Embed presentation
Download to read offline
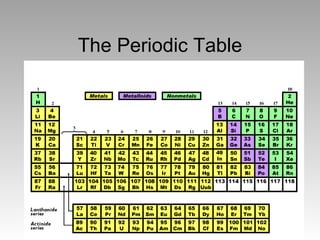


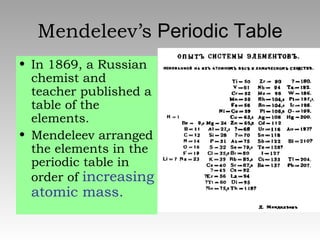

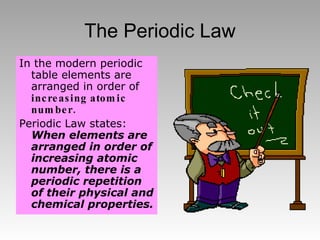
The document summarizes the key developments in the periodic table. It describes how elements are organized in the table with atomic numbers and weights. Early scientists like Dobreiner grouped elements by properties into triads. Mendeleev arranged the table by atomic mass, but Moseley correctly identified atomic number as the fundamental property through his work with X-rays. The modern periodic table arranges elements by increasing atomic number according to the Periodic Law of repeating physical and chemical properties.





