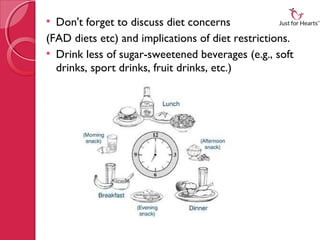
This document discusses the importance of pediatric nutrition at different age groups from infancy to adolescence. It outlines nutritional guidelines for each group, emphasizing the critical role of proper nutrition in growth and development. For infants, exclusive breastfeeding for six months and gradual introduction of complementary foods is recommended. For toddlers and preschoolers, a variety of nutritious foods from all food groups should be provided. School-aged children need a balanced diet and physical activity. Adolescents have increased nutritional needs to support development and should make healthy choices. Maintaining good oral health is also covered.