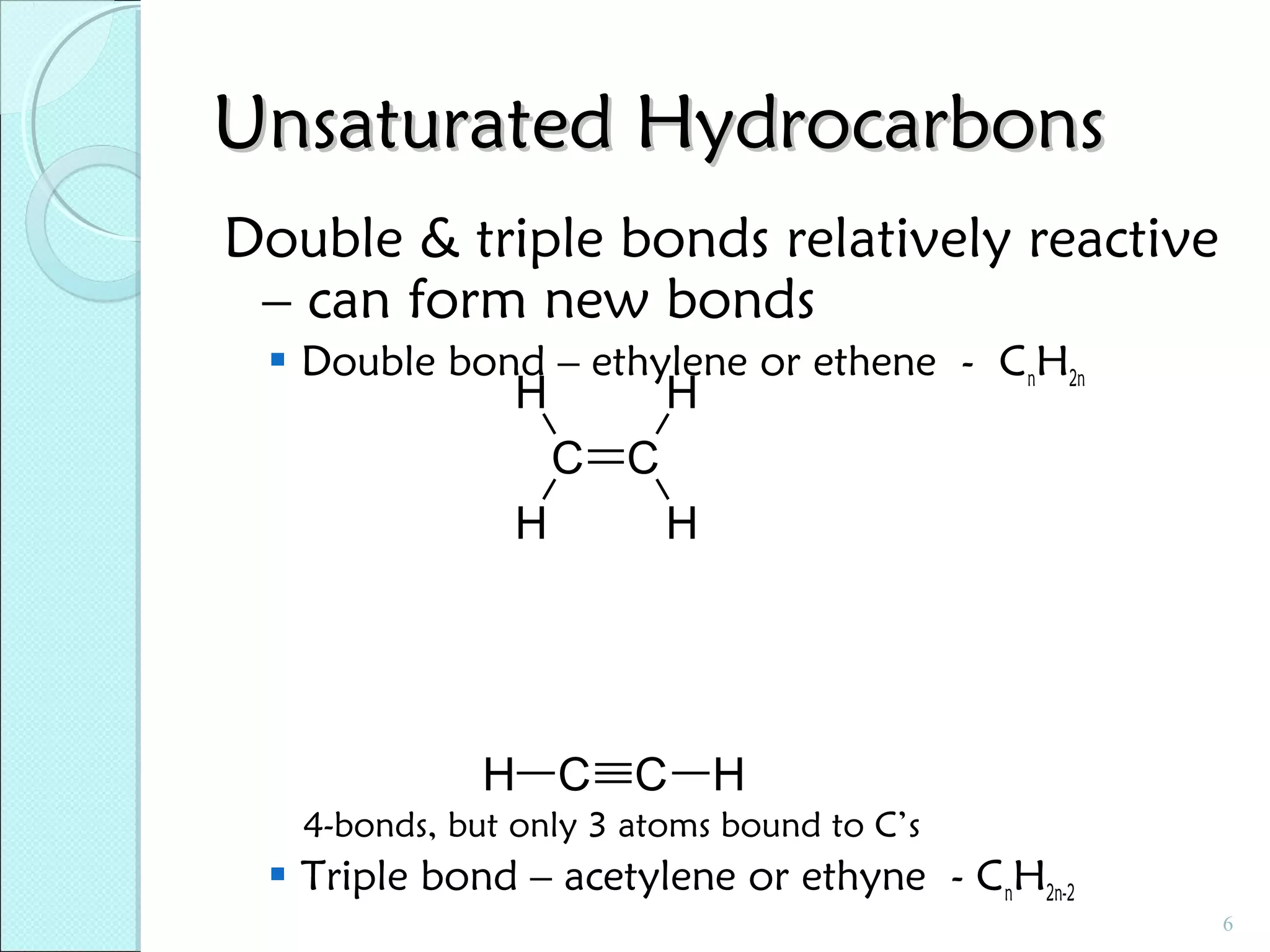
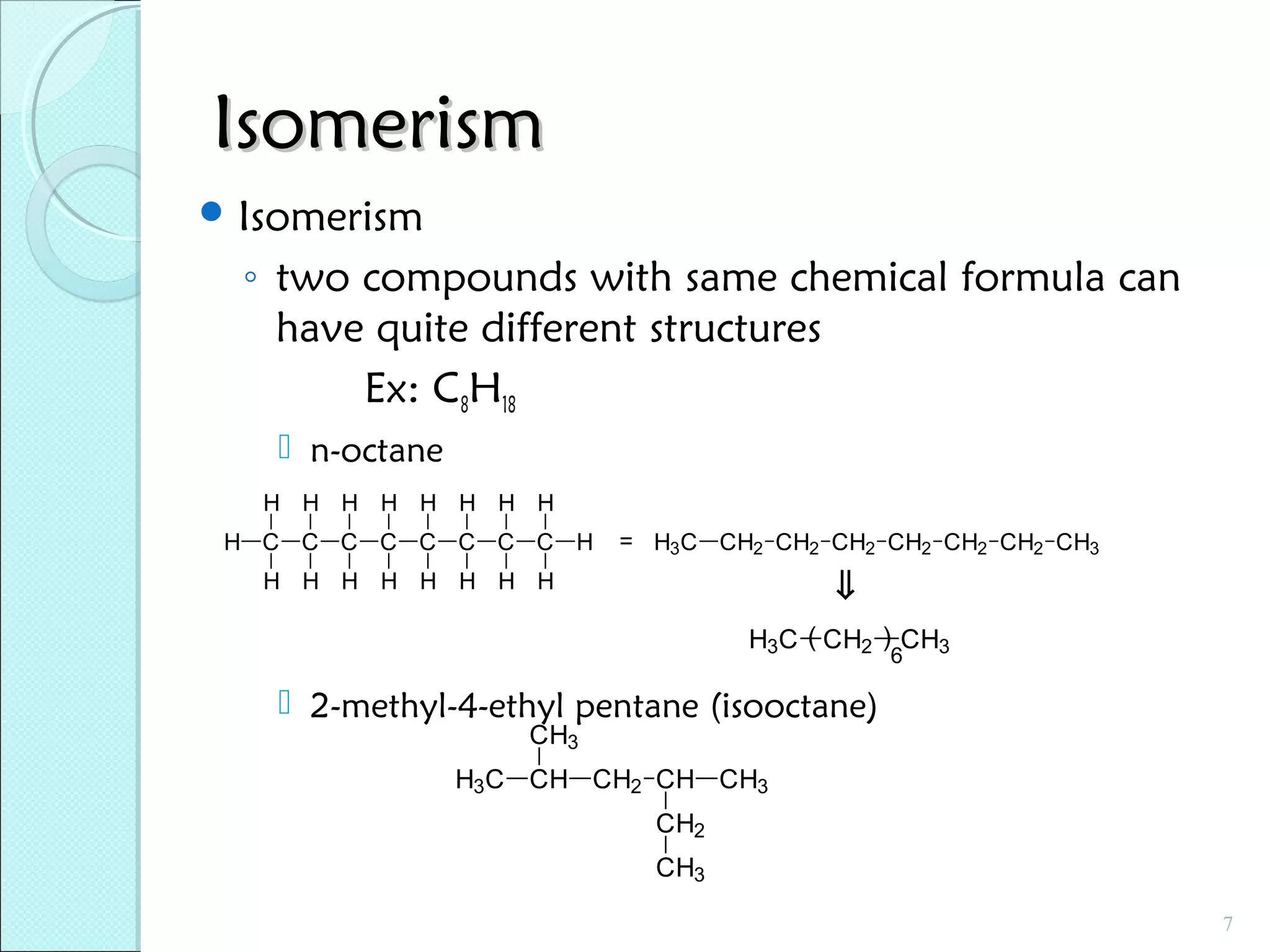
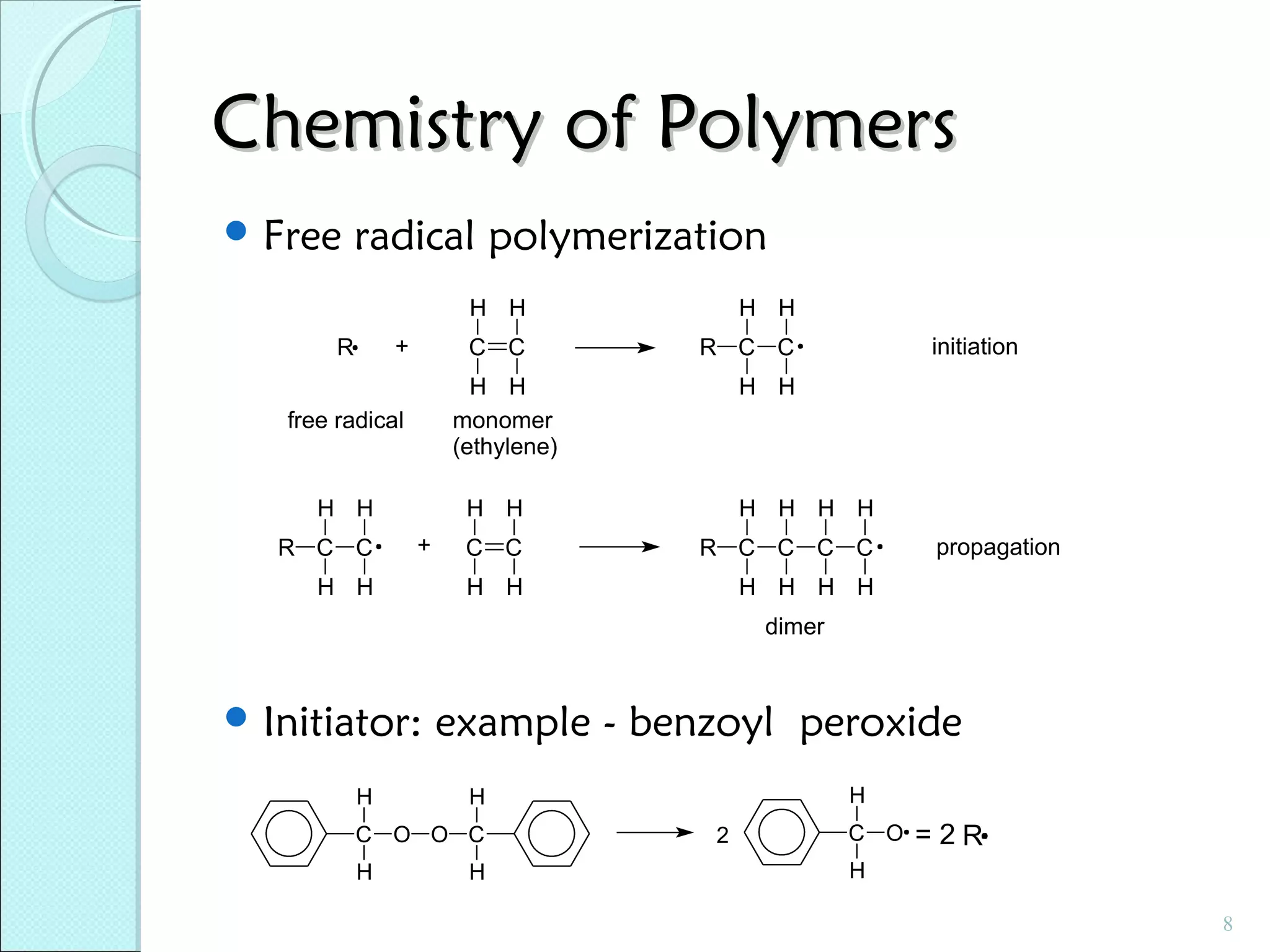
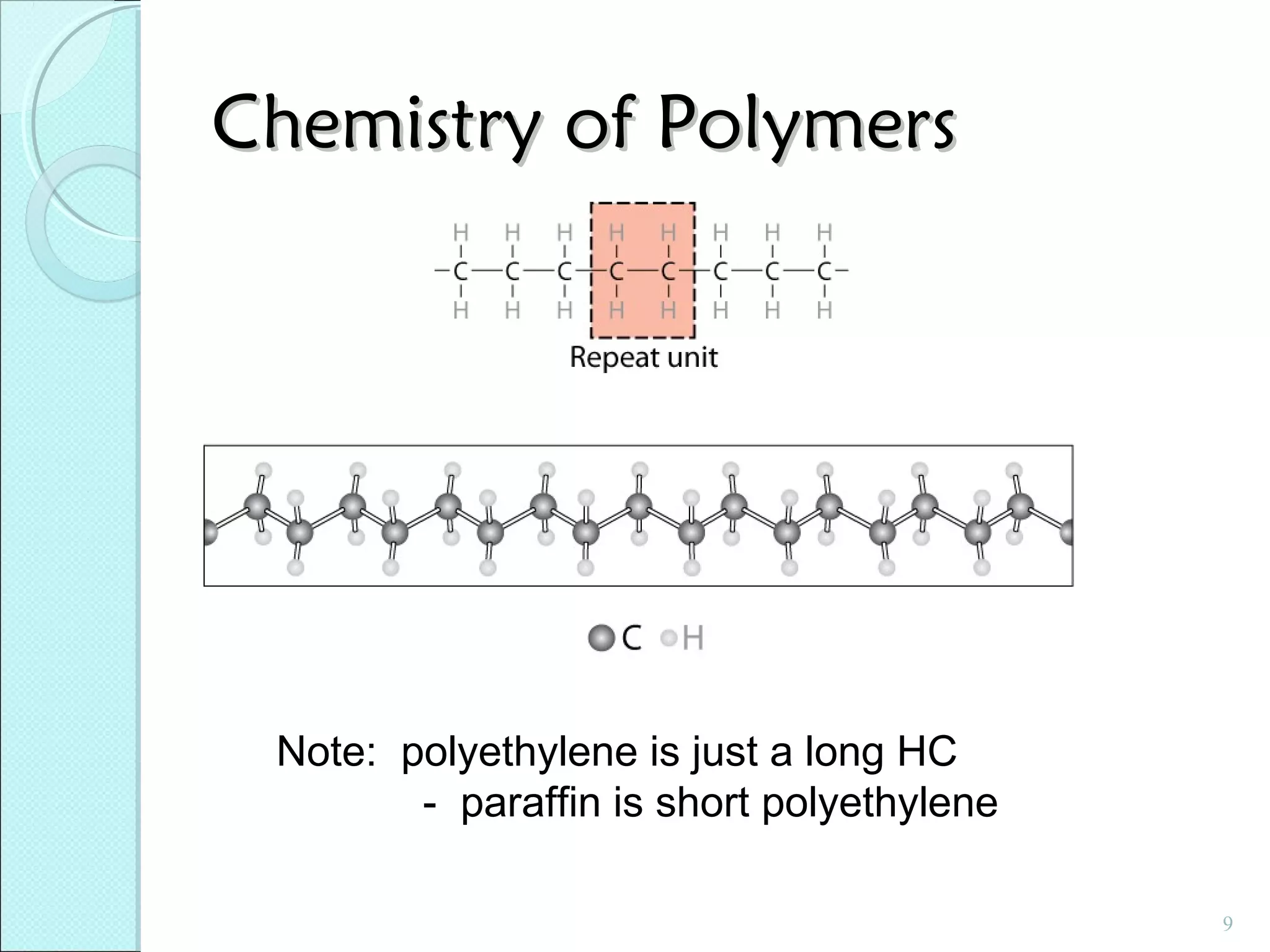
