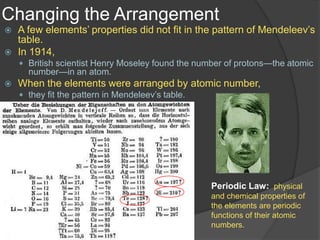
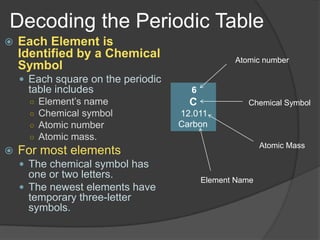
Dmitri Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass in 1869 and discovered repeating patterns in their properties. This became known as the periodic table. Mendeleev predicted properties of elements not yet discovered that would fill gaps in the table. Later, Henry Moseley arranged elements by atomic number in 1914, which better fit the periodic patterns. The periodic table classifies elements as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids based on their location and number of outer electrons. Periods are horizontal rows that show repeating patterns, and groups are vertical columns of elements with similar properties.