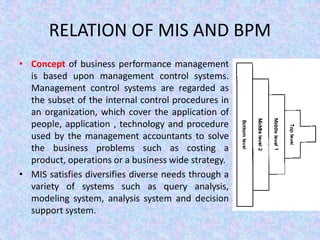
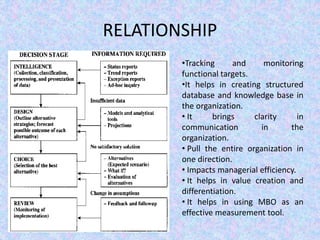
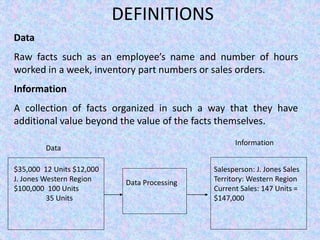
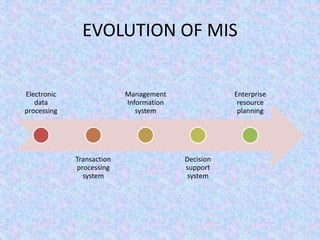
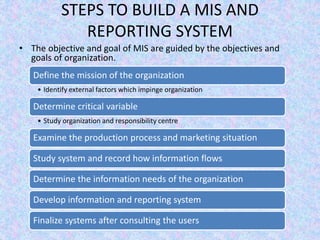
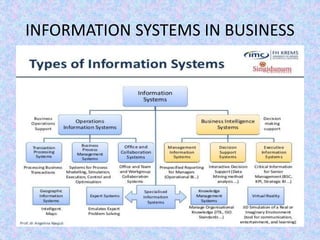
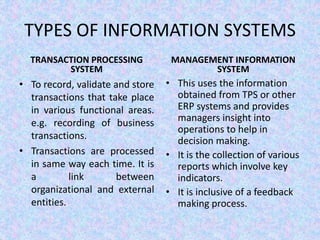
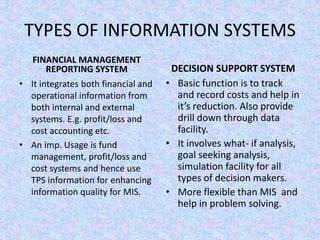
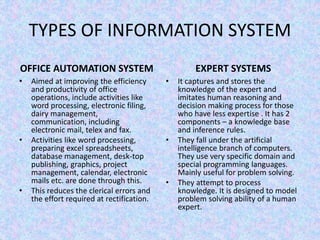
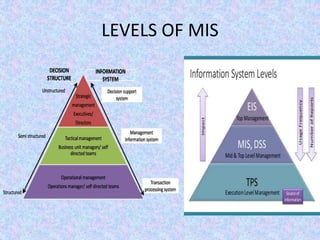
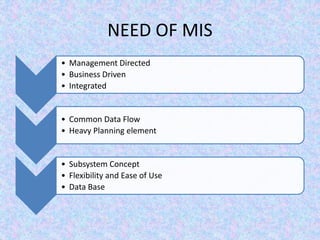
The document discusses the relationship between Management Information Systems (MIS) and Business Performance Management (BPM), emphasizing the role of MIS in organizational control and decision-making processes. It outlines various types of information systems, including Transaction Processing Systems, Management Information Systems, and Decision Support Systems, highlighting their functions and importance for effective management. Additionally, it addresses the need for comprehensive MIS development, training, and data analysis for improving organizational performance and efficiency.