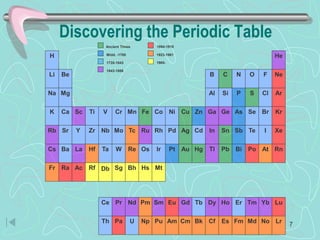
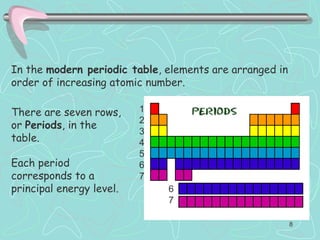
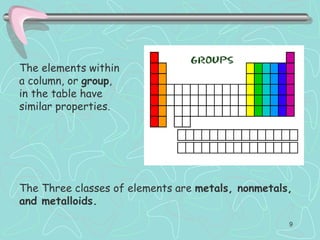
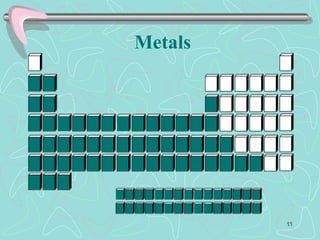
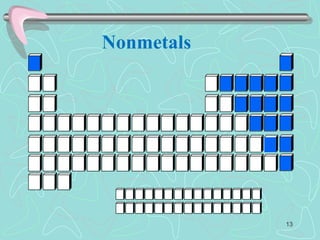
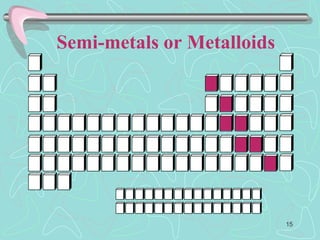
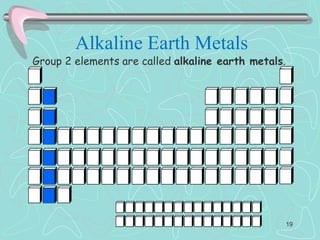
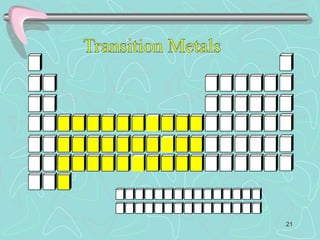
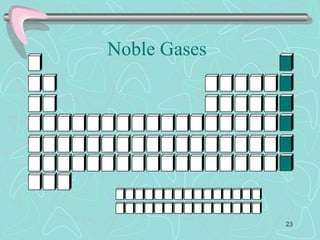
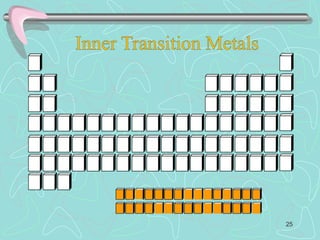
The document discusses the periodic table, including its history and development. It describes how Dmitri Mendeleev organized the elements based on atomic weight and chemical properties, though he left gaps for undiscovered elements. The modern periodic table arranges elements by atomic number and divides them into rows (periods) and columns (groups). Elements within the same group have similar properties due to their valence electrons. The periodic table is useful for organizing information about elements and predicting chemical behaviors.