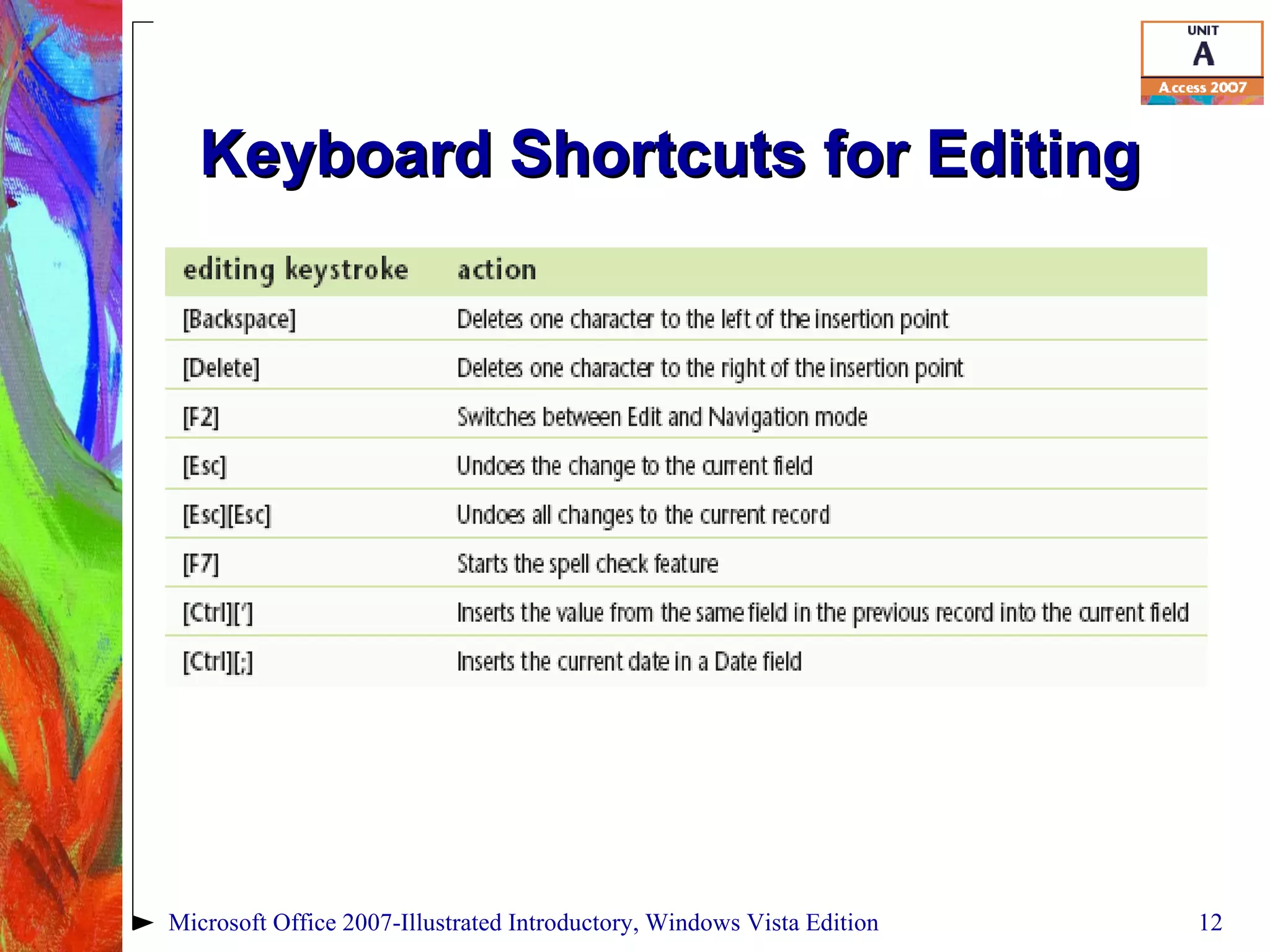
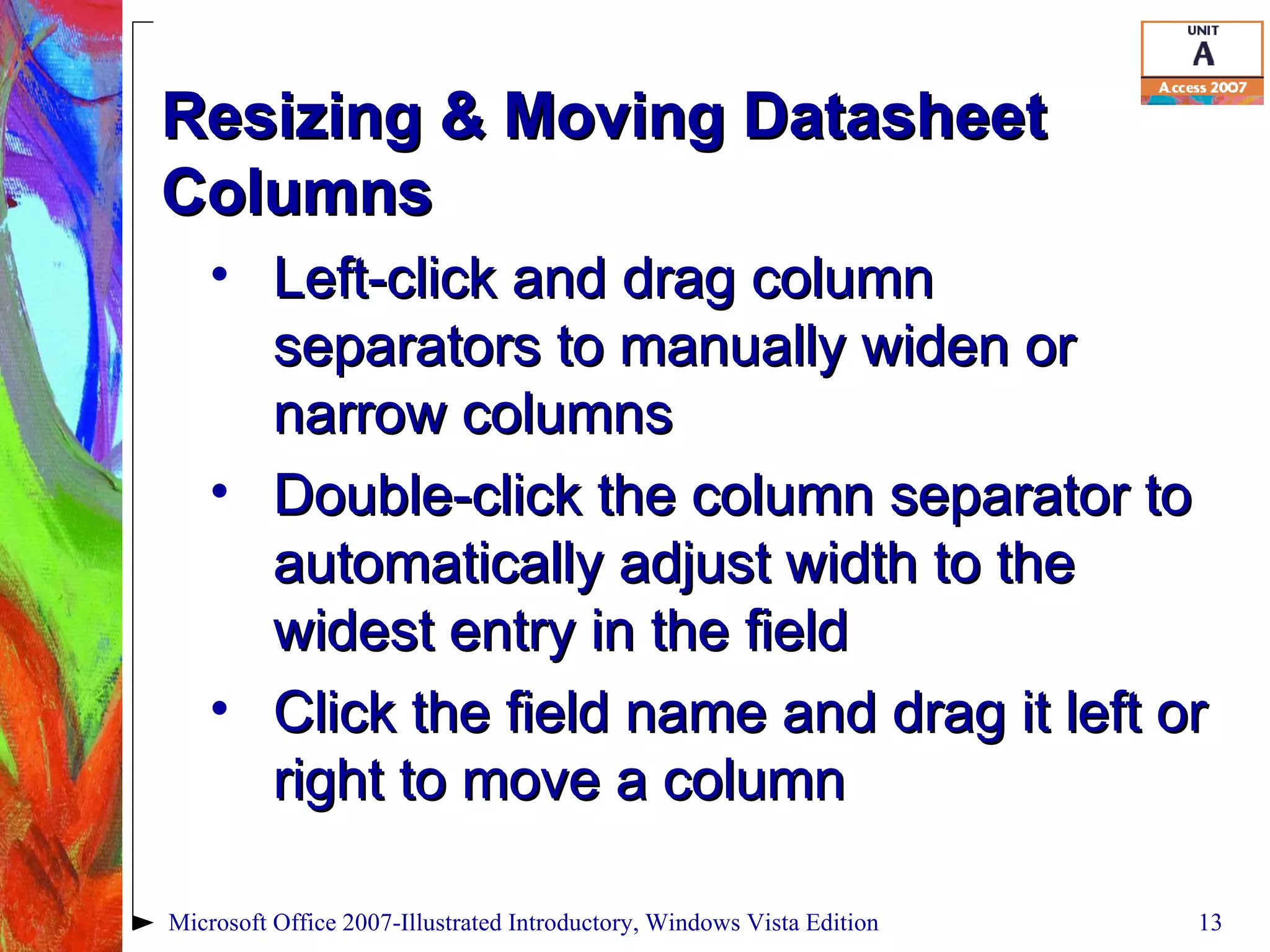
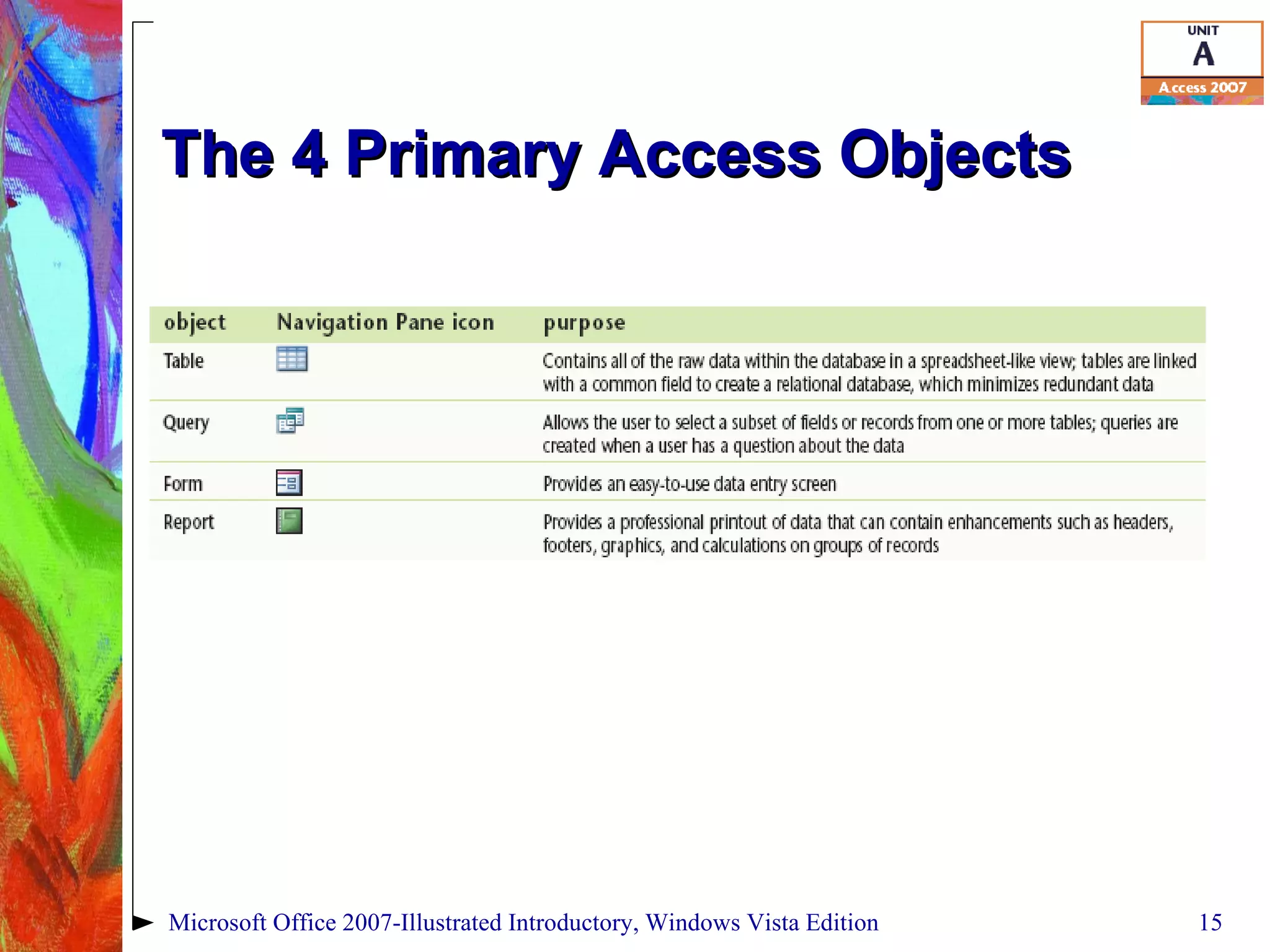