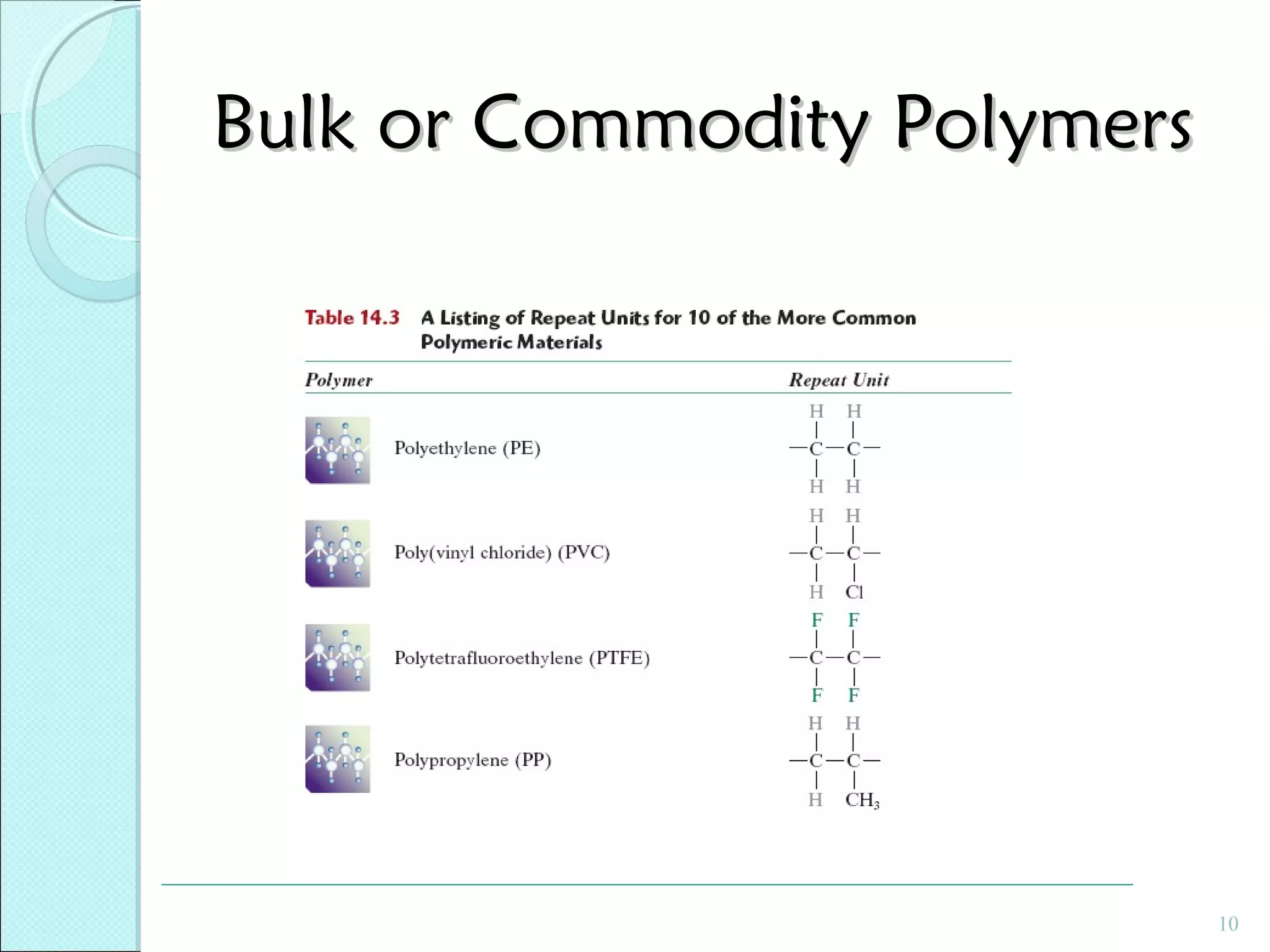
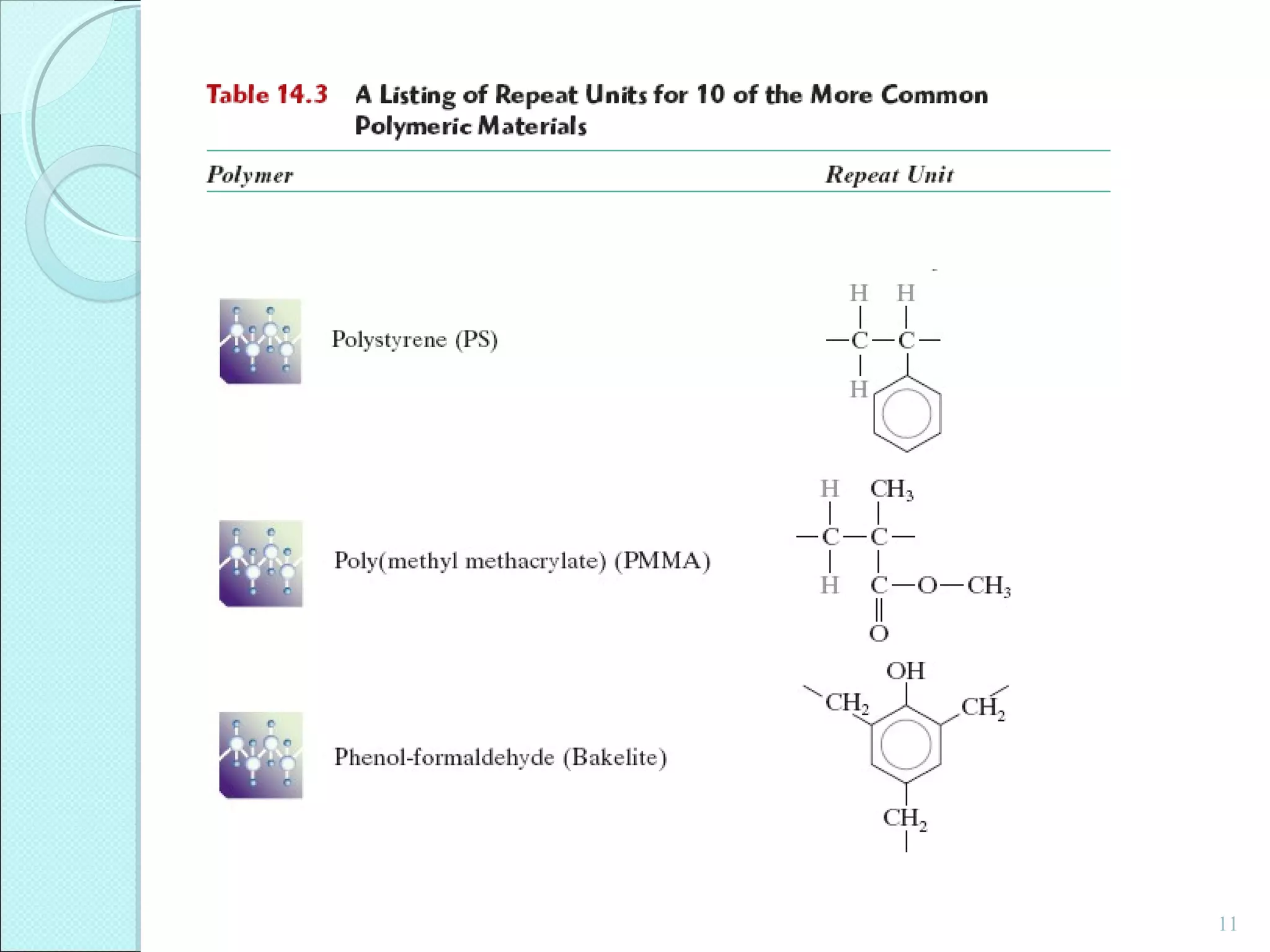
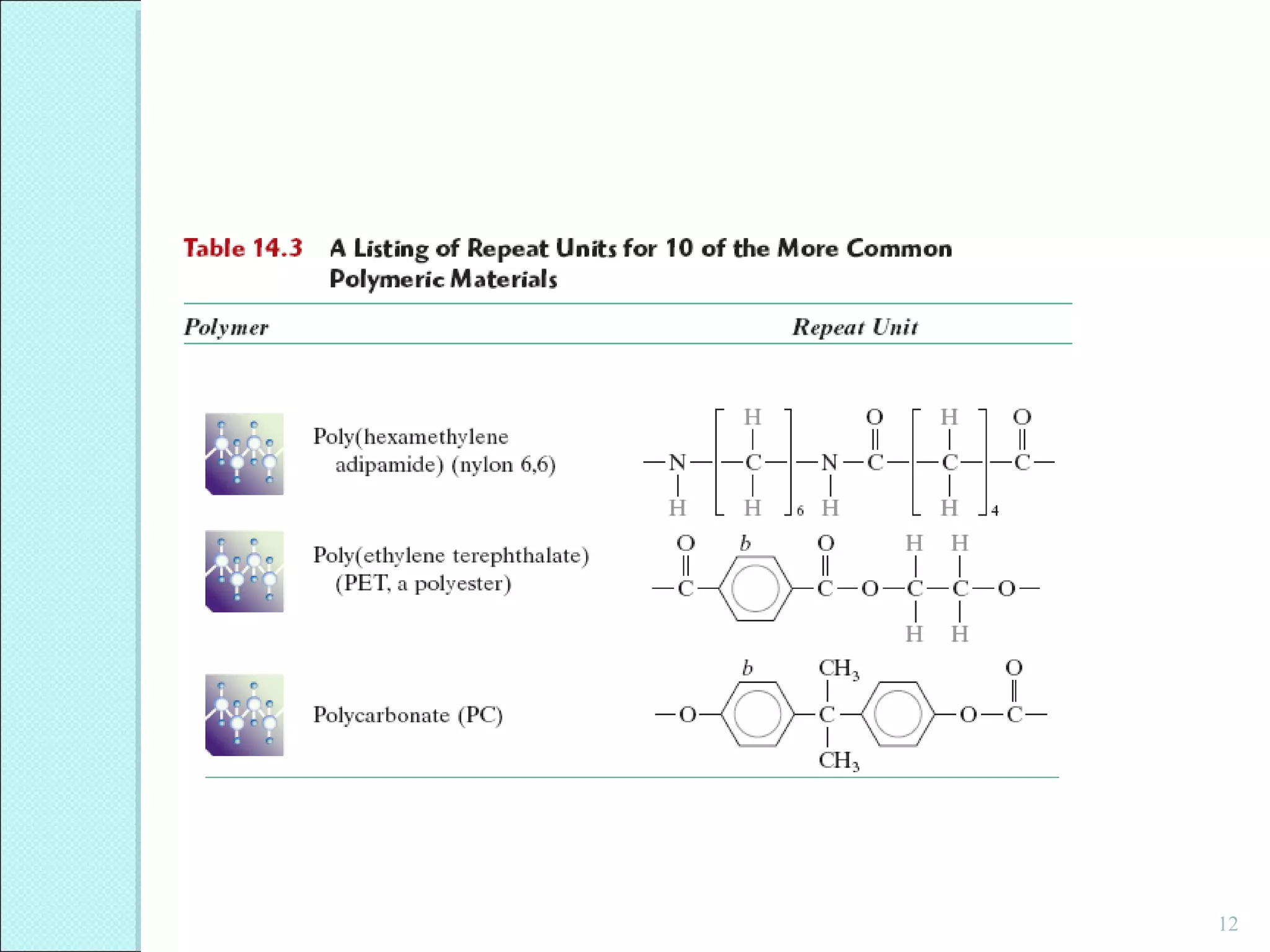
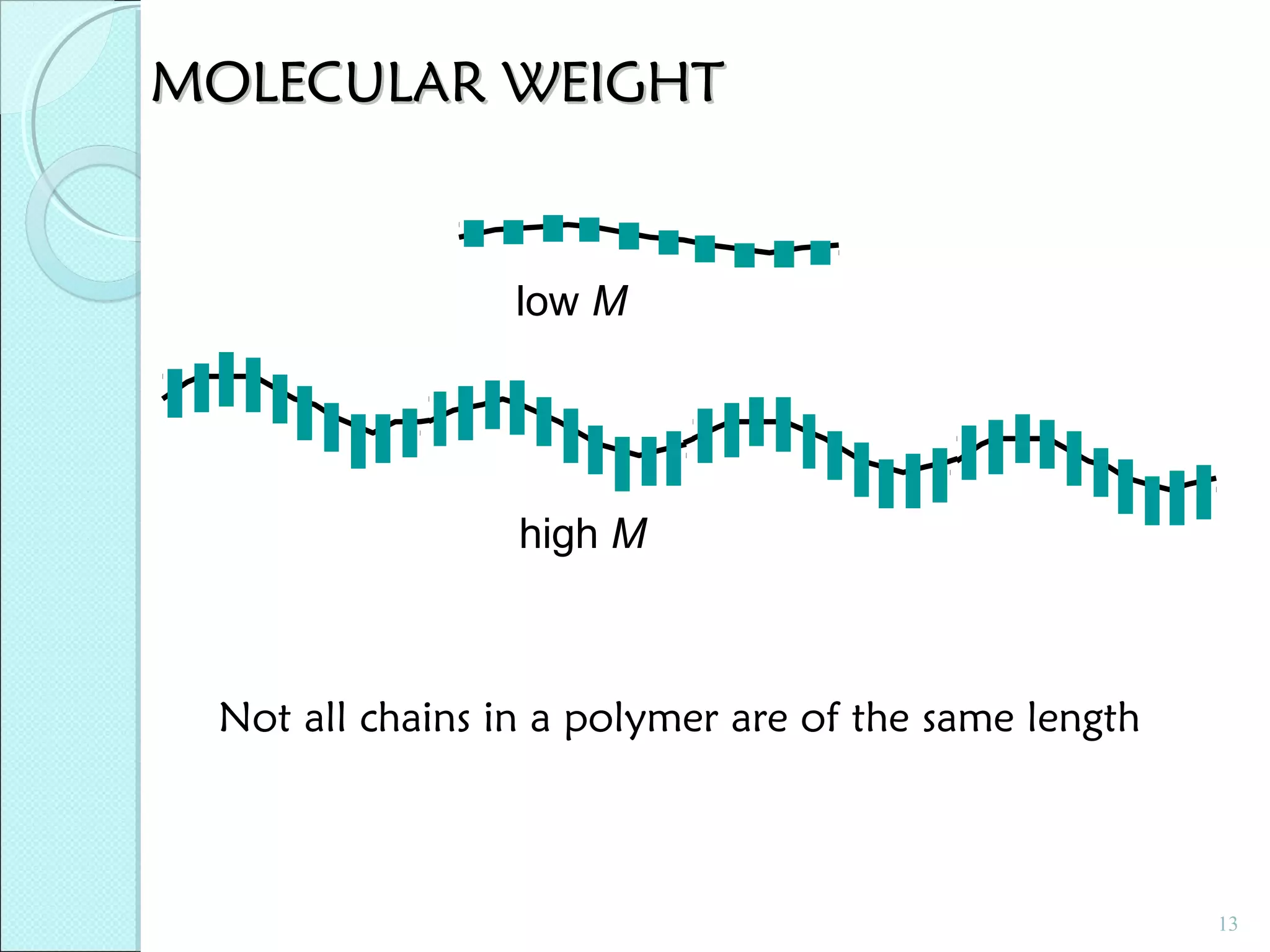
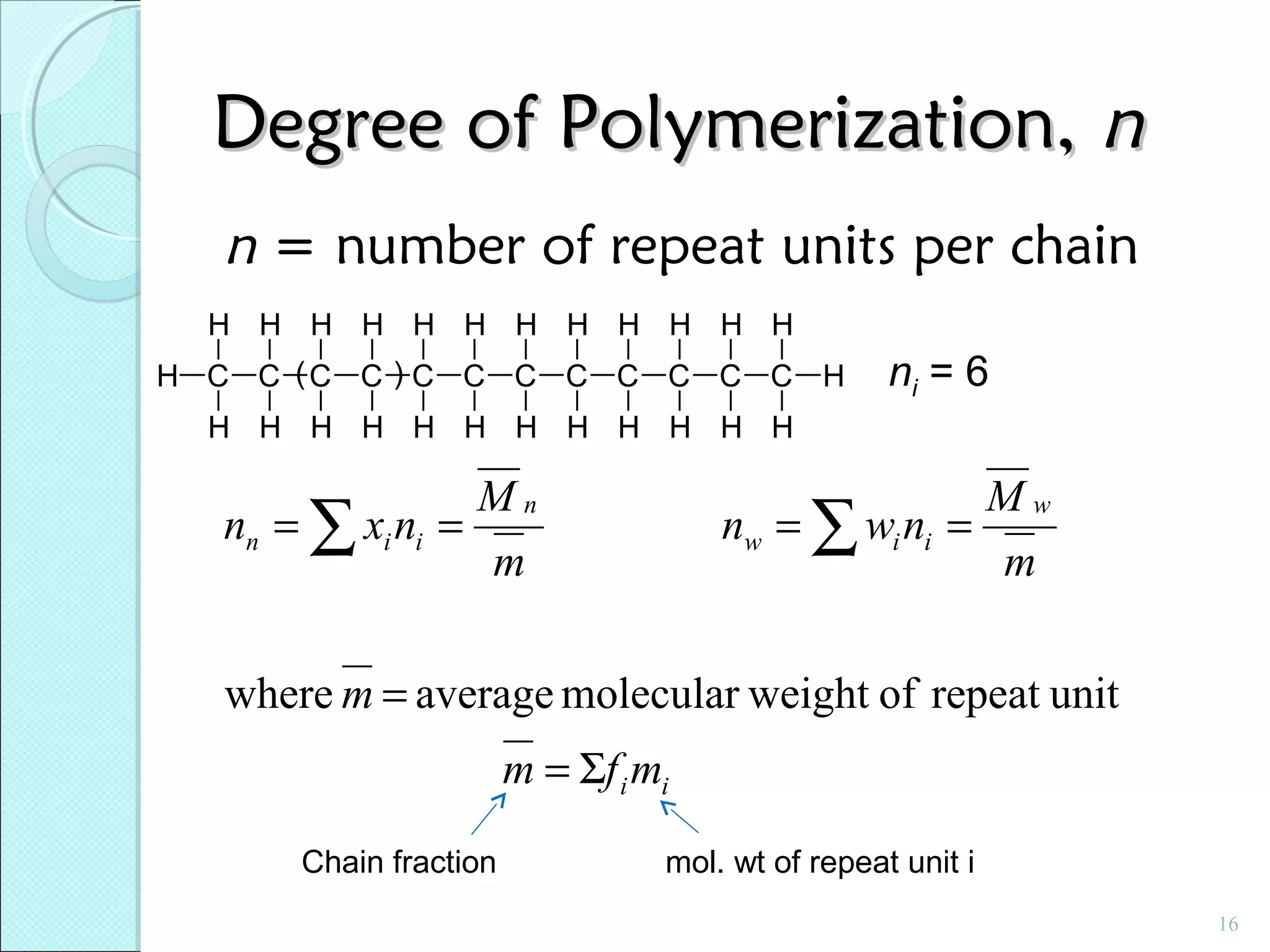
