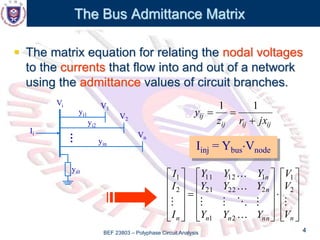
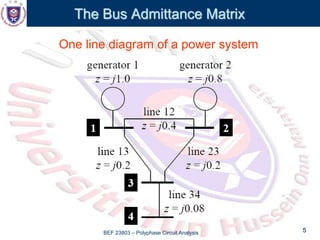
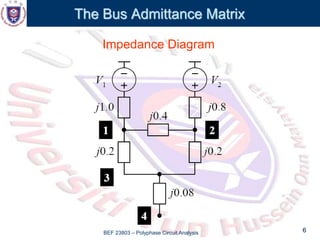
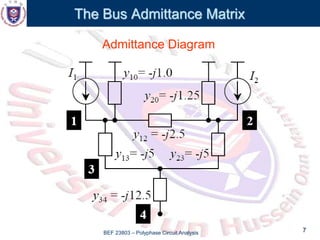
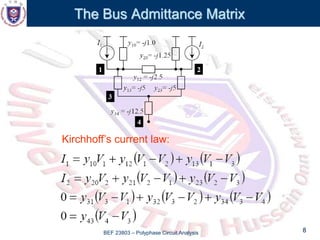
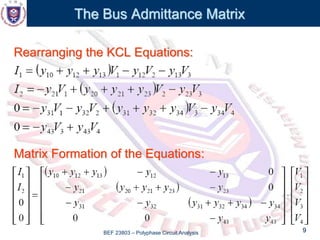
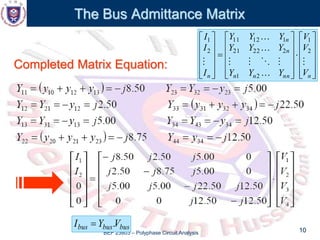
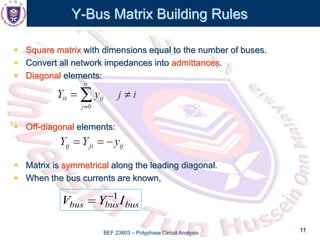
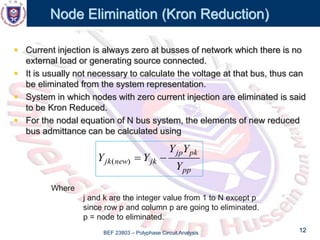
This document discusses the admittance and impedance bus models used in power flow analysis. It outlines the bus admittance matrix method for relating nodal voltages to branch currents using the admittance values. The bus admittance matrix is a square matrix with dimensions equal to the number of buses. Node elimination methods like Kron reduction can be used to reduce the matrix by eliminating buses with no current injection. The document provides an example of applying Kron reduction to eliminate a node from the bus admittance matrix.