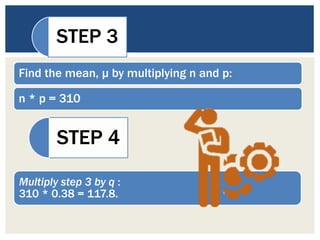
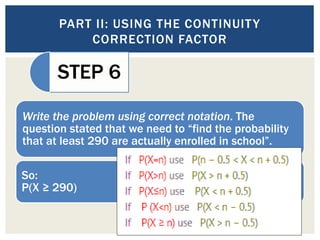
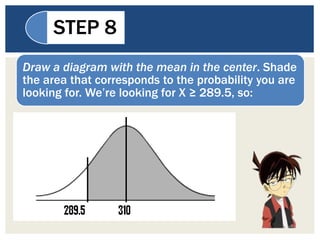
This document discusses the normal approximation to the binomial distribution. It explains that when the sample size (n) is large enough, the binomial distribution can be approximated by a normal distribution. It provides steps for using the normal approximation, including calculating n*p and n*q to determine if the approximation can be used, finding the mean and standard deviation, using the continuity correction factor, and looking up the probability in the z-table. An example problem demonstrates how to use these steps to calculate the probability that at least 290 students out of a sample of 500 are enrolled in school.