This document contains sections from a textbook on probability distributions. It discusses the binomial probability distribution, which models experiments with a fixed number of trials, two possible outcomes per trial (success/failure), and a constant probability of success. The key points are:
- A binomial distribution requires independent trials with two categories of outcomes and a constant success probability.
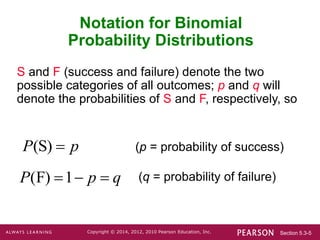
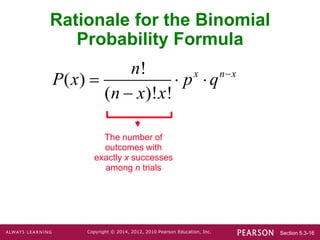
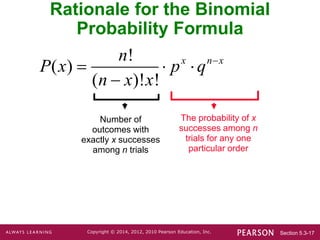
- Notation includes n for the number of trials, x for the number of successes, p for the success probability, and q for the failure probability.
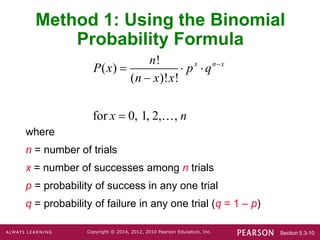
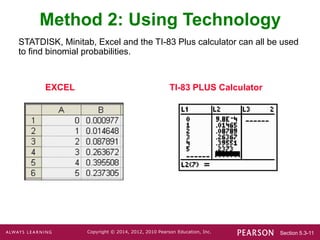
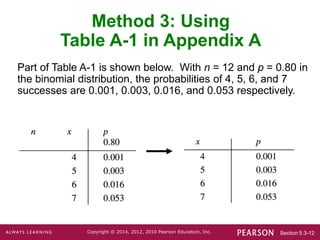
- Three methods are presented for calculating binomial probabilities: a formula, using technology, and using probability tables.
- An example calculates the probability of getting exactly 3 successes out of 5 trials using the binomial