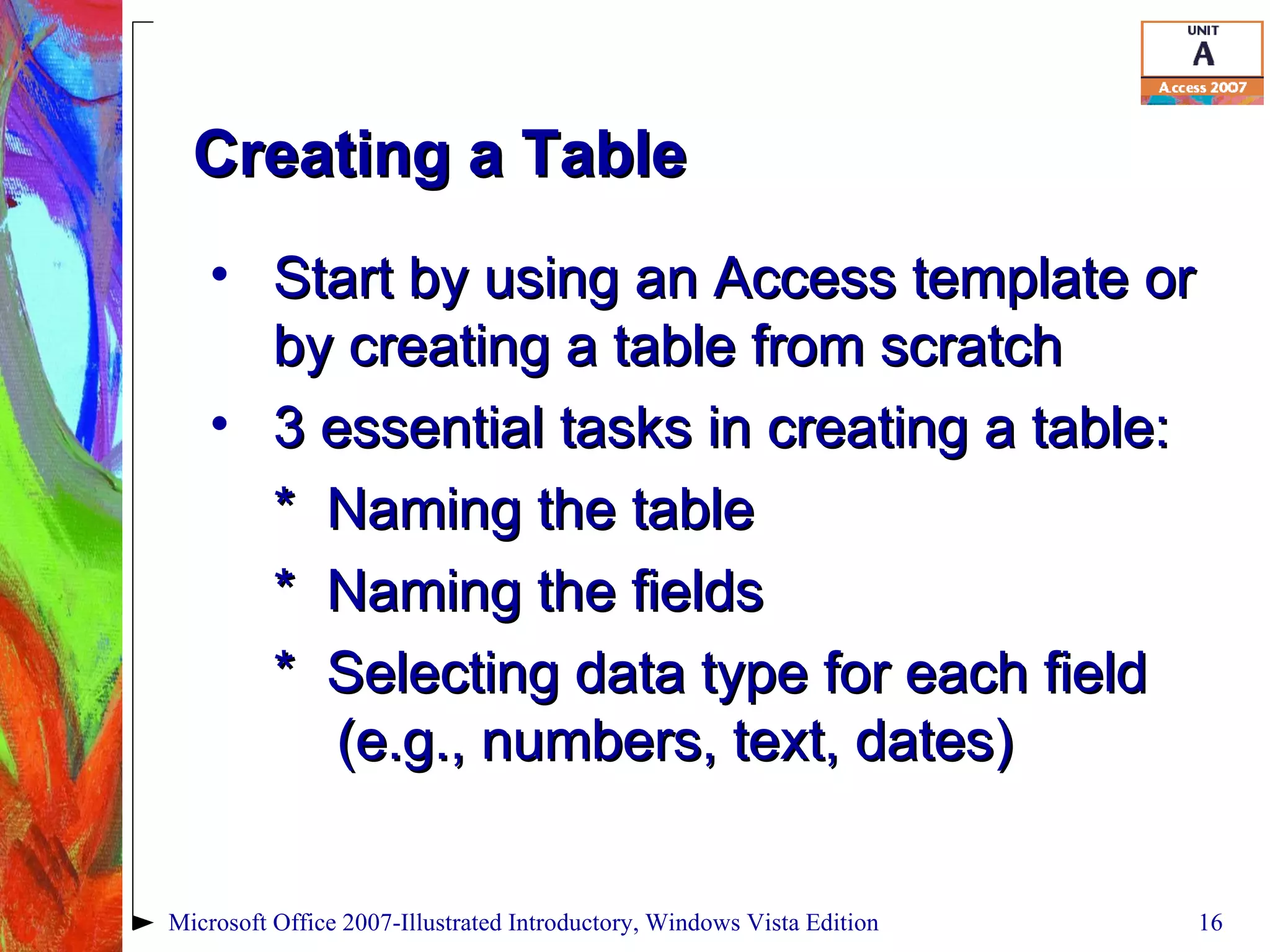
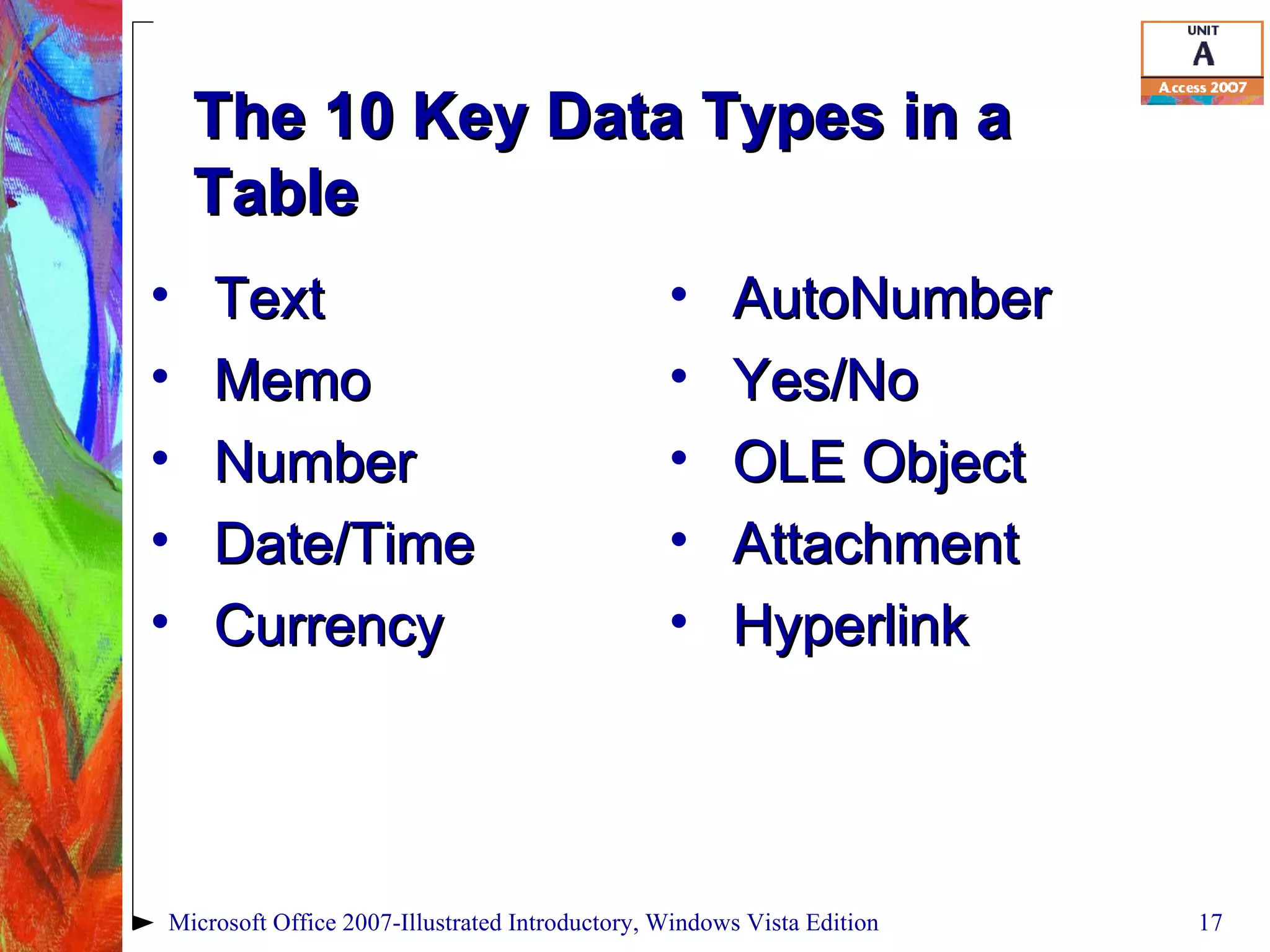
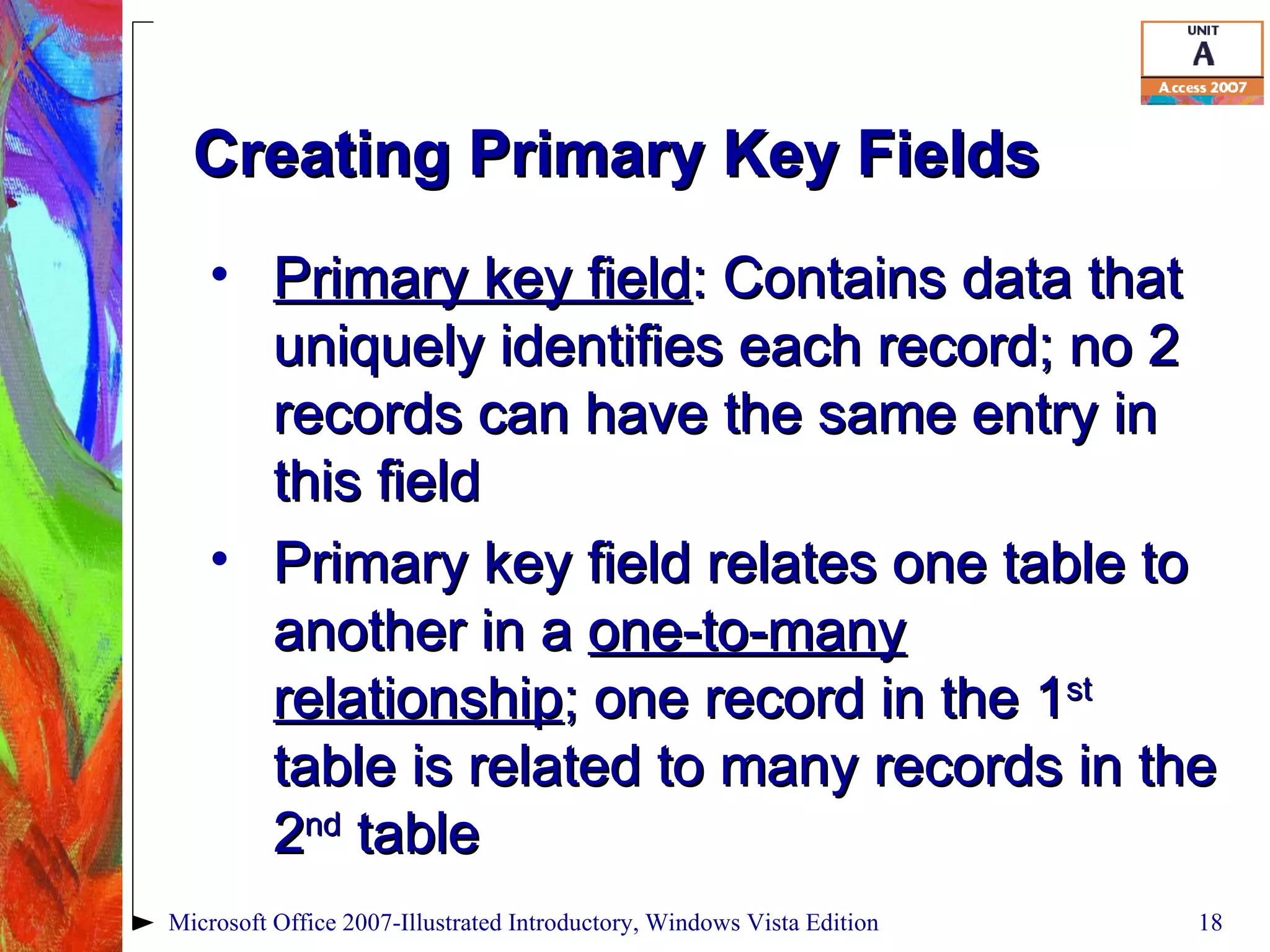
