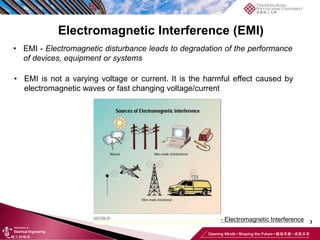
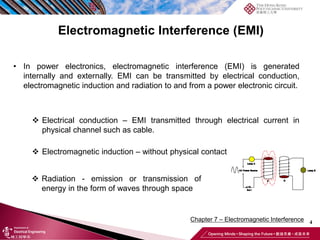
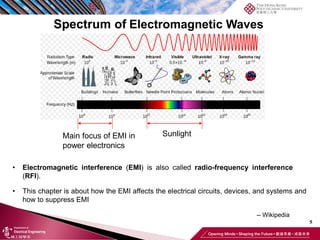
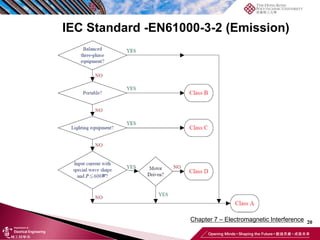
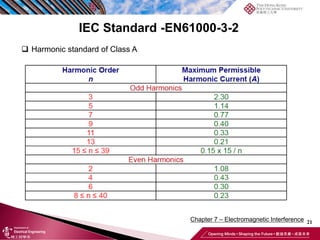
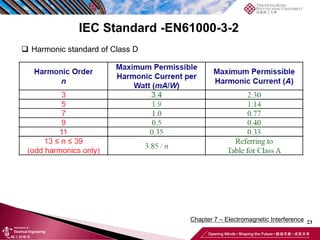
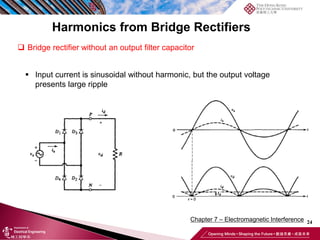
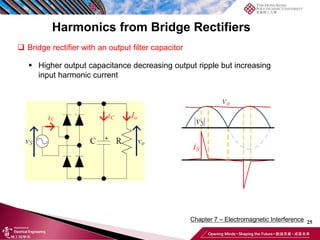
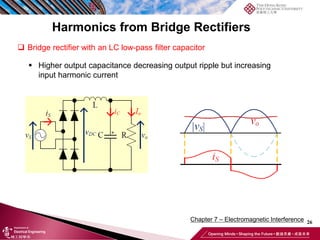
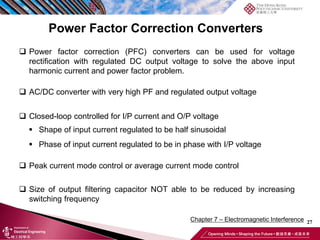
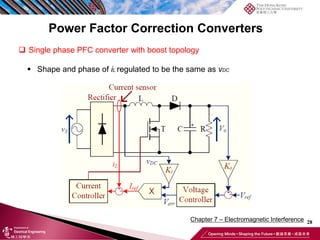
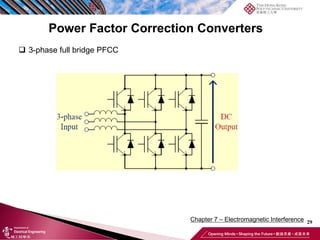
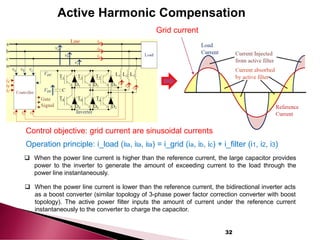
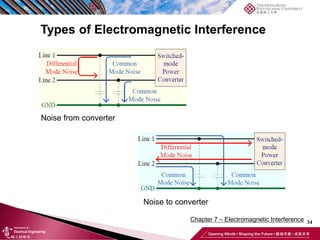
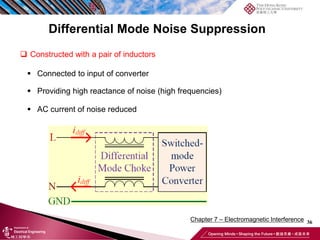
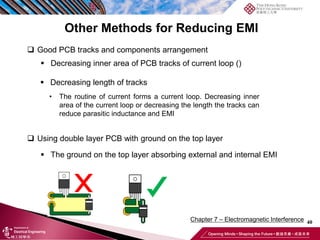
This document discusses electromagnetic interference (EMI) in power electronics. It defines EMI and describes how it is generated internally in power electronic circuits and transmitted through electrical conduction, electromagnetic induction, and radiation. The document outlines international standards for EMI, sources of EMI, and methods for suppressing EMI, including EMI filters, active harmonic compensation, and proper design of circuit components.