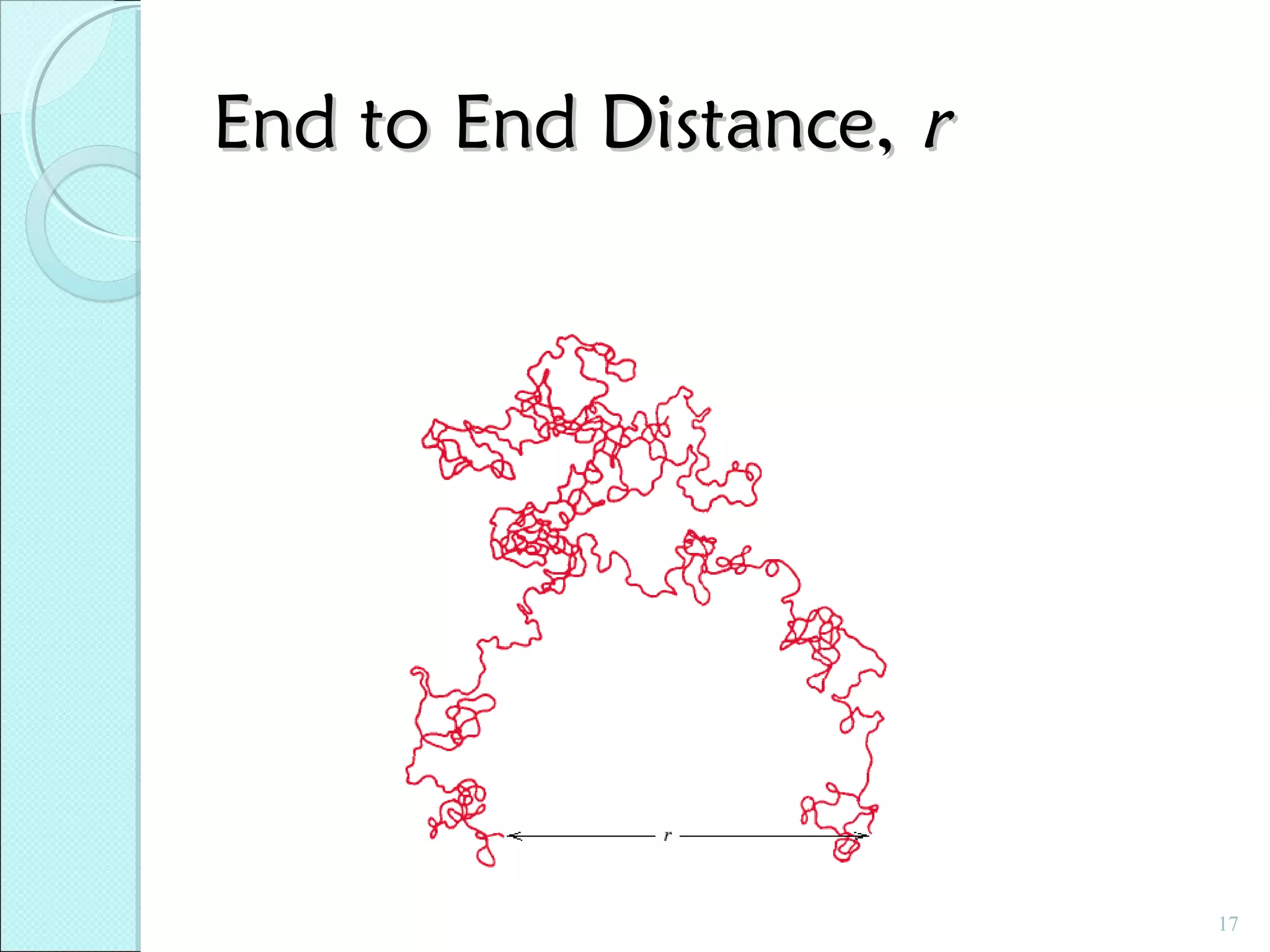
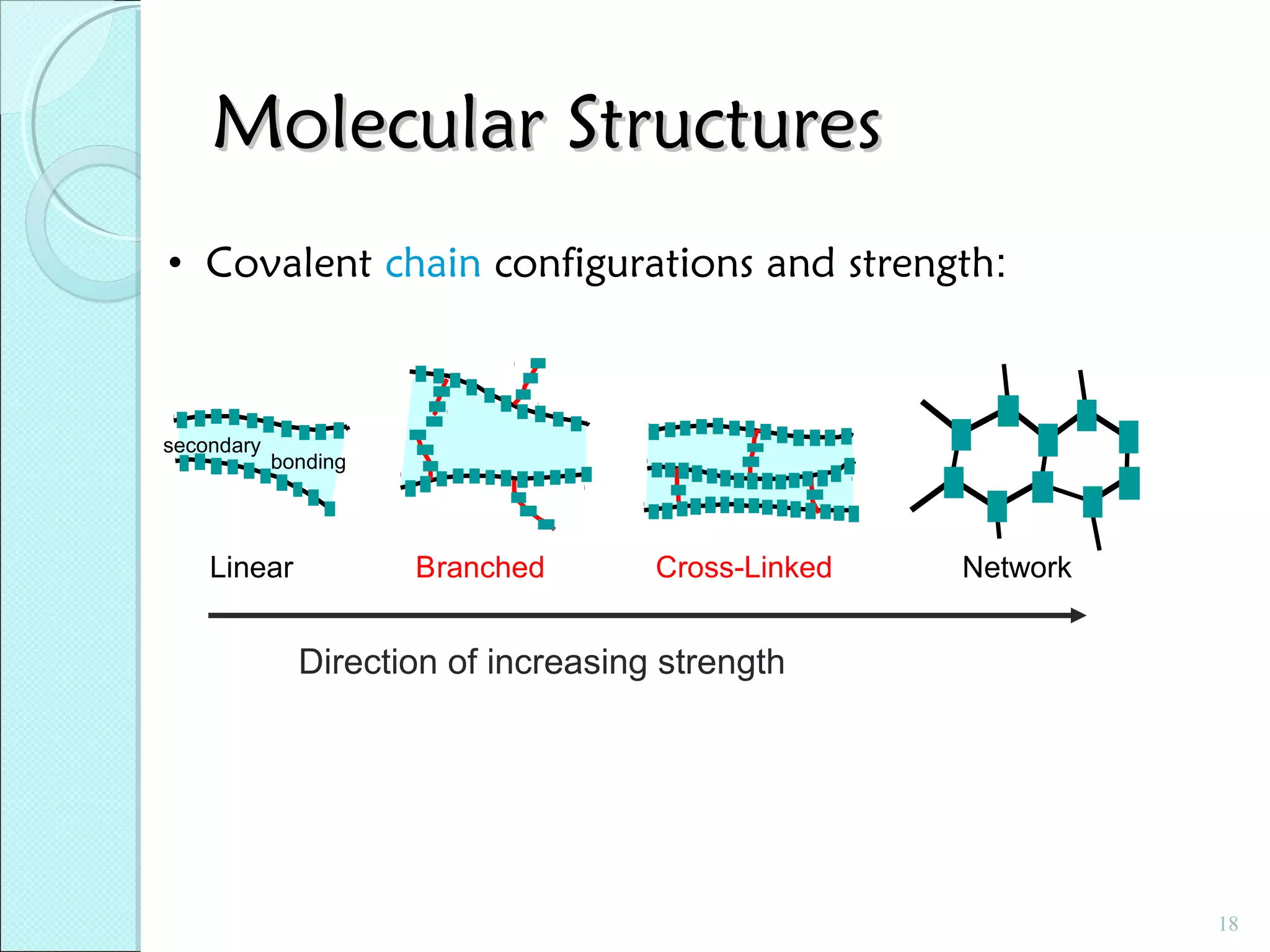
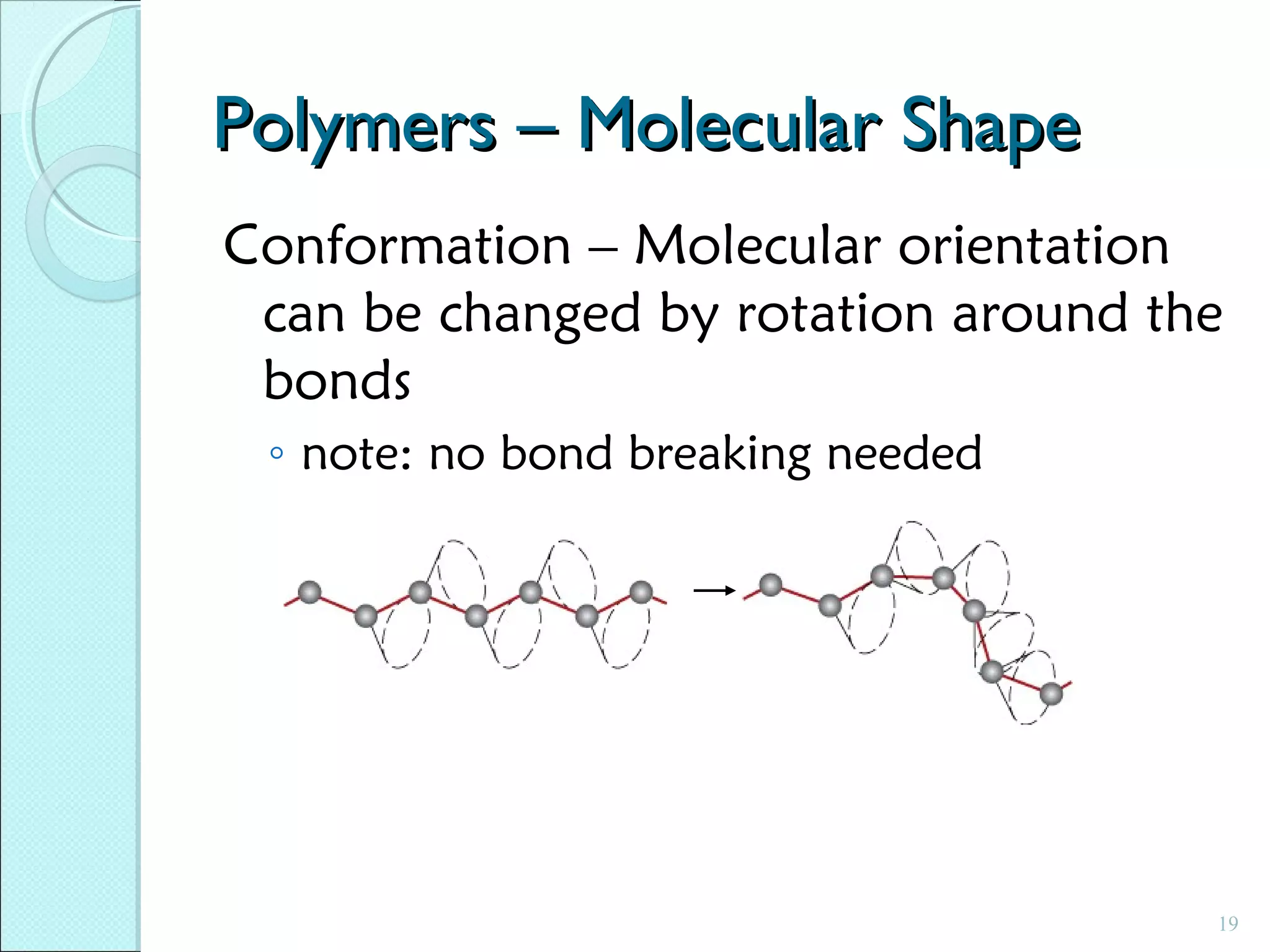
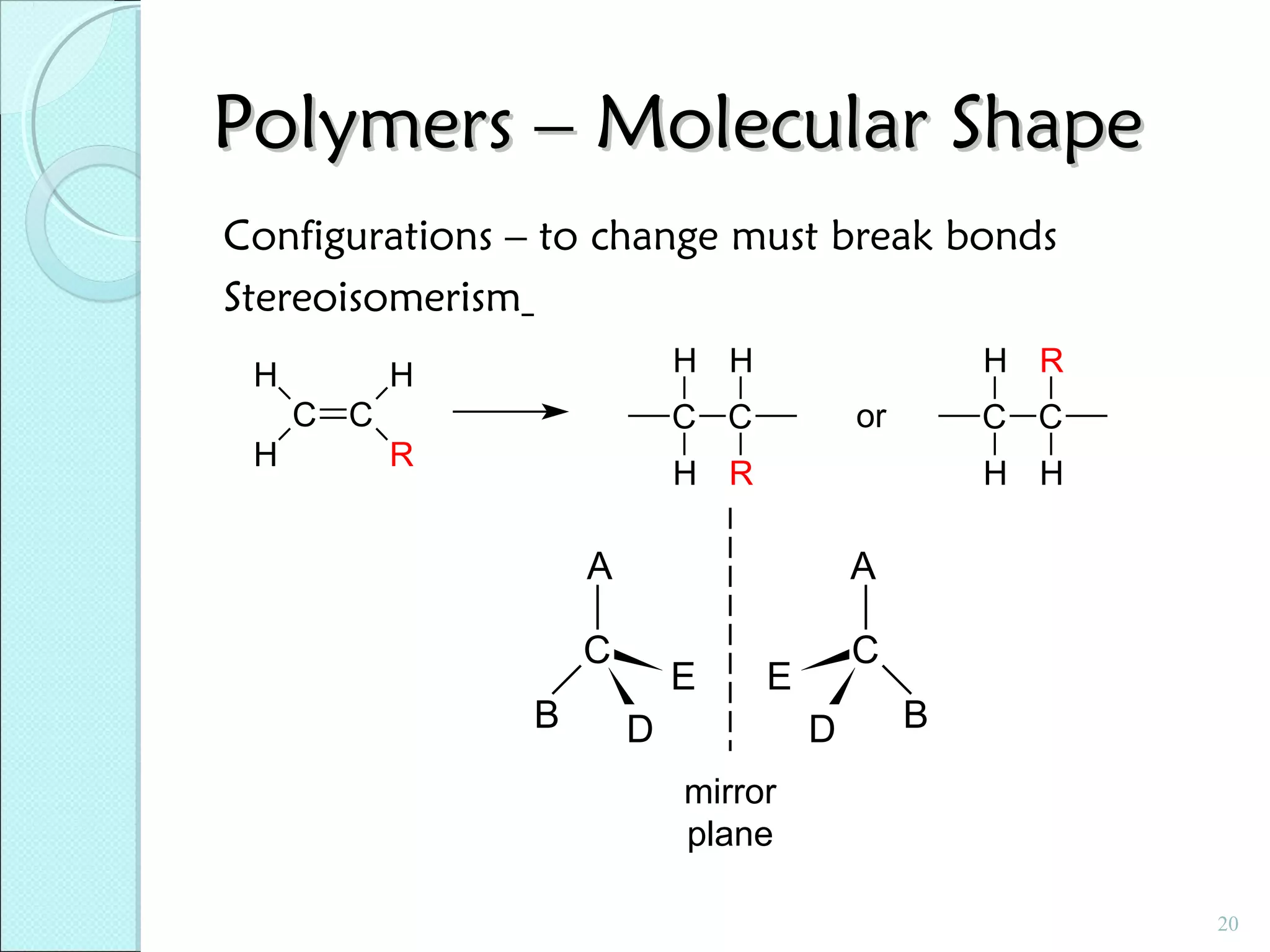