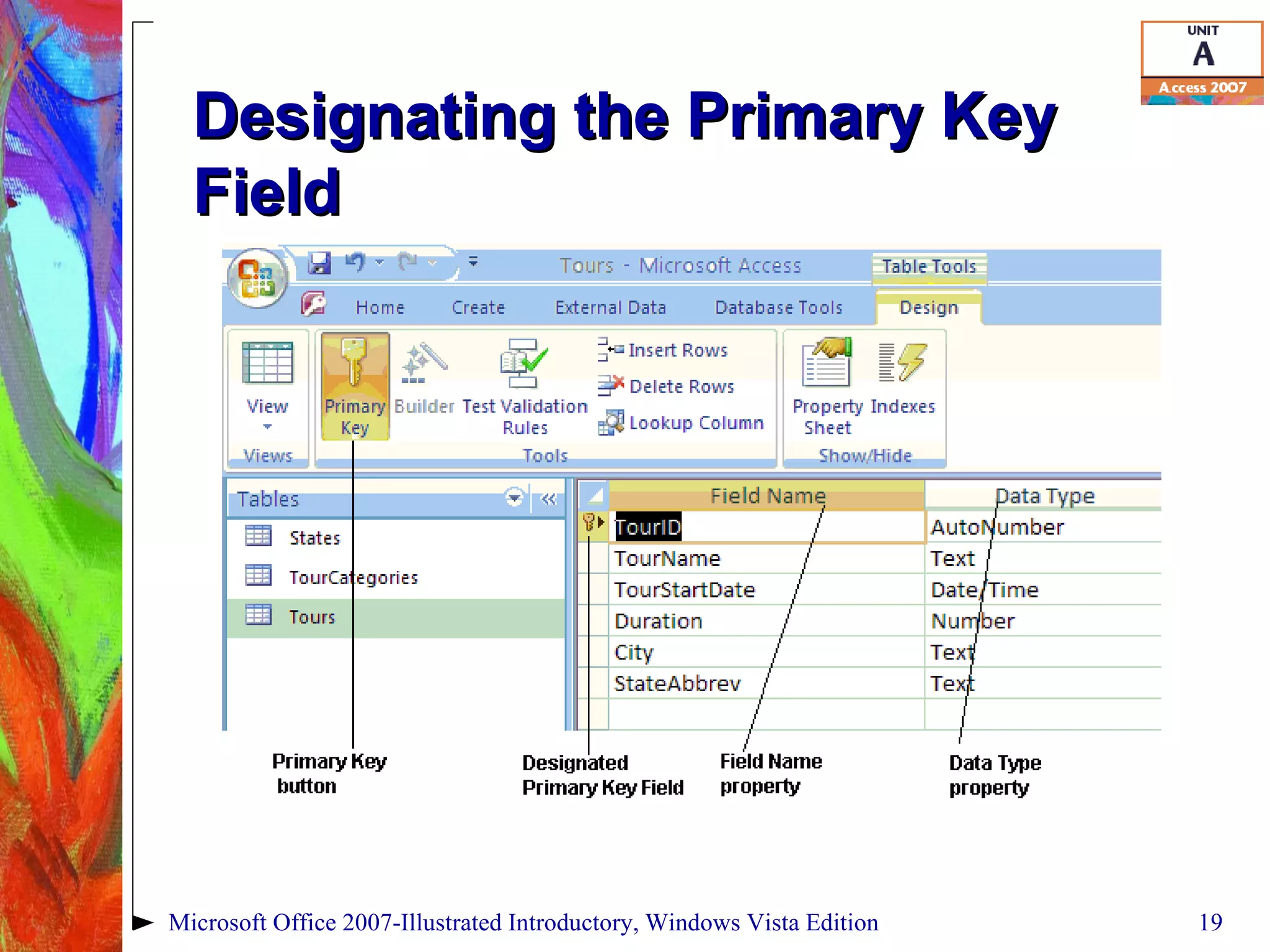
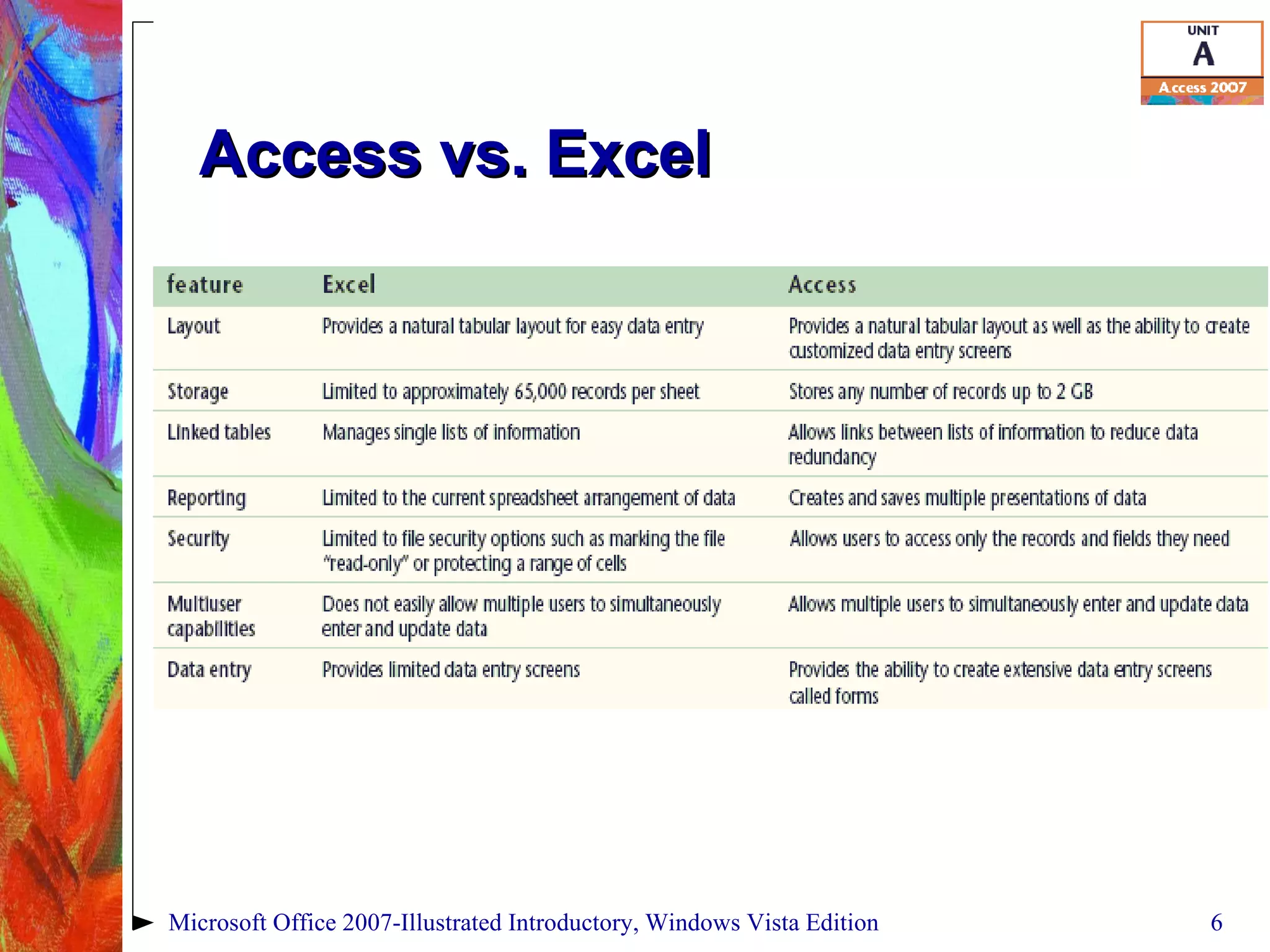
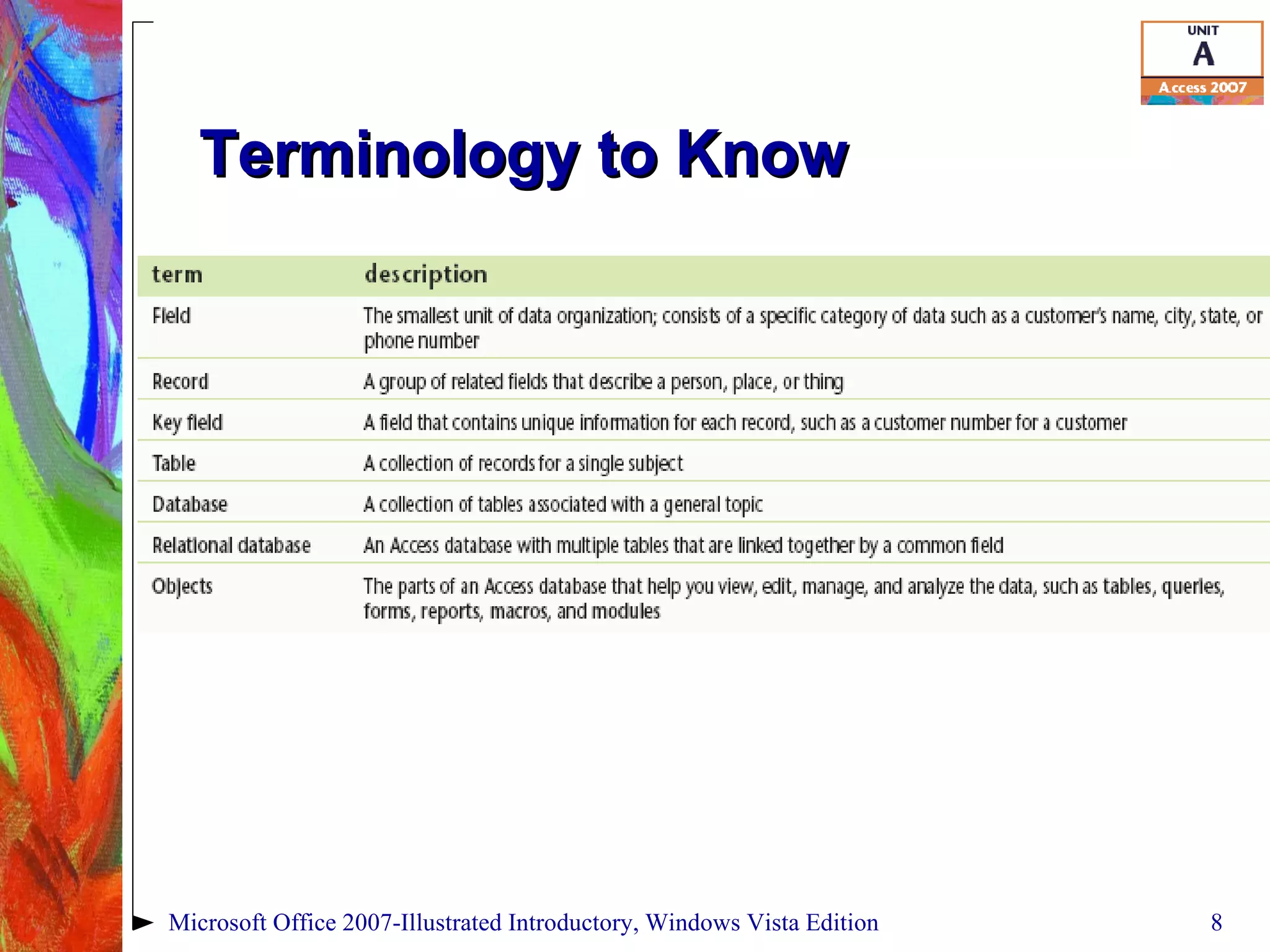
This document provides an overview of relational databases in Microsoft Access. It discusses opening and creating databases, tables, and relationships between tables. Key topics include entering and editing data, creating primary keys, and linking tables in a one-to-many relationship. The document also covers printing datasheets and using templates to build an Access database.






![Moving the Focus to Navigate Data Options [Tab] [Enter] Navigation buttons: Previous record Next record Microsoft Office 2007-Illustrated Introductory, Windows Vista Edition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/access-2007-unit-a-1234079440237413-3/75/Access-2007-Unit-A-10-2048.jpg)