The document provides an overview of the creation of the United States, including:
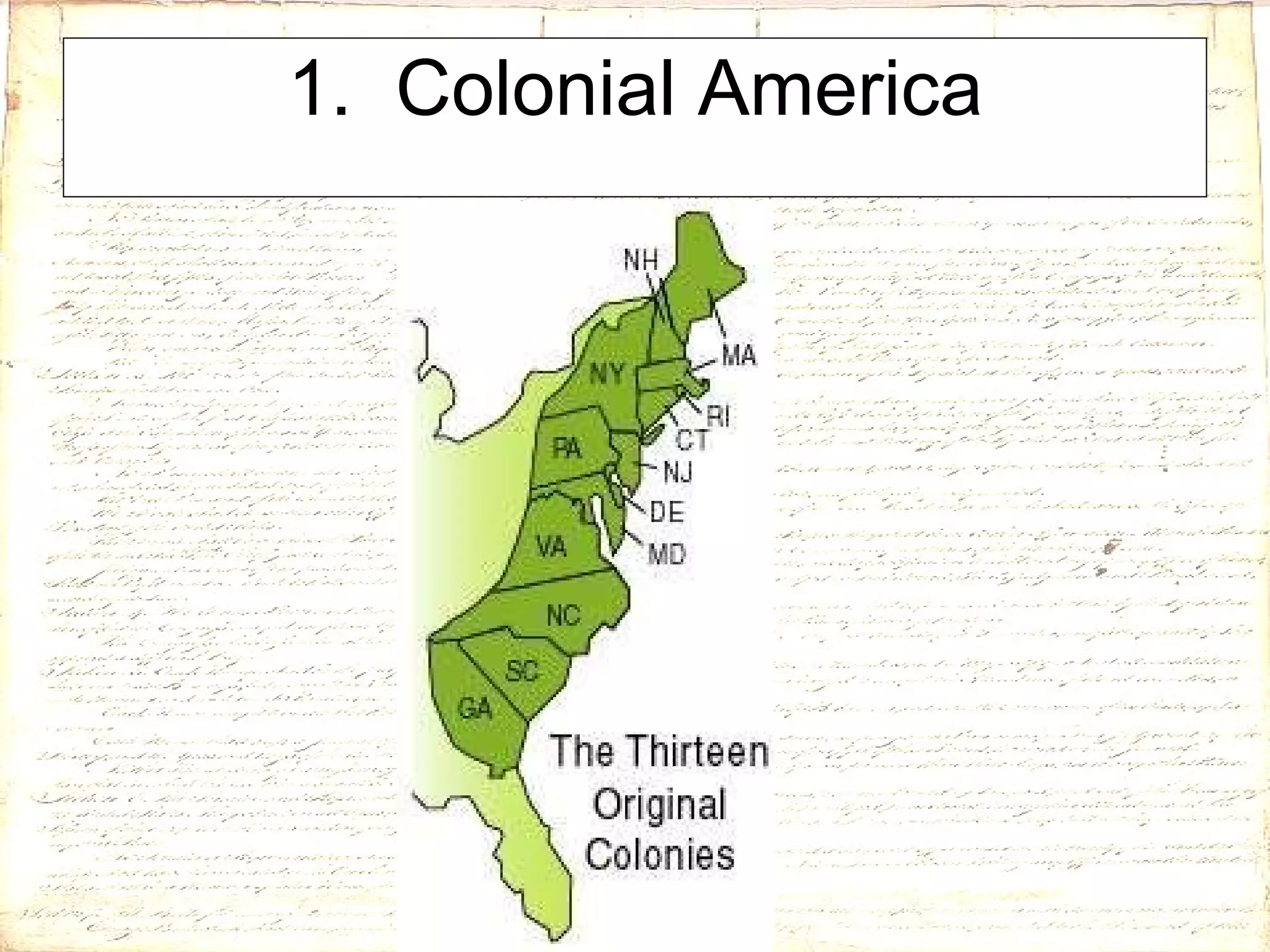
1) Colonial America started with charters that gave colonies varying levels of autonomy and self-governance.
2) Tensions rose between the colonies and Britain due to new taxes imposed after the French and Indian War, leading to the Declaration of Independence in 1776.