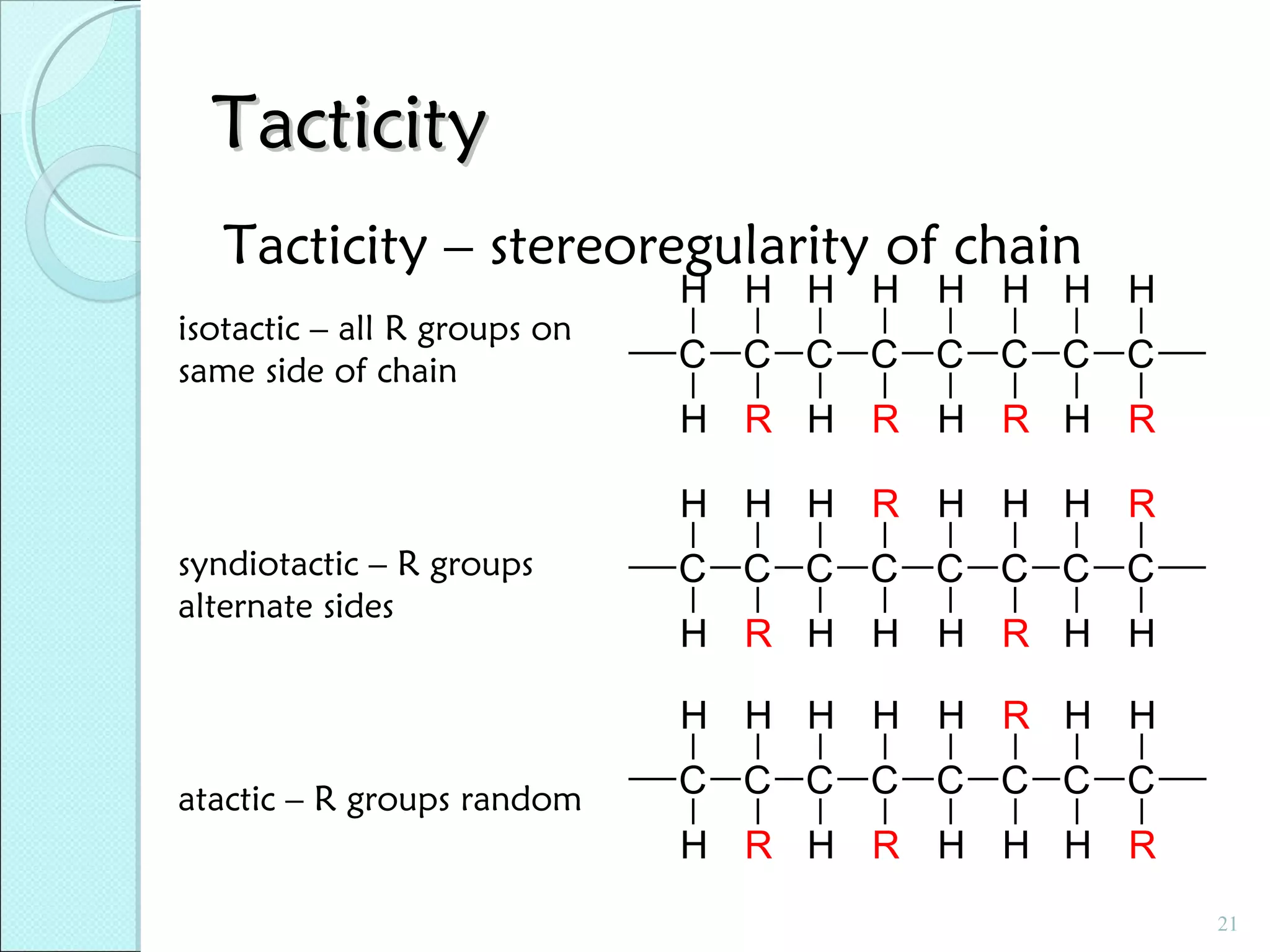
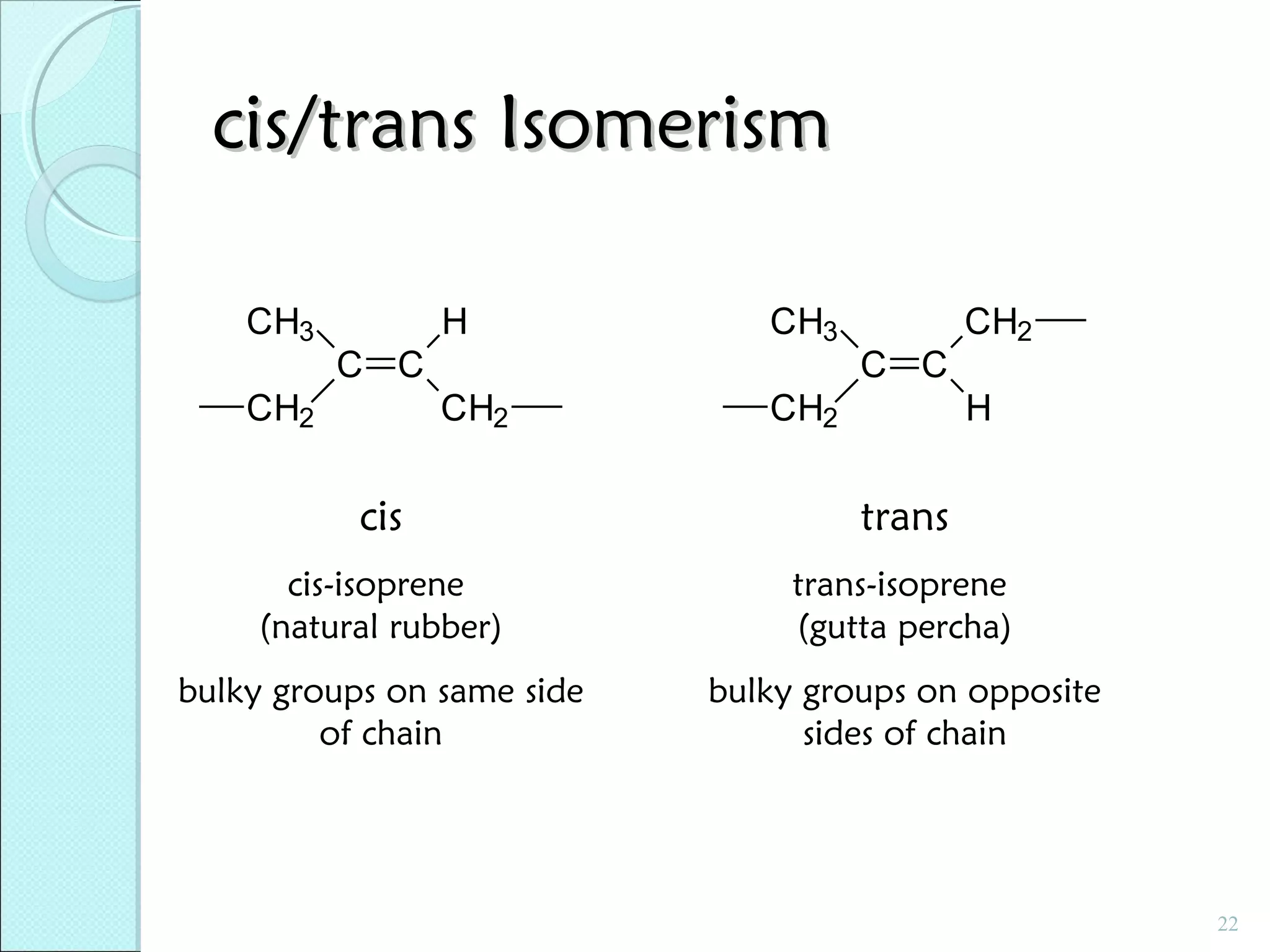
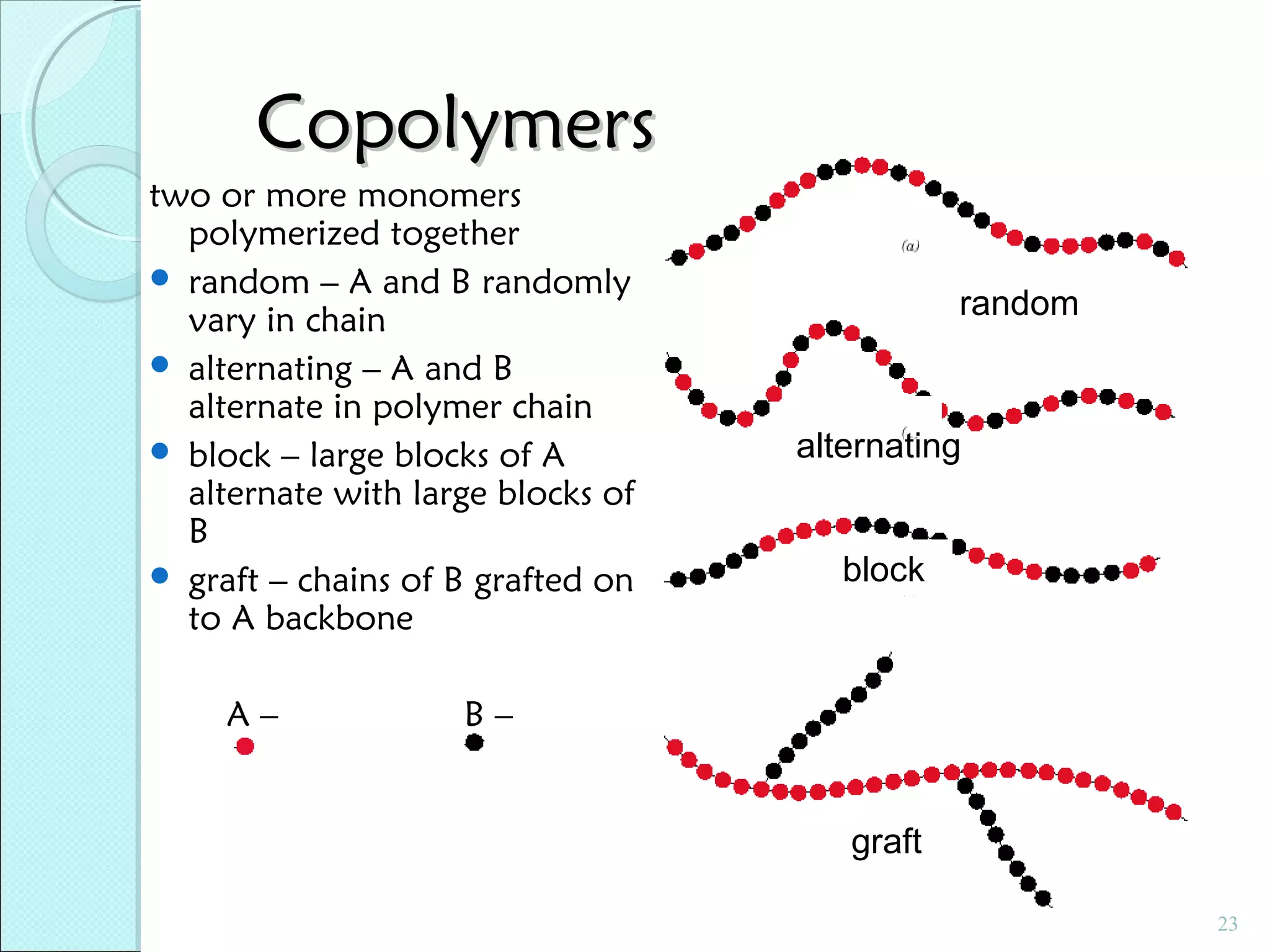
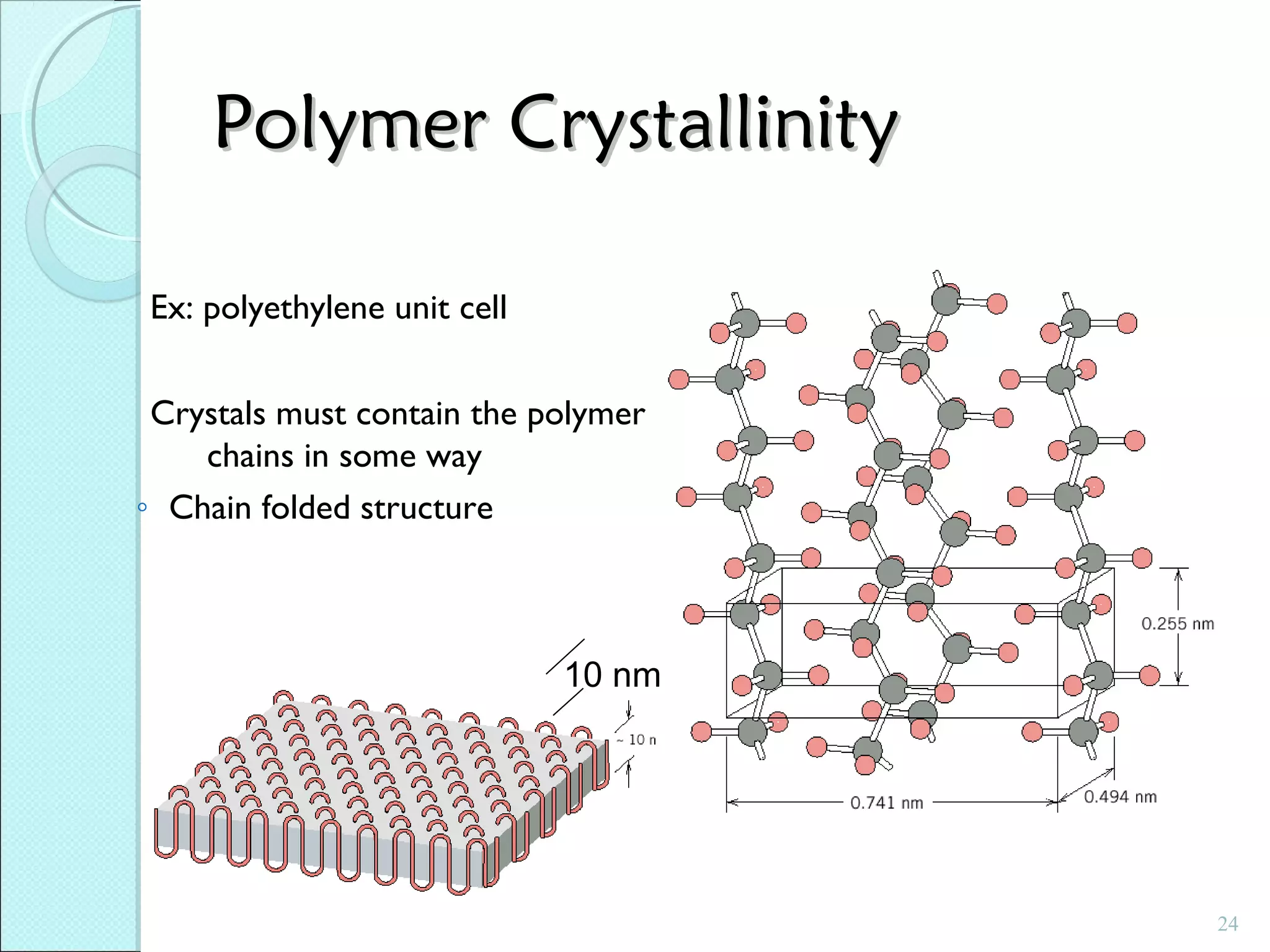
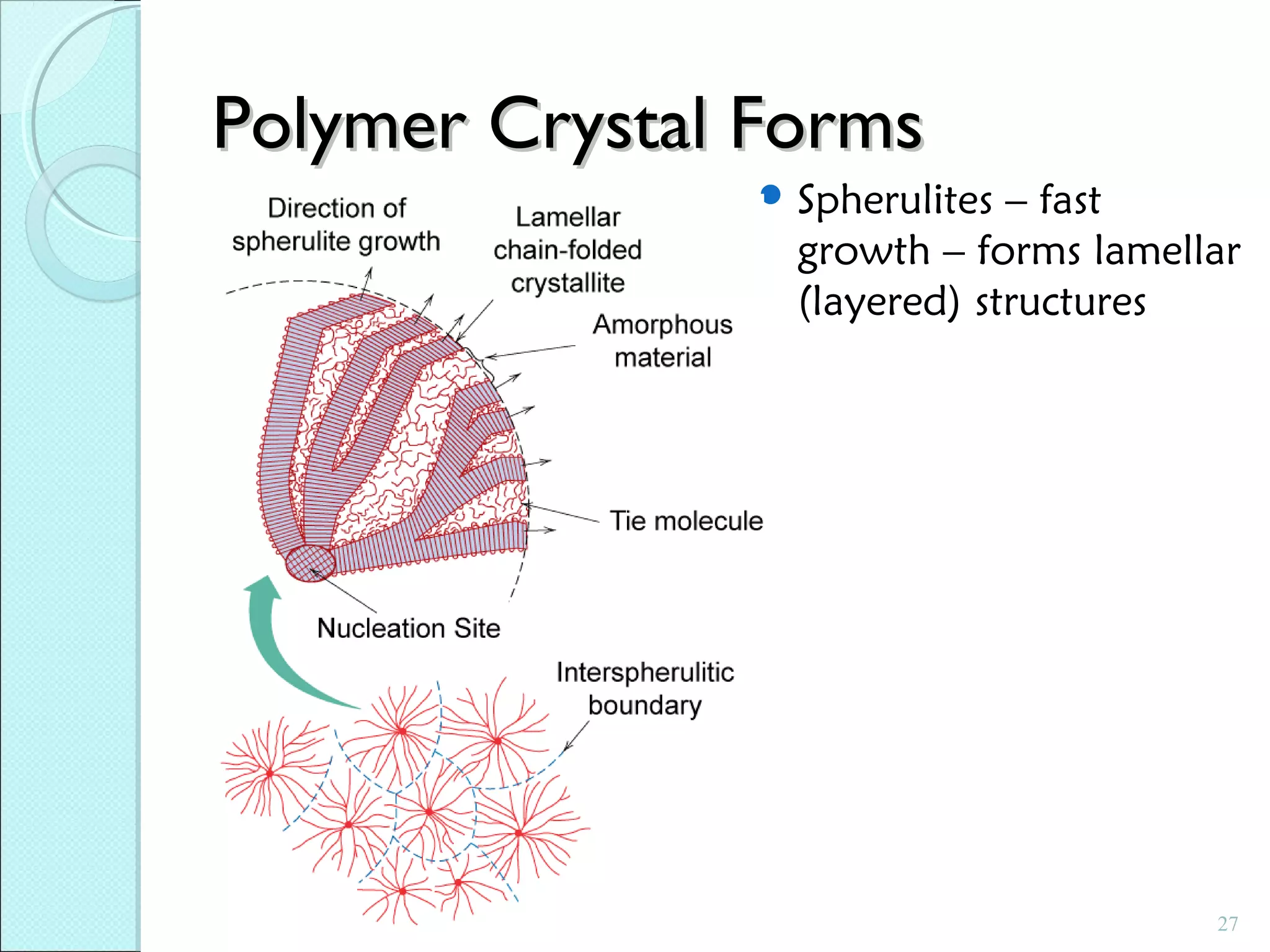
