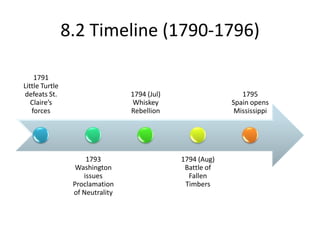
1) George Washington was sworn in as the first US President in 1789. His cabinet established the executive departments and he signed the Bill of Rights into law.
2) Political parties began emerging in the 1790s as Federalists led by Hamilton and Democratic-Republicans led by Jefferson disagreed on economic and foreign policy issues.
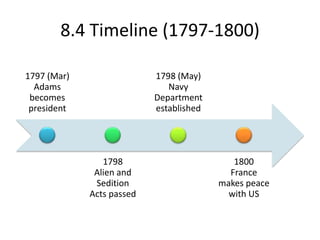
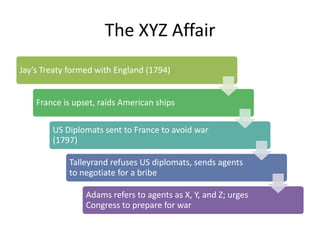
3) As president from 1797-1801, John Adams enacted the Alien and Sedition Acts to crack down on French immigrants, angering Democratic-Republicans. His reluctance to go to war with France helped Thomas Jefferson defeat him in the 1800 election.