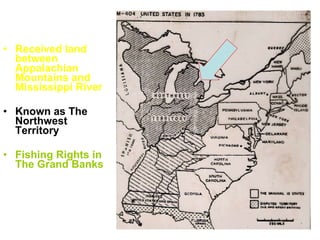
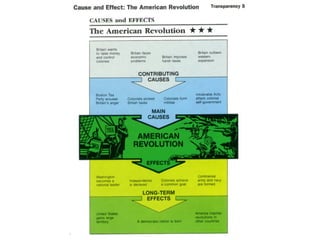
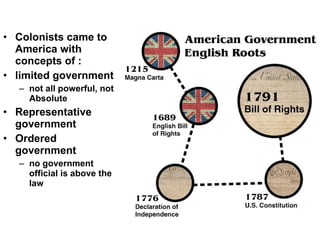
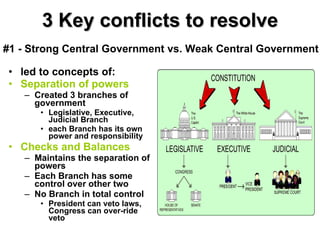
The document provides an overview of the American Revolution and early republic. It discusses the various acts passed by the British that angered the colonists and led to protests. Key events included the Boston Tea Party, Battles of Lexington and Concord, and the Declaration of Independence in 1776. After the Revolutionary War ended in 1783, the new nation struggled under the Articles of Confederation, leading to the Constitutional Convention of 1787 and the ratification of the U.S. Constitution. The first presidents Washington and Adams then helped establish the new federal government.