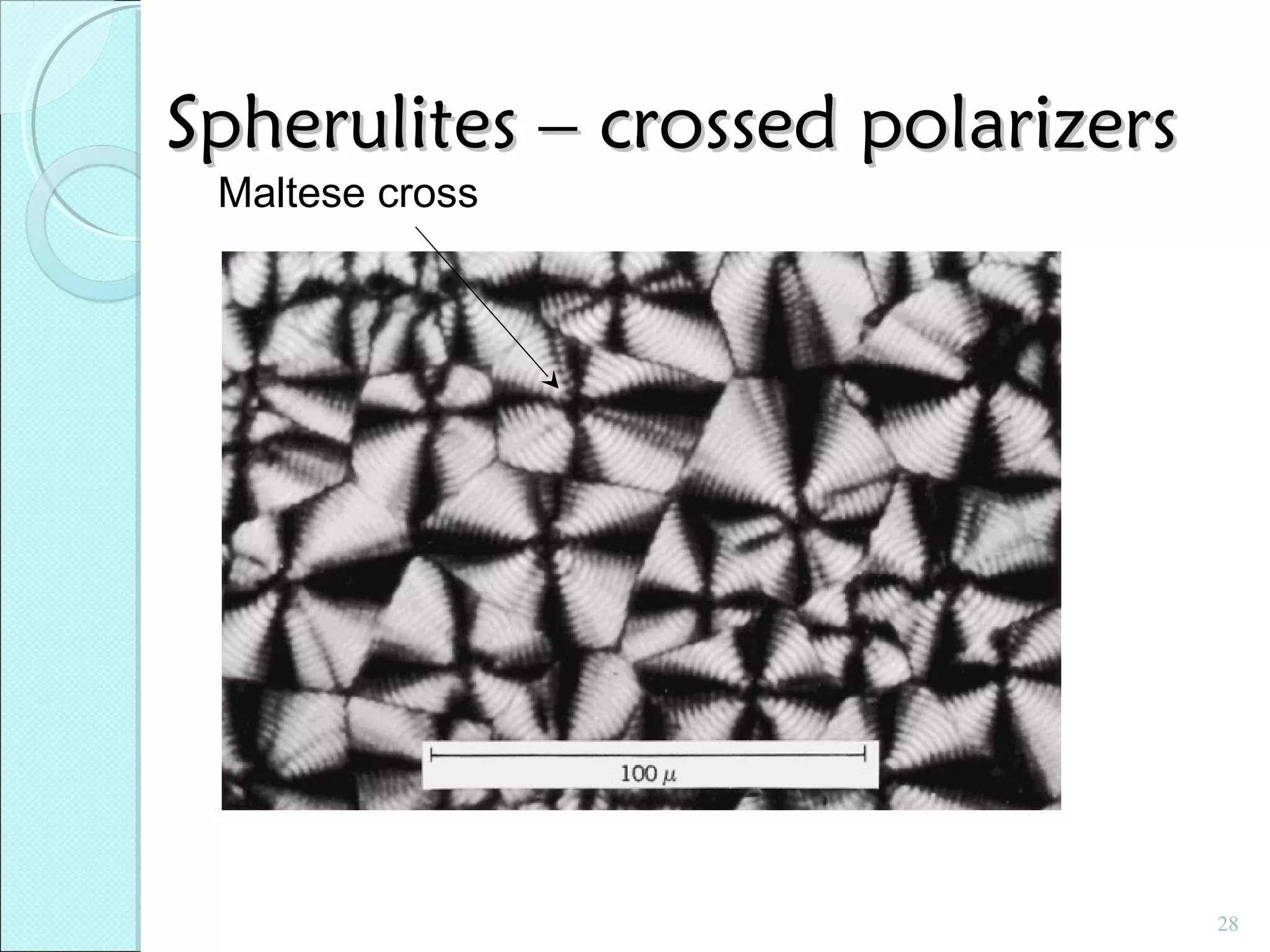
This document discusses polymer structure and composition. It begins by describing natural polymers like wood, cotton and rubber that were originally used. It then discusses the development of synthetic polymers like plastics, rubbers and fibers. Most polymers are hydrocarbons made of carbon and hydrogen. Polymers can have different compositions and structures including linear, branched, cross-linked and network configurations. The properties of a polymer depend on factors like its molecular weight, end-to-end distance, tacticity and crystallinity. Common techniques for characterizing polymers include determining the number average and weight average molecular weights.