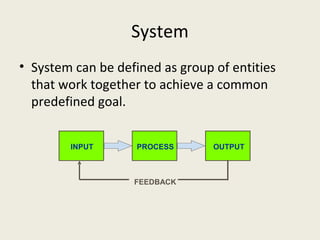
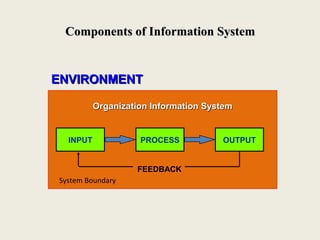
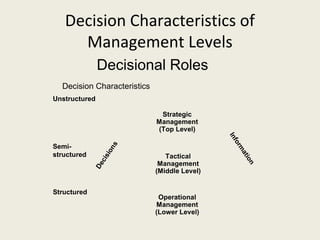
This document provides an introduction to information technology and information systems. It discusses why organizations should invest in IT solutions due to changes in business and technology. It defines key concepts like data, information, knowledge, and systems. It also describes different types of information systems like transaction processing systems, management information systems, and decision support systems. Finally, it discusses trends in IT and how IT is transforming businesses and organizations.