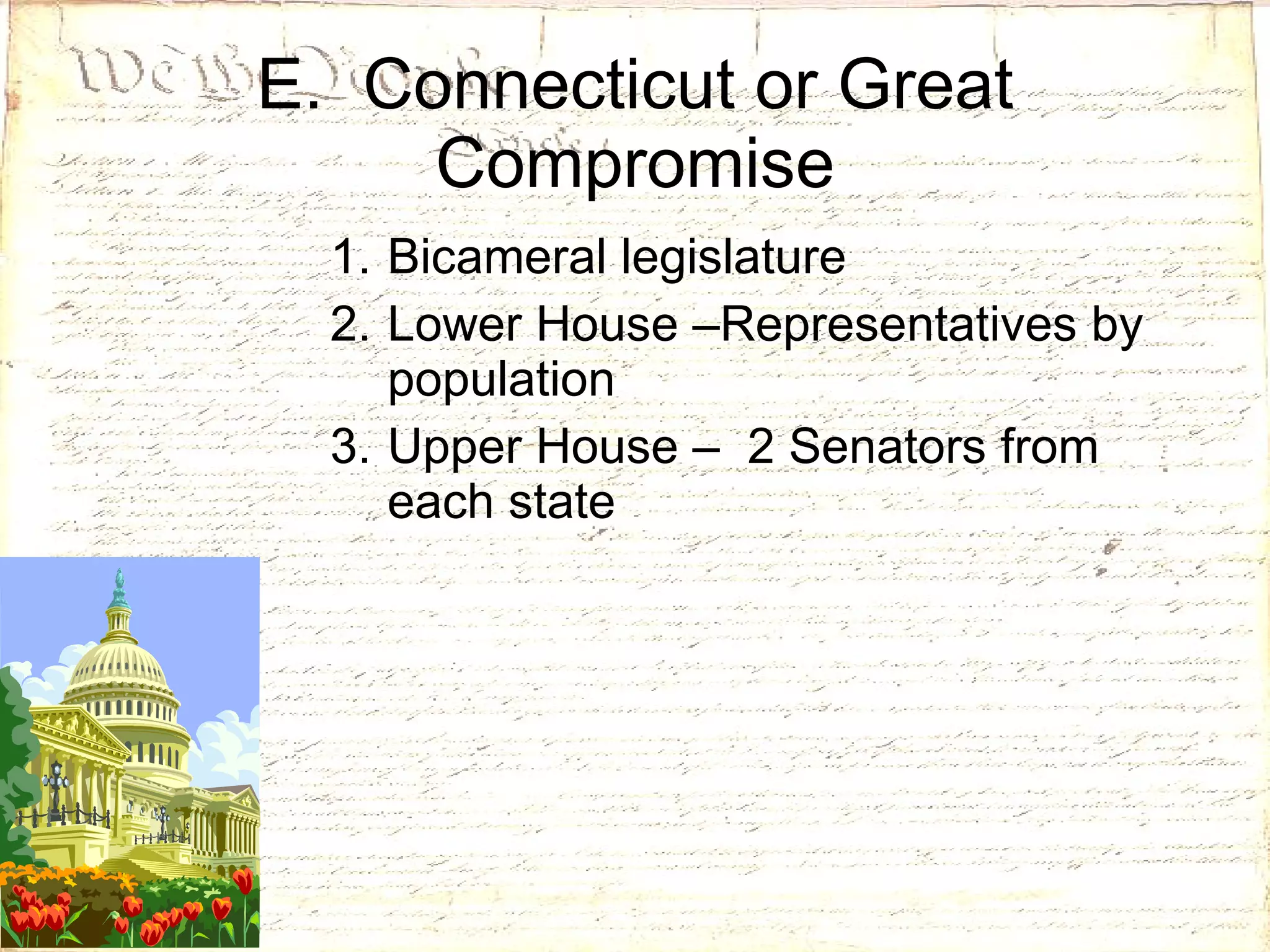
3) The Articles of Confederation established the first national government but had many weaknesses which led to calls for a stronger central government, resulting in the Constitutional Convention of 1787.