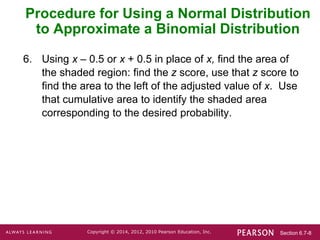
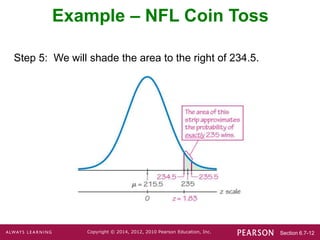
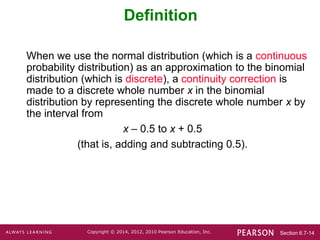
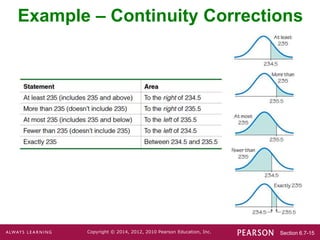
This document discusses using a normal distribution to approximate a binomial distribution. It provides the key steps for this approximation procedure:
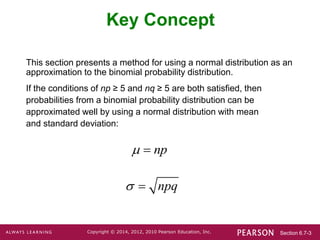
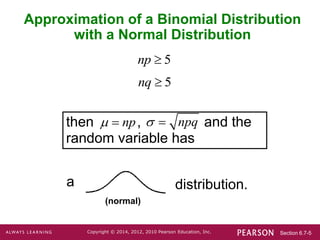
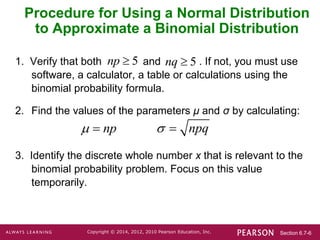
1. Verify that the conditions np ≥ 5 and nq ≥ 5 are met.
2. Calculate the mean (μ) and standard deviation (σ) of the normal distribution.
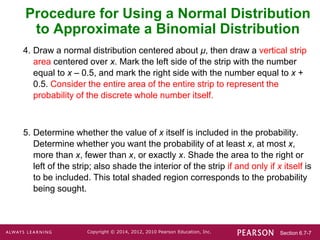
3. Identify the relevant value x from the binomial problem and draw a vertical strip centered over x from x - 0.5 to x + 0.5 on the normal distribution.
4. Determine the z-score for x - 0.5 or x + 0.5 and find the corresponding normal probability to approximate the binomial probability of x.
It then works through an example of